|
Laser Types
This is a list of laser types, their operational wavelengths, and their list of laser applications, applications. Thousands of kinds of laser are known, but most of them are used only for specialized research. Overview Gas lasers Chemical lasers Used as directed-energy weapons. Dye lasers Metal-vapor lasers Solid-state lasers Semiconductor lasers Other types of lasers See also *Laser construction *List of laser articles *Maser producing or amplifying a coherent microwave beam *X-ray laser producing a coherent x-ray or Extreme ultraviolet, EUV beam *Atom laser producing a coherent beam of atoms *Gravity laser, a hypothetical concept of producing coherent gravitation waves Notes Further references *Silfvast, William T. ''Laser fundamentals'', Cambridge University Press, 2004. *Weber, Marvin J. ''Handbook of laser wavelengths'', CRC Press, 1999. {{DEFAULTSORT:Laser Types Laser types, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
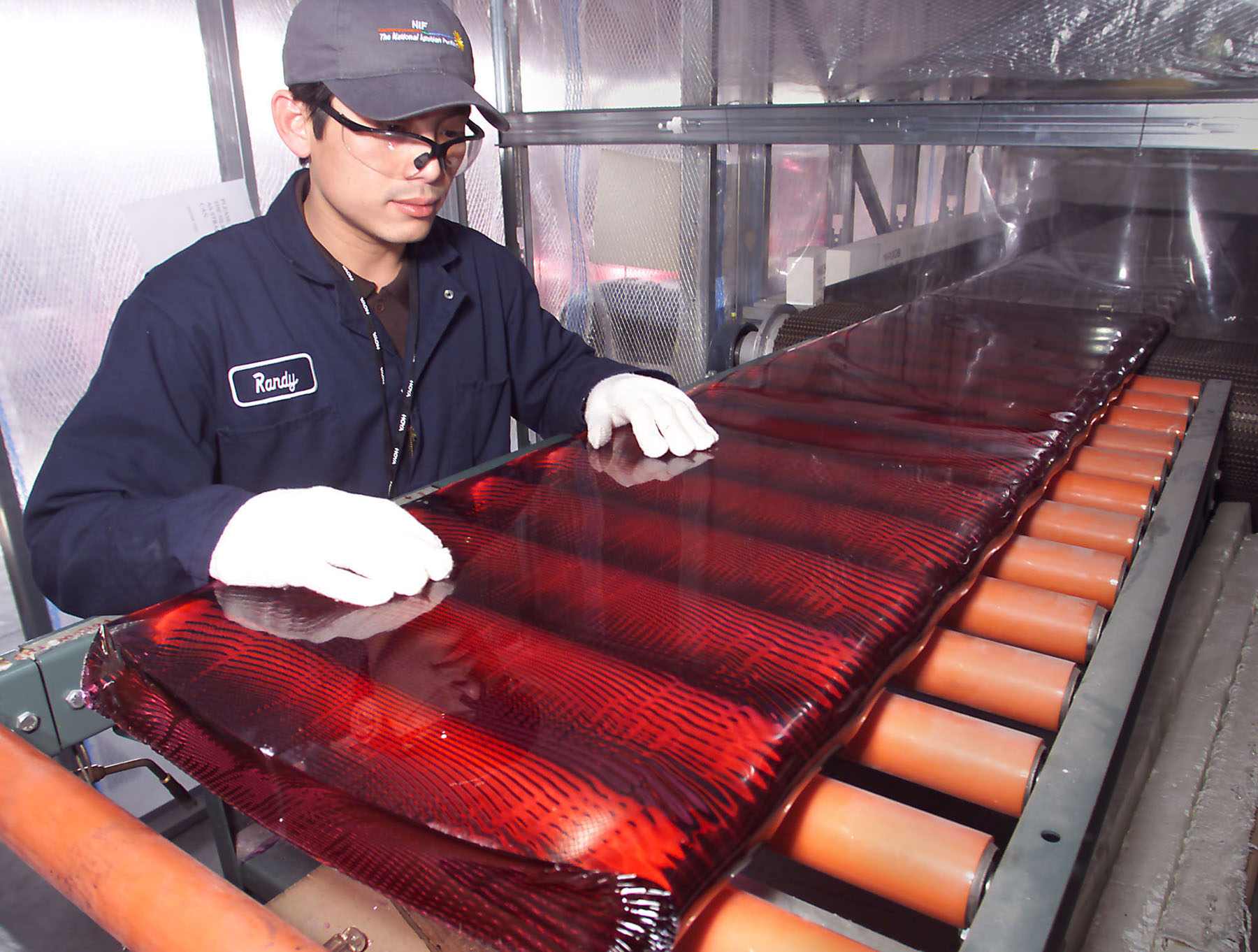
Laser Glass Slab
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow and the optical amplifier patented by Gordon Gould. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light that is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling uses such as optical communication, laser cutting, and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. It also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), used in laser pointers, lidar, and free-space optical communication. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which permits them to emit light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the miscibility, immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German author and actor Alois Senefelder and was initially used mostly for sheet music, musical scores and maps.Meggs, Philip B. ''A History of Graphic Design''. (1998) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 146, .Carter, Rob, Ben Day, Philip Meggs. ''Typographic Design: Form and Communication'', Third Edition. (2002) John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 11. Lithography can be used to print text or images onto paper or other suitable material. A lithograph is something printed by lithography, but this term is only used for printmaking, fine art prints and some other, mostly older, types of printed matter, not for those made by modern commercial lithography. Traditionally, the image to be printed was drawn with a greasy substance, such as oil, fat, or wax on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Laser
A dental laser is a type of laser designed specifically for use in oral surgery or dentistry. In the United States, the use of lasers on the gums was first approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the early 1990s, and use on hard tissue like teeth or the bone of the mandible gained approval in 1996. Several variants of dental lasers are in use with different wavelengths and these mean they are better suited for different applications. Soft tissue lasers * Diode lasers *Carbon dioxide lasers * Nd:YAG laser Diode lasers wavelengths in the 810–1,100 nm range are poorly absorbed by the soft tissues such as the gingivae, and cannot be used for soft tissue cutting or ablation. Instead, the distal end of diode's glass fiber is charred (by burned ink or by burned corkwood, etc.) and the char is heated by the 810-1,100 nm laser beam, which in turn heats up the glass fiber's tip. The soft tissue is cut, on contact, by the hot charred glass tip and not by the laser beam itself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance (cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissue (biology), tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, operating theater, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Beam Welding
Laser beam welding (LBW) is a welding technique used to join pieces of metal or thermoplastics through the use of a laser. The beam provides a concentrated heat source, allowing for narrow, deep welds and high welding rates. The process is frequently used in high volume and precision requiring applications using automation, as in the automotive and aeronautics industries. It is based on keyhole or penetration mode welding. Operation Like electron-beam welding (EBW), laser beam welding has high power density (on the order of 1 MW/cm2) resulting in small heat-affected zones and high heating and cooling rates. The spot size of the laser can vary between 0.2 mm and 13 mm, though only smaller sizes are used for welding. The depth of penetration is proportional to the amount of power supplied, but is also dependent on the location of the focal point: penetration is maximized when the focal point is slightly below the surface of the workpiece. A continuous or pulsed la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to vaporize materials, resulting in a cut edge. While typically used for industrial manufacturing applications, it is now used by schools, small businesses, architecture, and hobbyists. Laser cutting works by directing the output of a high-power laser most commonly through optics. The laser optics and CNC (computer numerical control) are used to direct the laser beam to the material. A commercial laser for cutting materials uses a motion control system to follow a CNC or G-code of the pattern to be cut onto the material. The focused laser beam is directed at the material, which then either melts, burns, vaporizes away, or is blown away by a jet of gas, leaving an edge with a high-quality surface finish. History In 1965, the first production laser cutting machine was used to drilling, drill holes in diamond Die (manufacturing), dies. This machine was made by the Western Electric Engineering Research Center. In 1967, the British pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide Laser
The carbon-dioxide laser (CO2 laser) was one of the earliest gas lasers to be developed. It was invented by C. Kumar N. Patel, Kumar Patel of Bell Labs in 1964 and is still one of the most useful types of laser. Carbon dioxide, Carbon-dioxide lasers are the highest-power continuous-wave lasers that are currently available. They are also quite efficient: the ratio of output power to Laser pumping, pump power can be as large as 20%. The CO2 laser produces a beam of infrared light with the principal wavelength bands centering on 9.6 and 10.6 Micrometre, micrometers (μm). Amplification The active laser medium (laser gain/Amplifier, amplification medium) is a gas discharge which is air- or water-cooled, depending on the power being applied. The filling gas within a sealed discharge tube consists of around 10–20% carbon dioxide (), around 10–20% nitrogen (), a few percent hydrogen () and/or xenon (Xe), with the remainder being helium (He). A different mixture is used in a ''fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TEA Laser
A TEA laser, or transversely excited atmospheric laser, is a gas laser energized by a high-voltage electrical discharge in a gas mixture generally at or above atmospheric pressure. The most common types are carbon dioxide lasers and excimer lasers, both used extensively in industry and research; less common are nitrogen lasers. History Invention The carbon dioxide (CO2) TEA laser was invented in the late 1960s by Jacques Beaulieu working at the Defence Research and Development Canada at Valcartier in Quebec, Canada. The development was kept secret until 1970, when brief details were published. In 1963, C. Kumar N. Patel, working at Bell Telephone Laboratories, first demonstrated laser output at 10.6 μm from a low pressure RF-excited CO2 gas discharge. With the addition of nitrogen and helium and using a DC electrical discharge, CW powers of around 100 W were achieved. By pulsing the discharge using higher voltages, or Q-switching using a rotating mirror, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superradiant Laser
A superradiant laser is a laser that does not rely on a large population of photons within the laser cavity to maintain coherence. Rather than relying on photons to store phase coherence, it relies on collective effects in an atomic medium to store coherence. Such a laser uses repumped Dicke superradiance In physics, superradiance, or superradiation, is the radiation enhancement effects in several contexts including quantum mechanics, astrophysics and relativity. Quantum optics In quantum optics, superradiance is a phenomenon that occurs when a ... (or superfluorescence) to sustain emission of light that can have a substantially narrower linewidth than a conventional laser. See also * Dicke model * Superradiant phase transition References Laser types {{optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Laser
A nitrogen laser is a gas laser operating in the ultraviolet rangeC. S. Willett, ''Introduction to Gas Lasers: Population Inversion Mechanisms'' (Pergamon, New York,1974). (typically 337.1 nm) using molecular nitrogen as its gain medium, laser pumping, pumped by an electrical discharge. The wall-plug efficiency of the nitrogen laser is low, typically 0.1% or less, though nitrogen lasers with efficiency of up to 3% have been reported in the literature. The wall-plug efficiency is the product of the following three efficiencies: * electrical: TEA laser * gain medium: This is the same for all nitrogen lasers and thus has to be at least 3% ** inversion by electron impact is 10 to 1 due to Franck–Condon principle ** energy lost in the lower laser level: 40% * optical: More stimulated emission than spontaneous emission Gain medium The gain medium is nitrogen molecules in the gas phase. The nitrogen laser is a three-level laser. In contrast to more typical four-level lasers, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |