|
Kiev Governorate
Kiev Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Russian Empire (1796–1917), Ukrainian People's Republic (1917–18; 1918–1921), Ukrainian State (1918), and the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic (1919–1925; part of the Soviet Union since 1922). It included the territory of the right-bank Ukraine and was formed after a division of the Kiev Viceroyalty into Kiev and Little Russia Governorates in 1796. Its capital was in Kiev. By the early 20th century, it consisted of 12 uyezds, 12 cities, 111 miasteczkos and 7344 other settlements. After the October Revolution, it became part of the administrative division of the Ukrainian SSR. In 1923 it was divided into several okrugs and on 6 June 1925 it was abolished by the Soviet administrative reforms. History Kiev Governorate on the right bank of Dnieper was officially established by Emperor Paul I's edict of November 30, 1796. However it was not until 1800 when the first governor was appoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governorate (Russia)
A governorate (, , ) was a major and principal administrative subdivision of the Russian Empire. After the October Revolution, Bolshevik Revolution in 1917, governorates remained as subdivisions in the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian, Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian and Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian Soviet republics, and in the Soviet Union from its formation in 1922 until 1929. The term is also translated as ''government'' or ''province''. A governorate was headed by a governor (), a word borrowed from Latin , in turn from Greek (). Selected governorates were united under an assigned governor-general such as the Grand Duchy of Finland, Congress Poland, Russian Turkestan and others. There were also military governors such as Kronstadt, Vladivostok and others. Aside from governorates, other types of divisions were oblasts (region) and okrugs (district). First reform This subdivision type was created by the edict (ukas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiev
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2,952,301, making Kyiv the List of European cities by population within city limits, seventh-most populous city in Europe. Kyiv is an important industrial, scientific, educational, and cultural center. It is home to many High tech, high-tech industries, higher education institutions, and historical landmarks. The city has an extensive system of Transport in Kyiv, public transport and infrastructure, including the Kyiv Metro. The city's name is said to derive from the name of Kyi, one of its four legendary founders. During History of Kyiv, its history, Kyiv, one of the oldest cities in Eastern Europe, passed through several stages of prominence and obscurity. The city probably existed as a commercial center as early as the 5th century. A Slav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiev Voivodeship
The Kiev Voivodeship (; ; ) was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1471 until 1569 and of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland from 1569 until 1793, as part of Lesser Poland Province of the Polish Crown. On some maps Kiev Voivodeship was also named as the Lower Volhynia. The voivodeship was established in 1471 upon the death of the last prince of Kiev Simeon Olelkovich and transformation of the Duchy of Kiev (appanage duchy of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania) into the Voivodeship of Kiev. Description The voivodeship was established in 1471 under the order of King Casimir IV Jagiellon soon after the death of Semen Olelkovich. It had replaced the former Principality of Kiev, ruled by Lithuanian-Ruthenian Olelkovich princes (related to House of Algirdas and Olshansky family). Its first administrative center was Kiev, but when the city was given to Tsardom of Russia in 1667 by Treaty of Andrusovo, the capital moved to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
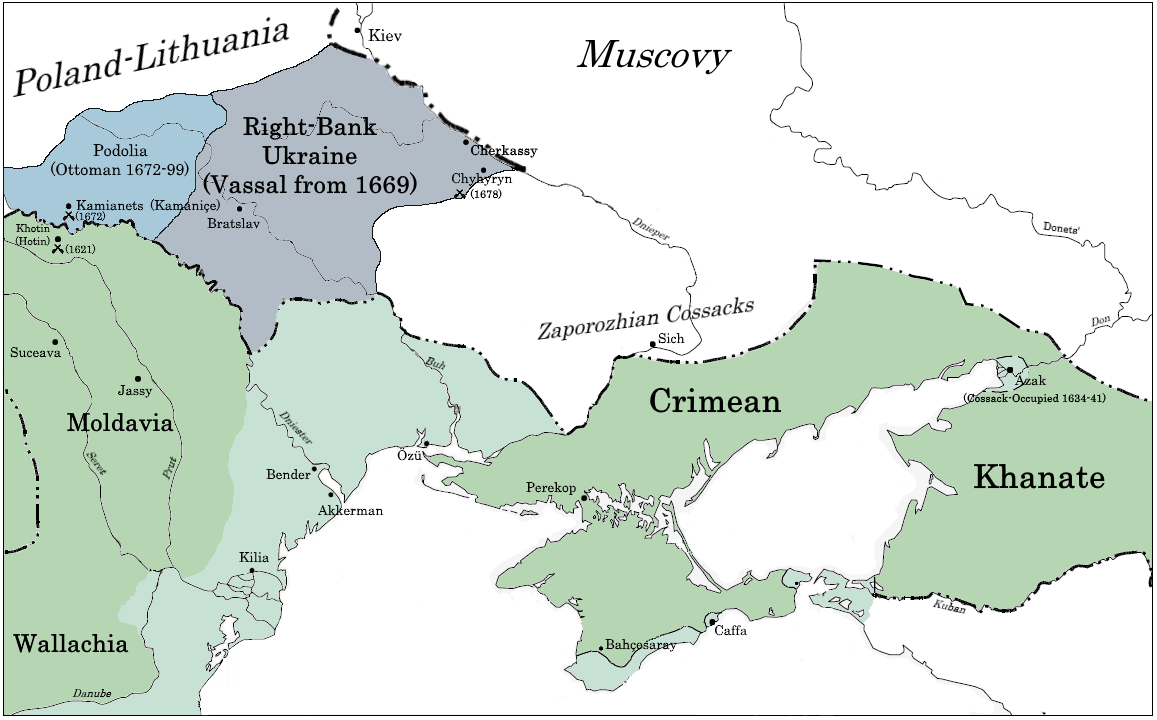
Right-bank Ukraine
The Right-bank Ukraine is a historical and territorial name for a part of modern Ukraine on the right (west) bank of the Dnieper River, corresponding to the modern-day oblasts of Vinnytsia, Zhytomyr, Kirovohrad, as well as the western parts of Kyiv and Cherkasy. It was separated from the left bank during the Ruin. Right-bank Ukraine is bordered by the historical regions of Volhynia and Podolia to the west, Moldavia to the southwest, Yedisan and Zaporizhzhia to the south, left-bank Ukraine to the east, and Polesia to the north. Main cities of the region include Cherkasy, Kropyvnytskyi, Bila Tserkva, Zhytomyr and Oleksandriia. History Since the Middle Ages, the region formed part of the Khazar Khanate, Kievan Rus', Mongol Empire, Golden Horde, Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland. Right-bank Ukraine was the target of slave raids by Tatars from the Black Sea steppes. The history of right- and left-bank Ukraine is closely associated with the Khmelnyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chernihiv
Chernihiv (, ; , ) is a city and municipality in northern Ukraine, which serves as the administrative center of Chernihiv Oblast and Chernihiv Raion within the oblast. Chernihiv's population is The city was designated as a Hero City of Ukraine by the Ukrainian government during the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Names and etymology The name ''Chernihiv''/''Chernigov'' is a compound name, which begins with the Slavic root ''Cherni-''/''Cherno-'', which means 'black'. Scholars vary with interpretations of the second part of the name (''-hiv''/''-gov'', ) though scholars such as Dr. Martin Dimnik, Professor of Medieval History at University of Toronto, connect Chernihov with the worship of "the black god" Chernibog. The city of Chernihiv is also historically known by different names in other languages – ; . History Early history Chernihiv was first mentioned (as ) in the Rus'–Byzantine Treaty (907), but the time of its establishment is unknown. Artifacts from the Khazar Khaga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Russia Governorate (1796-1802)
Little Russia Governorate may refer to: 1764–1781 The First Little Russia Governorate or Malorossiya Governorate, was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Russian Empire, which existed in 1764–1781. It was created after the abolition of Cossack Hetmanate and was governed by Pyotr Rumyantsev. With another administrative reform of 1781 the governorate and its subdivisions (regiments) were liquidated and replaced with vice-royalties divided into counties ( uezds). Subdivisions The governorate was divided into 10 regiments (polk) which were equivalent to counties (uezd). * (1663–1782) * * * Nizhyn Regiment * Chernihiv Regiment * Pryluky Regiment * Lubny Regiment * Myrhorod Regiment * Hadiach Regiment * Poltava Regiment Coat of arms Until 1767 the coat of arms for the governorate was Cossack with musket when it was replaced with the Russian double headed eagle. 1796–1802 Little Russia Governorate or Malorossiya Governorate was an admini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left-bank Ukraine
The Left-bank Ukraine is a historic name of the part of Ukraine on the left (east) bank of the Dnieper River, comprising the modern-day oblasts of Chernihiv, Poltava and Sumy as well as the eastern parts of Kyiv and Cherkasy. Left-bank Ukraine is bordered by the historical regions of Right-bank Ukraine to the southwest, Zaporizhzhia to the southeast, Sloboda Ukraine to the east, and Polesia and White Ruthenia to the north. History Since the Middle Ages, the region formed part of the Khazar Khanate, Kievan Rus', Mongol Empire, Golden Horde, Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland. The term appeared in 1663 with the election of Ivan Bryukhovetsky as the hetman of Ukraine in opposition to Pavlo Teteria. Bryukhovetsky was the first known "left-bank Ukraine" hetman over the area, that was under the Russian influence. Up until the mid-17th century, the area had belonged to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Treaty of Pereyaslav of 1654 saw the region tent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul I Of Russia
Paul I (; – ) was Emperor of Russia from 1796 until his assassination in 1801. Paul remained overshadowed by his mother, Catherine the Great, for most of his life. He adopted the Pauline Laws, laws of succession to the Russian throne—rules that lasted until the end of the Romanov dynasty and of the Russian Empire. He also imposed the first limitations on serfdom in Russia, serfdom with the Manifesto of three-day corvee, sought to curtail the privileges of the Russian nobility, nobility, pursued various military reforms which were highly unpopular among officers and was known for his unpredictable behavior, all of which contributed to the conspiracy that would take his life. In 1799 he brought Russia into the War of the Second Coalition, Second Coalition against First French Republic, Revolutionary France alongside Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain and Habsburg monarchy, Austria; the Russian forces achieved several victories at first but withdrew after facing setbacks. Paul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiev Governorate (1913)
Kiev Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Russian Empire (1796–1917), Ukrainian People's Republic (1917–18; 1918–1921), Ukrainian State (1918), and the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic (1919–1925; part of the Soviet Union since 1922). It included the territory of the right-bank Ukraine and was formed after a division of the Kiev Viceroyalty into Kiev and Little Russia Governorates in 1796. Its capital was in Kiev. By the early 20th century, it consisted of 12 uyezds, 12 cities, 111 miasteczkos and 7344 other settlements. After the October Revolution, it became part of the administrative division of the Ukrainian SSR. In 1923 it was divided into several okrugs and on 6 June 1925 it was abolished by the Soviet administrative reforms. History Kiev Governorate on the right bank of Dnieper was officially established by Emperor Paul I's edict of November 30, 1796. However it was not until 1800 when the first governor was appointed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yury Osipov
Yury Sergeyevich Osipov (; born 7 July 1936) is a Soviet and Russian mathematician. He was elected a full member of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union in 1987 and was a president of its successor, the Russian Academy of Sciences from 17 December 1991 to 29 May 2013. Biography Osipov was born in Tobolsk. In 1959 he graduated from the Department of Mechanics and Mathematics of the Ural State University. His teacher was Nikolay Krasovsky, scientist and founder of the Ural scientific school in mathematical theory of control and the theory of differential games. From 1961 to 1969 he worked at the Ural State University. From 1970 to 1993 he worked at the Institute of Mathematics and Mechanics of the Ural Branch of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union (later, of the Russian Academy of Sciences) in Yekaterinburg (from 1986 to 1993 he was the chief of the Institute). In 1971 he defended his second thesis and received the rank of professor in 1973. In 1984 he was elected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Russian Encyclopedia
The ''Great Russian Encyclopedia'' (''GRE''; , БРЭ, transliterated as ''Bolshaya rossiyskaya entsiklopediya'' or academically as ''Bol'šaja rossijskaja ènciklopedija'') is a universal Russian encyclopedia, completed in 36 volumes, published between 2004 and 2017 by Great Russian Encyclopedia, JSC (, transliterated as ''Bolshaya rossiyskaya entsiklopediya PAO''). A successor to the ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'', it was released under the auspices of the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS) after President Vladimir Putin signed a presidential decree №1156 in 2002. The complete edition was released by 2017. The chief editor of the encyclopedia was Yury Osipov, the president of the RAS. The editorial board had more than 80 RAS members. The first, introductory volume, released in 2004, was dedicated to Russia. Thirty-five volumes were released between 2005 and 2017, covering the range from "A" to " Яя" (''Yaya''). The RAS plans to publish an updated version every five years, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okrug
An okrug is a type of administrative division in some Slavic-speaking states. The word ''okrug'' is a loanword in English, alternatively translated as area, district, county, or region. Etymologically, ''okrug'' literally means ' circuit', derived from Proto-Slavic , in turn from "around" + "circle". In meaning, the word is similar to the German term ''Bezirk'' or '' Kreis'' ('district') and the French word ''arrondissement''; all of which refer to something "encircled" or "surrounded". Bulgaria In Bulgaria, ''s'' are the abolished primary unit of the administrative division and implied "districts" or "counties". They existed in the postwar Bulgaria between 1946 and 1987 and corresponded approximately to today's oblasts. Kazakhstan In Kazakhstan, an ''okrug'' () refers to an administrative-territorial unit that operates below the district (''raion'') level. The term is most commonly used in the form of rural district (), which encompasses one or several rural settleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |