 |
Lectures
A lecture (from ) is an speech, oral presentation intended to present information or teach people about a particular subject, for example by a university or college teacher. Lectures are used to convey critical information, history, background, theories, and equations. A politician's speech, a minister's sermon, or even a business person's sales presentation may be similar in form to a lecture. Usually the lecturer will stand at the front of the room and recite information relevant to the lecture's content. Though lectures are much criticised as a teaching method, universities have not yet found practical alternative teaching methods for the large majority of their courses. Critics point out that lecturing is mainly a one-way method of communication that does not involve significant audience participation but relies upon passive learning. Therefore, lecturing is often contrasted to active learning. Lectures delivered by talented speakers can be highly stimulating; at the ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
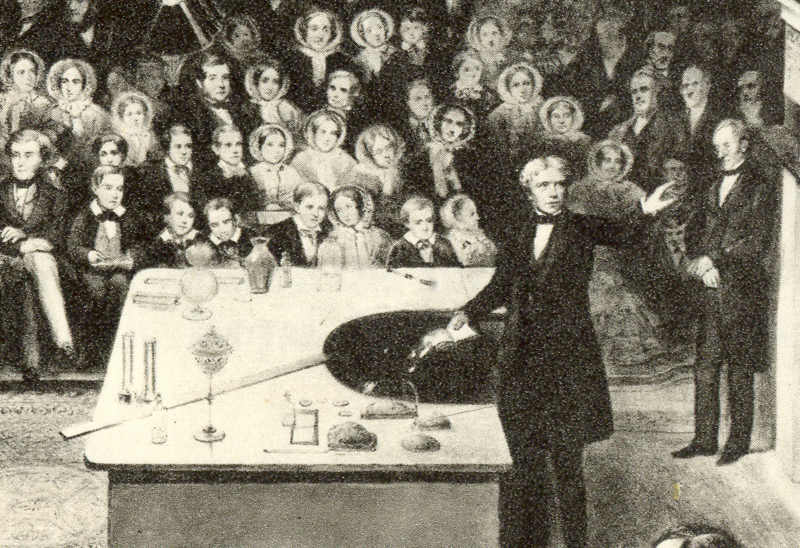 |
Public Lecture
A public lecture (also known as an open lecture) is one means employed for educating the public. Gresham College, in London, has been providing free public lectures since its founding in 1597 through the will of Sir Thomas Gresham. The Royal Society held its first ever meeting at Gresham College in November 1660, after one of Christopher Wren's lectures, and continued to meet there for the next fifty years. The Royal Institution, Royal Institution of Great Britain has a long history of public lectures and demonstrations given by prominent experts in the field. In the 19th century, the popularity of the public lectures given by Sir Humphry Davy at the Royal Institution was so great that the volume of carriage traffic in Albemarle Street caused it to become the first one-way street in London. The Royal Institution's Christmas Lectures for young people are nowadays also shown on television. Alexander von Humboldt delivered a series of public lectures at the University of Berlin i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Sermon
A sermon is a religious discourse or oration by a preacher, usually a member of clergy. Sermons address a scriptural, theological, or moral topic, usually expounding on a type of belief, law, or behavior within both past and present contexts. Elements of the sermon often include exposition, exhortation, and practical application. The act of delivering a sermon is called preaching. In secular usage, the word ''sermon'' may refer, often disparagingly, to a lecture on morals. In Christian practice, a sermon is usually preached to a congregation in a place of worship, either from an elevated architectural feature, known as a pulpit or an ambo, or from behind a lectern. The word ''sermon'' comes from a Middle English word which was derived from Old French, which in turn originates from the Latin word meaning 'discourse.' A ''sermonette'' is a short sermon (usually associated with television broadcasting, as stations would present a sermonette before Sign-off (broadcast) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Teaching Method
A teaching method is a set of principles and methods used by teachers to enable student learning. These strategies are determined partly by the subject matter to be taught, partly by the relative expertise of the learners, and partly by constraints caused by the learning environment. For a particular teaching method to be appropriate and efficient it has to take into account the learner, the nature of the subject matter, and the type of learning it is supposed to bring about. The approaches for teaching can be broadly classified into teacher-centered and student-centered, but in practice teachers will often adapt instruction by moving back and forth between these methodologies depending on learner prior knowledge, learner expertise, and the desired learning objectives. In a teacher-centered approach to learning, teachers are the main authority figure in this model. Students are viewed as "empty vessels" whose primary role is to passively receive information (via lectures and di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Ferdinand De Saussure
Ferdinand Mongin de Saussure (; ; 26 November 185722 February 1913) was a Swiss linguist, semiotician and philosopher. His ideas laid a foundation for many significant developments in both linguistics and semiotics in the 20th century. He is widely considered one of the founders of 20th-century linguistics and one of two major founders (together with Charles Sanders Peirce) of semiotics, or ''semiology'', as Saussure called it. One of his translators, Roy Harris, summarized Saussure's contribution to linguistics and the study of "the whole range of human sciences. It is particularly marked in linguistics, philosophy, psychoanalysis, psychology, sociology and anthropology." Although they have undergone extension and critique over time, the dimensions of organization introduced by Saussure continue to inform contemporary approaches to the phenomenon of language. As Leonard Bloomfield stated after reviewing Saussure's work: "he has given us the theoretical basis for a science of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Active Learning
Active learning is "a method of learning in which students are actively or experientially involved in the learning process and where there are different levels of active learning, depending on student involvement." states that "students participate n active learningwhen they are doing something besides passively listening." According to Hanson and Moser (2003) using active teaching techniques in the classroom can create better academic outcomes for students. Scheyvens, Griffin, Jocoy, Liu, & Bradford (2008) further noted that "by utilizing learning strategies that can include small-group work, role-play and simulations, data collection and analysis, active learning is purported to increase student interest and motivation and to build students ‘critical thinking, problem-solving and social skills". In a report from the Association for the Study of Higher Education, authors discuss a variety of methodologies for promoting active learning. They cite literature that indicates stude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Oral Tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication in which knowledge, art, ideas and culture are received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another.Jan Vansina, Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (1985), reported statements from present generation which "specifies that the message must be oral statements spoken, sung or called out on musical instruments only"; "There must be transmission by word of mouth over at least a generation". He points out, "Our definition is a working definition for the use of historians. Sociologists, linguists or scholars of the verbal arts propose their own, which in, e.g., sociology, stresses common knowledge. In linguistics, features that distinguish the language from common dialogue (linguists), and in the verbal arts features of form and content that define art (folklorists)."Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: "Methodology and African Pre-history", 1990, ''UNESCO International Scientific Committee for the Drafting of a G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Grey Literature
Grey literature (or gray literature) is material and research produced by organizations outside of the traditional publishing, commercial or academic publishing and distribution channels. Common grey literature publication types include reports (annual report, annual, research, technical report, technical, project, etc.), working papers, government documents, white papers and evaluations. Organizations that produce grey literature include government departments and agencies, civil society or Non-governmental organization, non-governmental organizations, academic centres and departments, and private companies and consultants. Grey literature may be difficult to discover, access, and evaluate, but this can be addressed through the formulation of sound search strategies. Grey literature may be made available to the public, or distributed privately within organizations or groups, and may lack a systematic means of distribution and collection. The standard of quality, review and product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Golan Levin
Golan (; ) is the name of a biblical town later known from the works of Josephus (first century CE) and Eusebius (''Onomasticon'', early 4th century CE). Archaeologists localize the biblical city of Golan at Sahm el-Jaulān, a Syrian village east of Wadi ar- Ruqqad in the Daraa Governorate, where early Byzantine ruins were found. Israeli historical geographer, Zev Vilnay, tentatively identified the town Golan with the Goblana (Gaulan) of the Talmud which he thought to be the ruin ''ej-Jelêbîne'' on the Wâdy Dabûra, near the Lake of Huleh, by way of a corruption of the site's original name. According to Vilnay, the village took its name from the district Gaulanitis (Golan). The ruin is not far from the Daughters of Jacob Bridge. The traces of the town were described by G. Schumacher in the late 19th-century as being "a desert ruin", having "no visible remains of importance, but avingthe appearance of great antiquity." In the Grecised form Gaulanitis (), it is the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
ADFA Lecture Theatres
The Australian Defence Force Academy (ADFA) is a tri-service military academy that provides military and academic education for junior officers of the Australian Defence Force in the Royal Australian Navy (RAN), Australian Army and Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) as well as international trainee officers from a variety of countries. In 2016, the academy began accepting civilian students in its undergraduate courses. Tertiary education is provided by the University of New South Wales' Canberra campus, known as UNSW Canberra at ADFA, which is the awarding body for ADFA qualifications. Apart from educating future leaders of the Australian Defence Force, UNSW Canberra also provides postgraduate programs and short courses both to Department of Defence personnel and the general public. The stated purpose of ADFA is "to serve Australia by providing the Australian Defence Force (ADF) with tertiary graduates who have the attributes, intellect and skills required of an officer". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Library
A library is a collection of Book, books, and possibly other Document, materials and Media (communication), media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or electronic media, digital (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location, a virtual space, or both. A library's collection normally includes printed materials which may be borrowed, and usually also includes a reference section of publications which may only be utilized inside the premises. Resources such as commercial releases of films, television programmes, other video recordings, radio, music and audio recordings may be available in many formats. These include DVDs, Blu-rays, CDs, Cassette tape, cassettes, or other applicable formats such as microform. They may also provide access to information, music or other content held on bibliographic databases. In addition, some libraries offer Library makerspace, creation stations for wiktionar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also follows a structured approach but occurs outside the formal schooling system, while informal education involves unstructured learning through daily experiences. Formal and non-formal education are categorized into levels, including early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, and tertiary education. Other classifications focus on teaching methods, such as teacher-centered and student-centered education, and on subjects, such as science education, language education, and physical education. Additionally, the term "education" can denote the mental states and qualities of educated individuals and the academic field studying educational phenomena. The precise definition of education is disputed, and there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |