|
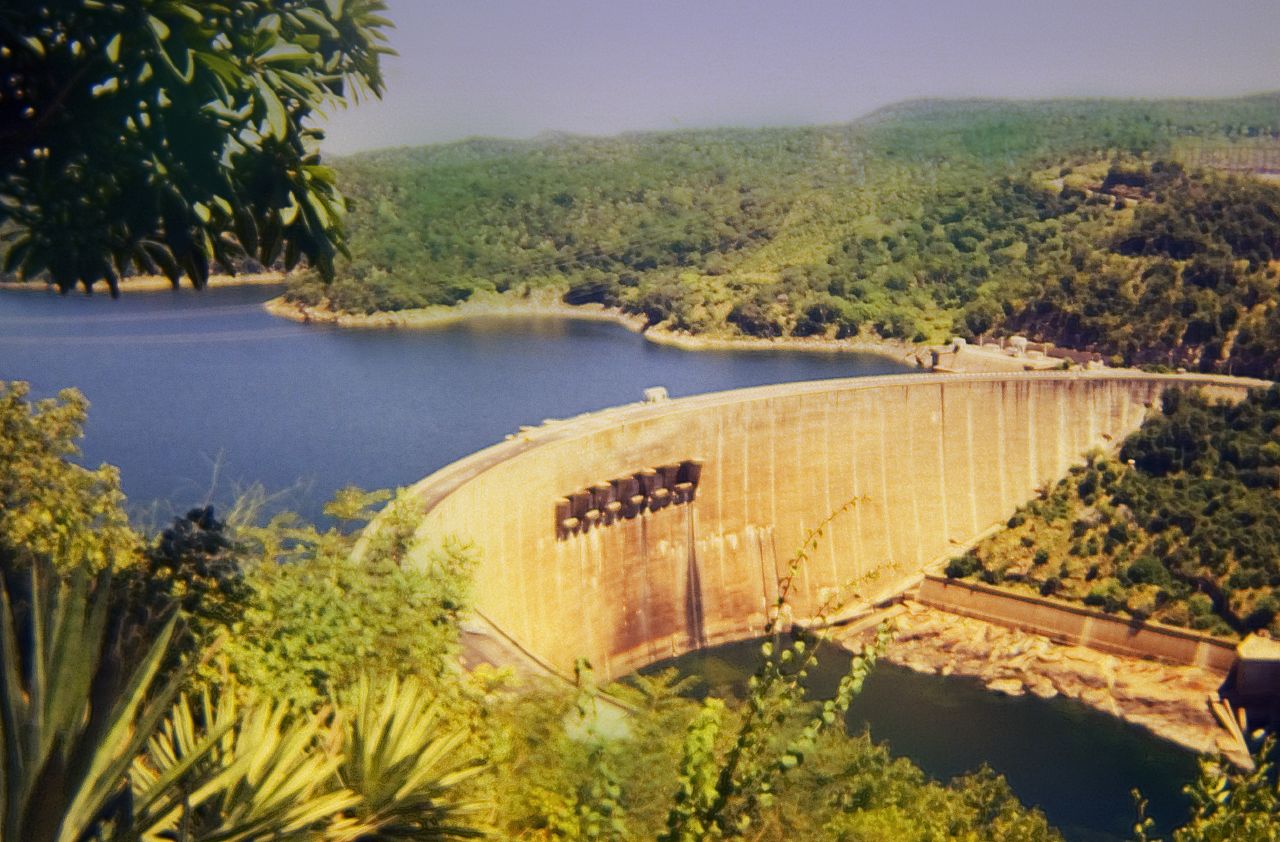
Lake Kariba
Lake Kariba is the world's largest artificial lake and reservoir by volume. It lies upstream from the mouth of the Zambezi river on the Indian Ocean, along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe. Lake Kariba was filled between 1958 and 1963 following the completion of the Kariba Dam at its northeastern end, flooding the Kariba Gorge on the Zambezi River. The Zimbabwean town of Kariba was built for construction workers on the lake's dam, while some other settlements such as Binga village and Mlibizi in Zimbabwe and Siavonga and Sinazongwe in Zambia have expanded to house people displaced by the damming of the river. Physical characteristics Lake Kariba is over long and up to in width. It covers an area of and its storage capacity is . The mean depth of the lake is ; the maximum depth is . It is the world's largest man-made reservoir by volume, four times as large as the Three Gorges Dam. The enormous mass of water is believed to have caused induced seismicity in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mlibizi
Mlibizi is a village on the southern shore of Lake Kariba. Mlibizi is situated in Matabeleland North province in Zimbabwe. Mlibizi is a popular fishing resort amongst the white community and is the terminal of the Kariba Ferries,http://www.karibaferries.com , Kariba Ferries Website which offers car and passenger ferry service. Mlibizi Aerodrome A single untarred runway exists outside the camp for use by light aircraft.Mlibizi Aerodrome Mlibizi Aerodrome on Google maps Kariba Ferries Kariba Ferries is a company that operates car and passenger ferries from Kariba town to Mlibizi. In recent years their services have been ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bed Island
A bed is a piece of furniture that is used as a place to sleep, rest, and relax. Most modern beds consist of a soft, cushioned mattress on a bed frame. The mattress rests either on a solid base, often wood slats, or a sprung base. Many beds include a box spring inner-sprung base, which is a large mattress-sized box containing wood and springs that provide additional support and suspension for the mattress. Beds are available in many sizes, ranging from infant-sized bassinets and cribs, to small beds for a single person or adult, to large queen and king-size beds designed for two people. While most beds are single mattresses on a fixed frame, there are other varieties, such as the murphy bed, which folds into a wall, the sofa bed, which folds out of a sofa, the trundle bed, which is stored under a low, twin-sized bed and can be rolled out to create a larger sleeping area, and the bunk bed, which provides two mattresses on two tiers as well as a ladder to access the upper tier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fothergill Island '', a plant genus
{{disambig ...
Fothergill may refer to: *Fothergill, Cumbria, a place in England * Fothergill (surname), people with the surname ''Fothergill'' See also * Fothergill gold medal, awarded triennially by the Medical Society of London. * Fothergill medal, previously awarded by the Royal Humane Society. *Fothergill–Round–Mitchell Medal, a Victoria Football League award that is presented to the most promising young talent. * Fothergill's sign, a medical sign * Fothergill island, an island in Lake Kariba * Milner-Fothergill gold medal, awarded by the University of Edinburgh for contribution to therapeutics. * ''Fothergilla ''Fothergilla'' (witch alder) is a genus of two to four species of flowering plants in the family Hamamelidaceae, native to woodland and swamps of the southeastern United States. They are low-growing deciduous shrubs growing to tall with downy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampa Karuma
The Speech Assessment Methods Phonetic Alphabet (SAMPA) is a computer-readable phonetic script using 7-bit printable ASCII characters, based on the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). It was originally developed in the late 1980s for six European languages by the EEC ESPRIT information technology research and development program. As many symbols as possible have been taken over from the IPA; where this is not possible, other signs that are available are used, e.g. @">code>@for schwa (IPA ), 2">code>2for the vowel sound found in French (IPA ), and 9">code>9for the vowel sound found in French (IPA ). The characters "s{mp@">code>"s{mp@represent the pronunciation of the name SAMPA in English, with the initial symbol indicating primary stress (in IPA, ). Like IPA, SAMPA is usually enclosed in square brackets or slashes, which are not part of the alphabet proper and merely signify that it is phonetic as opposed to regular text. Languages Today, officially, SAMPA has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been part of a continent. Oceanic islands can be formed from volcano, volcanic activity, grow into atolls from coral reefs, and form from sediment along shorelines, creating barrier islands. River islands can also form from sediment and debris in rivers. Artificial islands are those made by humans, including small rocky outcroppings built out of lagoons and large-scale land reclamation projects used for development. Islands are host to diverse plant and animal life. Oceanic islands have the sea as a natural barrier to the introduction of new species, causing the species that do reach the island to evolve in isolation. Continental islands share animal and plant life with the continent they split from. Depending on how long ago the continental is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richter Magnitude Scale
The Richter scale (), also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale, is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Richter in collaboration with Beno Gutenberg, and presented in Richter's landmark 1935 paper, where he called it the "magnitude scale". This was later revised and renamed the local magnitude scale, denoted as ML or .. Because of various shortcomings of the original scale, most seismological authorities now use other similar scales such as the moment magnitude scale () to report earthquake magnitudes, but much of the news media still erroneously refers to these as "Richter" magnitudes. All magnitude scales retain the logarithmic character of the original and are scaled to have roughly comparable numeric values (typically in the middle of the scale). Due to the variance in earthquakes, it is essential to understand the Richter scale uses common logarithms simply to make the measurements man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. In its most general sense, the word ''earthquake'' is used to describe any seismic event that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes can occur naturally or be induced by human activities, such as mining, fracking, and nuclear weapons testing. The initial point of rupture is called the hypocenter or focus, while the ground level directly above it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
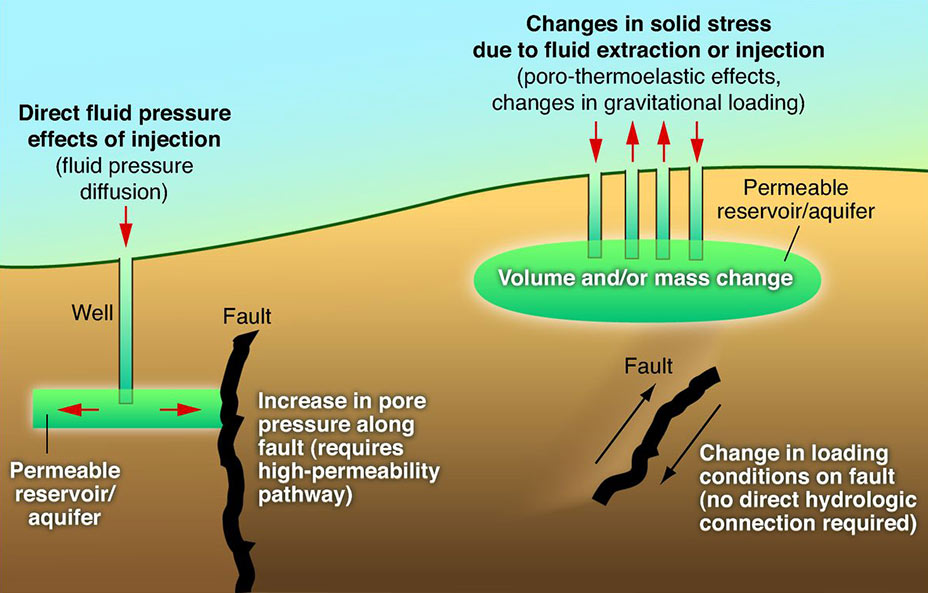
Induced Seismicity
Induced seismicity is typically earthquakes and tremors that are caused by human activity that alters the stresses and strains on Earth's crust. Most induced seismicity is of a low magnitude. A few sites regularly have larger quakes, such as The Geysers geothermal plant in California which averaged two M4 events and 15 M3 events every year from 2004 to 2009. The Human-Induced Earthquake Database (''HiQuake'') documents all reported cases of induced seismicity proposed on scientific grounds and is the most complete compilation of its kind. Results of ongoing multi-year research on induced earthquakes by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) published in 2015 suggested that most of the significant earthquakes in Oklahoma, such as the 1952 magnitude 5.7 El Reno earthquake may have been induced by deep injection of wastewater by the oil industry. A huge number of seismic events in oil and gas extraction states like Oklahoma is caused by increasing the volume of wastewater injec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam (), officially known as Yangtze River Three Gorges Water Conservancy Project () is a hydroelectric gravity dam that spans the Yangtze River near Sandouping in Yiling District, Yichang, Hubei province, central China, downstream of the Three Gorges. The List of reservoirs by volume, world's 27th largest dam by reservoir volume, and the List of largest power stations, world's largest power station by installed capacity (22,500 Megawatt, MW), the Three Gorges Dam generates 95±20 TWh of electricity per year on average, depending on the amount of precipitation in the river basin. After the extensive monsoon rainfalls of 2020, the dam produced nearly 112 TWh in a year, breaking the previous world record of ~103 TWh set by the Itaipu Dam in 2016. The dam's body was completed in 2006; the power plant became fully operational in 2012, when the last of the main water turbines in the underground plant began production. The last major component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |