|
Languages Of Thailand
Thailand is home to 51 living indigenous languages and 24 living non-indigenous languages, with the majority of people speaking languages of the Southwestern Tai family, and the national language being Central Thai. Lao is spoken along the borders with the Lao PDR, Karen languages are spoken along the border with Myanmar, Khmer is spoken near Cambodia and Malay is spoken in the south near Malaysia. Sixty-two 'domestic' languages are officially recognized, and international languages spoken in Thailand, primarily by international workers, expatriates and business people, include Burmese, Karen, English, Chinese, Japanese, and Vietnamese, among others. Officially recognized languages National breakdown The following table comprises all 62 ethnolinguistic groups recognized by the Royal Thai Government in the 2011 Country Report to the UN Committee responsible for the ''International Convention for the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination'', available from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Khmer Dialect
Northern Khmer (; ), also called Surin Khmer (), is the dialect of the Khmer language spoken by approximately 1.4 million Khmers native to the Thai provinces of Surin, Sisaket, Buriram and Roi Et as well as those that have migrated from this region into Cambodia. Northern Khmer differs from the standard language, based on a dialect of Central Khmer, in the number and variety of vowel phonemes, consonantal distribution, lexicon, grammar, and, most notably, pronunciation of syllable-final , giving Northern Khmer a distinct accent easily recognizable by speakers of other dialects. Some speakers of Northern Khmer may understand other varieties of Khmer but speakers of standard Khmer who have not been exposed to Northern Khmer often have trouble understanding Northern Khmer at first. The two varieties are 80–85% cognate on a basic 270-word list. These facts have led some linguists to advocate considering Northern Khmer a separate, but closely related language. History Afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
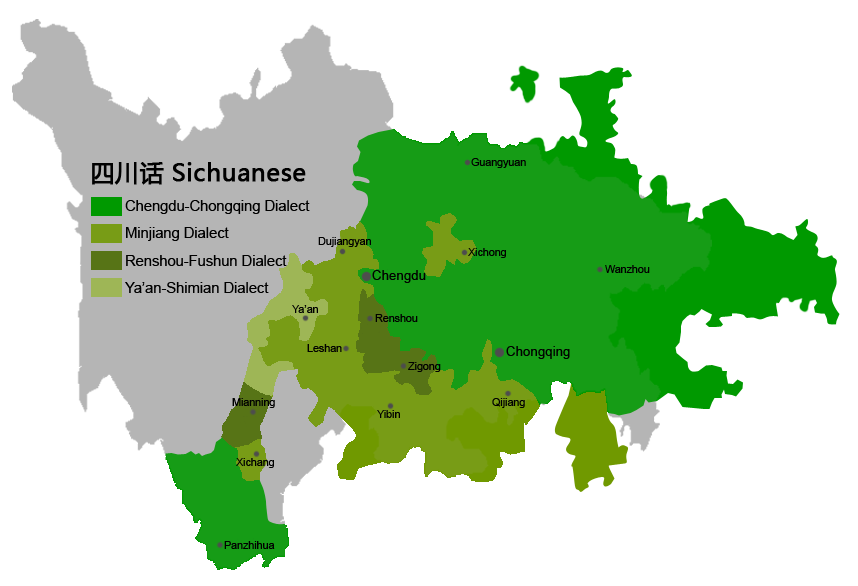
Southwestern Mandarin
Southwestern Mandarin (), also known as Upper Yangtze Mandarin (), is a Mandarin Chinese dialect spoken in much of Southwestern China, including in Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing, Guizhou, most parts of Hubei, the northwestern part of Hunan, the northern part of Guangxi and some southern parts of Shaanxi and Gansu. Southwestern Mandarin is spoken by roughly 260 million people. If considered a language distinct from central Mandarin, it would be the eighth-most spoken language by native speakers in the world, behind Mandarin itself, Spanish, English, Hindi, Portuguese, Arabic and Bengali. Overview Modern Southwestern Mandarin was formed by the waves of immigrants brought to the regions during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. Because of the comparatively recent move, such dialects show more similarity to modern Standard Mandarin than to other varieties of Chinese like Cantonese or Hokkien. For example, like most Southern Chinese dialects, Southwestern Mandarin does not possess the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin ( ; zh, s=, t=, p=Guānhuà, l=Mandarin (bureaucrat), officials' speech) is the largest branch of the Sinitic languages. Mandarin varieties are spoken by 70 percent of all Chinese speakers over a large geographical area that stretches from Yunnan in the southwest to Xinjiang in the northwest and Heilongjiang in the northeast. Its spread is generally attributed to the greater ease of travel and communication in the North China Plain compared to the more mountainous south, combined with the relatively recent spread of Mandarin to frontier areas. Many varieties of Mandarin, such as Southwestern Mandarin, those of the Southwest (including Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese) and the Lower Yangtze Mandarin, Lower Yangtze, are not mutually intelligible with the Beijing dialect (or are only partially intelligible). Nevertheless, Mandarin as a group is often placed first in lists of languages by number of native speakers (with nearly one billion). Because Mandarin originated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Songkhla Malay
Songkhla (, ), also known as Singgora or Singora (Pattani Malay: ซิงกอรอ, Singoro), is a city (''thesaban nakhon'') in Songkhla Province of southern Thailand, near the border with Malaysia. Songkhla lies south of Bangkok and as of 2020 had a population of 61,758. Despite being smaller than the neighboring city Hat Yai, Songkhla is the capital of Songkhla Province as well as the Mueang Songkhla District (Songkhla town district). Together with Hat Yai, Songkhla is part of the Greater Hat Yai-Songkhla Metropolitan Area (a conurbation with a population of around 800,000), the third largest metropolitan area in Thailand. At the opening of Songkhla Lake to the Gulf of Thailand, Songkhla is a fishing town and also an important harbour. It is the major seaport on the east side of the Isthmus of Kra. History The name ''Songkhla'' means 'the city of lions' (not to be confused with Singapura) and is the Thai variant of "Singgora" ( Malay and Jawi: سيڠڬو� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangkok Malay
Bangkok Malay, also referred to as Bangkok Melayu or Nayu, is a local variant of Malay spoken by the Bangkok Malays, an ethnic Malay community in Bangkok and its surrounding areas. It emerged from the interaction of the Malay community from Southern Thailand, as well as northern and eastern Peninsula Malaysia, gradually evolving into a distinct variety of Malay. Despite historical Malay presence in what is now Bangkok dated as early as the Ayutthaya era, the dialect nonetheless only began to develop after the settlement of deportees from Kedah, Kelantan, Patani, Satun, Terengganu, and Yaring in 1786, 1791, and 1832. The speakers of Bangkok Malay can be found throughout the city, with higher concentrations in Malay enclaves in Thon Buri, Thung Khru, Phra Pradaeng, Bang Kho Laem, Phra Khanong, Khlong Saen Saep, Min Buri, Nong Chok, Bang Nam Priao, Chachoengsao, Thon Buri, and Pom Prap Sattru Phai. There are several variations of Bangkok Malay, owing to the various wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satun Malay
Kedah Malay or Kedahan (; also known as ''Pelat Utara'' or ''Loghat Utara'' 'Northern Dialect') or as it is known in Thailand, Syburi Malay ( ''Phasa Malāyū Saiburī'') is a Malayic language mainly spoken in the northwestern Malaysian states of Perlis, Kedah, Penang, and northern Perak and in the southern Thai provinces of Trang and Satun. The usage of Kedah Malay was historically prevalent in southwestern Thailand before being superseded by the Thai language. Enclaves of Kedah Malay can be found in Kawthaung District in Myanmar; Ranong and Krabi in upper southern Thailand; Jaring Halus, Langkat and Aceh in Sumatra, Indonesia and up north in Bangkok, central Thailand, where most of the Kedah Malay speakers are descendants of historical settlers from Kedah. Kedah Malay can be divided into several dialects, namely ''Kedah Persisiran'' (Littoral Kedah; which is the de facto prestige dialect of Kedah Malay), ''Kedah Utara'' (Northern Kedah), Perlis-Langkawi, Penang and some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayan Languages
The Malayic languages are a branch of the Malayo-Polynesian languages, Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian languages, Austronesian language family. The two most prominent members of this branch are Indonesian language, Indonesian and Malay language, Malay. Indonesian is the official language of Indonesia and has evolved as a standardized form of Malay with distinct influences from local languages and historical factors. Malay, in its various forms, is recognized as a national language in Brunei, Malaysia, and Singapore. The Malayic branch also includes local languages spoken by Malay people, ethnic Malays (e.g. Jambi Malay, Kedah Malay), further several languages spoken by various other ethnic groups of Sumatra, Indonesia (e.g. Minangkabau language, Minangkabau) and Borneo (e.g. Banjar language, Banjarese, Iban language, Iban) even as far as Urak Lawoiʼ language, Urak Lawoi in the southwestern coast of Thailand. The most probable candidate for the urheimat of the Malay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mal Language
Mal, also known as Thin or T'in, is a Mon–Khmer language The Austroasiatic languages ( ) are a large language family spoken throughout Mainland Southeast Asia, South Asia and East Asia. These languages are natively spoken by the majority of the population in Vietnam and Cambodia, and by minority popu ... of Laos and Thailand. It is one of several closely related languages which go by the names Thin or Prai. Tayten (300 speakers as of 1995) is spoken in the 2 villages of Ban Phia and Ban Tenngiou in Pakxeng District, Luang Prabang Province, Laos. It is either Thin or Tai Then. See also * Lua peopleReferences External links * http:/ ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisu Language
Lisu ( Fraser alphabet: , or ; Latin: ; Lisu syllabary: ; zh, c=傈僳语, p=Lìsùyǔ; , ) is a tonal Tibeto-Burman language spoken in Yunnan (Southwestern China), Northern Burma (Myanmar) and Thailand and a small part of India. Along with Lipo, it is one of two languages of the Lisu people. Lisu has many dialects that originate from the country in which they live. Hua Lisu, Pai Lisu and Lu Shi Lisu dialects are spoken in China. Although they are mutually intelligible, some have many more loan words from other languages than others. The Lisu language is closely related to the Lahu and Akha languages and is also related to Burmese, Jingphaw and Yi languages. Demographics In China, the Lisu people are mostly found in Yunnan, the majority living mainly in Nujiang and Weixi, but also in Baoshan, Dehong, Dêqên, Lijiang, Lincang, Pu'er, Chuxiong, Luquan and Dali. In Liangshan and Panzhihua, Sichuan, where they make a small minority, some speak Lisu and others ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lahu Language
Lahu (autonym: ''Ladhof'' ) is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken by the Lahu people of China, Thailand, Myanmar, Vietnam and Laos. It is widely used in China, both by Lahu people, and by other ethnic minorities in Yunnan, who use it as a lingua franca. However, the language is not widely used nor taught in any schools in Thailand, where many Lahu are in fact refugees and illegal immigrants, having crossed into Thailand from Myanmar. Distribution by dialect Lahu Na (Black Lahu) is the northern and standard Lahu dialect and is spoken in most of Yunnan, China, in Kengtung District of Shan State, Myanmar and in Thailand. It should not be confused with Lahu Aga (Black Lahu of Laos ( See below) or Kucong (Black Lahu of Vietnam). Lahu Phu (White Lahu) is the southern dialect of the Lahu language. It is spoken in 3 countries: China, Vietnam and Laos, including in Muong Te District of Lai Châu Province. Lahu Nyi (Red Lahu) is only spoken in Thailand, including in the southern Yala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |