|
Kappa-opioid Receptor Antagonists
An opioid antagonist, or opioid receptor antagonist, is a receptor antagonist that acts on one or more of the opioid receptors. Naloxone and naltrexone are commonly used opioid antagonist drugs which are competitive antagonists that bind to the opioid receptors with higher affinity than agonists but do not activate the receptors. This effectively blocks the receptor, preventing the body from responding to opioids and endorphins. Some opioid antagonists are not pure antagonists but do produce some weak opioid partial agonist effects, and can produce analgesic effects when administered in high doses to opioid-naive individuals. Examples of such compounds include nalorphine and levallorphan. However, the analgesic effects from these specific drugs are limited and tend to be accompanied by dysphoria, most likely due to additional agonist action at the κ-opioid receptor. As they induce opioid withdrawal effects in people who are taking, or have recently used, opioid full agonists, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid Overdose
An opioid overdose is toxicity due to excessive consumption of opioids, such as morphine, codeine, heroin, fentanyl, tramadol, and methadone. This preventable pathology can be fatal if it leads to respiratory depression, a lethal condition that can cause hypoxia from slow and shallow breathing. Other symptoms include small pupils and unconsciousness; however, its onset can depend on the method of ingestion, the dosage and individual risk factors. Although there were over 110,000 deaths in 2017 due to opioids, individuals who survived also faced adverse complications, including permanent brain damage. Opioid overdoses are diagnosed based on symptoms and examination. Risk factors for opioid overdose include high levels of opioid dependence, use of opioids via injection, high-dose opioid usage, having a mental disorder or having a predisposition for one, and use of opioids in combination with other substances, such as alcohol, benzodiazepines, or cocaine. Dependence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Addict
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can alter brain function in synapses similar to natural rewards like food or falling in love in ways that perpetuate craving and weakens self-control for people with pre-existing vulnerabilities. This phenomenon – drugs reshaping brain function – has led to an understanding of addiction as a brain disorder with a complex variety of psychosocial as well as neurobiological factors that are implicated in the development of addiction. While mice given cocaine showed the compulsive and involuntary nature of addiction, for humans this is more complex, related to behavior or personality traits. Classic signs of addiction include compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, ''preoccupation'' with substances or behavior, and continued use des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression (mood)
Depression is a mental state of low Mood (psychology), mood and aversion to activity. It affects about 3.5% of the global population, or about 280 million people worldwide, as of 2020. Depression affects a person's thoughts, behavior, feelings, and subjective well-being, sense of well-being. The pleasure or joy that a person gets from certain experiences is reduced, and the afflicted person often experiences a loss of motivation or interest in those activities. People with depression may experience sadness, feelings of dejection or hopelessness, difficulty in thinking and concentration, or a significant change in appetite or time spent sleeping; Suicidal ideation, suicidal thoughts can also be experienced. Depression can have multiple, sometimes overlapping, origins. Depression can be a symptom of some mood disorders, some of which are also commonly called ''depression'', such as major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder and dysthymia. Additionally, depression can be a norm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Acute Withdrawal Syndrome
Post-acute withdrawal syndrome (PAWS) is a hypothesized set of persistent impairments that occur after Drug withdrawal, withdrawal from Alcohol (drug), alcohol, opioids, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and other substances. Infants born to mothers who used substances of dependence during pregnancy may also experience a PAWS. While PAWS has been frequently reported by those withdrawing from opioid and alcohol dependence, the research has limitations. Protracted benzodiazepine withdrawal has been observed to occur in some individuals prescribed benzodiazepines. Drug use, including alcohol and prescription drugs, can induce symptomatology which resembles mental illness. This can occur both in the intoxicated state and during the Drug withdrawal, withdrawal state. In some cases these substance-induced psychiatric disorders can persist long after detoxification from amphetamine, cocaine, opioid, and alcohol use, causing prolonged psychosis, anxiety or major depression, depression. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Other variables include the pH of extracellular fluid, the concentrations of sodium, potassium, and calcium ions, as well as the blood sugar level, and these need to be regulated despite changes in the environment, diet, or level of activity. Each of these variables is controlled by one or more regulators or homeostatic mechanisms, which together maintain life. Homeostasis is brought about by a natural resistance to change when already in optimal conditions, and equilibrium is maintained by many regulatory mechanisms; it is thought to be the central motivation for all organic action. All home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-dose Naltrexone
Low-dose naltrexone (LDN) refers to daily naltrexone dosages that are roughly one-tenth or less of the standard opioid addiction treatment dosage. Most published research suggests a daily dosage of 4.5 mg, but this can vary by a few milligrams. Low-dose naltrexone has been studied for the treatment of multiple chronic pain disorders including fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, Crohn’s disease, and complex regional pain syndrome. Naltrexone is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for medication-assisted treatment of alcoholism and opioid use disorders. Bernard Bihari's initial off-label usage of naltrexone in doses ranging from 1.5 mg to 3 mg as an adjuvant therapy for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) in the 1980s led to the introduction of LDN into clinical practice. Due to a lack of large-scale clinical trials and standardized research aimed at determining appropriate indications for LDN, it has remained an off-label option. Mechanism of action Nalt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid Addiction
Opioids are a class of drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, including pain relief. The terms "opioid" and "opiate" are sometimes used interchangeably, but the term "opioid" is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain. Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium poppy plant ''Papaver somniferum''. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, and suppressing cough. The opioid receptor antagonist naloxone is used to reverse opioid overdose. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for veterinary use. Opioids are also frequently used recreationally for their euphoric effects or to prevent withdrawal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidote
An antidote is a substance that can counteract a form of poisoning. The term ultimately derives from the Greek term φάρμακον ἀντίδοτον ''(pharmakon antidoton)'', "(medicine) given as a remedy". An older term in English which is now rare is atterlothe, derived from " atter" ("poison" or "venom"). Antidotes for anticoagulants are sometimes referred to as reversal agents. The antidotes for some particular toxins are manufactured by injecting the toxin into an animal in small doses and extracting the resulting antibodies from the host animals' blood. This results in an antivenom that can be used to counteract venom produced by certain species of snakes, spiders, and other venomous animals. Some animal venoms, especially those produced by arthropods (such as certain spiders, scorpions, and bees) are only potentially lethal when they provoke allergic reactions and induce anaphylactic shock; as such, there is no "antidote" for these venoms; however anaphylactic shoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
μ-opioid Receptor
The μ-opioid receptors (MOR) are a class of opioid receptors with a high affinity for enkephalins and beta-endorphin, but a low affinity for dynorphins. They are also referred to as μ(''mu'')-opioid peptide (MOP) receptors. The prototypical μ-opioid receptor agonist is morphine, the primary psychoactive alkaloid in opium and for which the receptor was named, with Mu (letter), mu being the first letter of Morpheus, the compound's namesake in the original Greek. It is an inhibitory G-protein coupled receptor that activates the Gi alpha subunit, Gi alpha subunit, inhibiting adenylate cyclase activity, lowering Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP levels. Structure The structure of the inactive μ-opioid receptor has been determined with the antagonists Beta-Funaltrexamine, β-FNA and alvimopan. Many structures of the active state are also available, with agonists including DAMGO, Β-Endorphin, β-endorphin, fentanyl and morphine. The structure with the agonist BU72 has the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
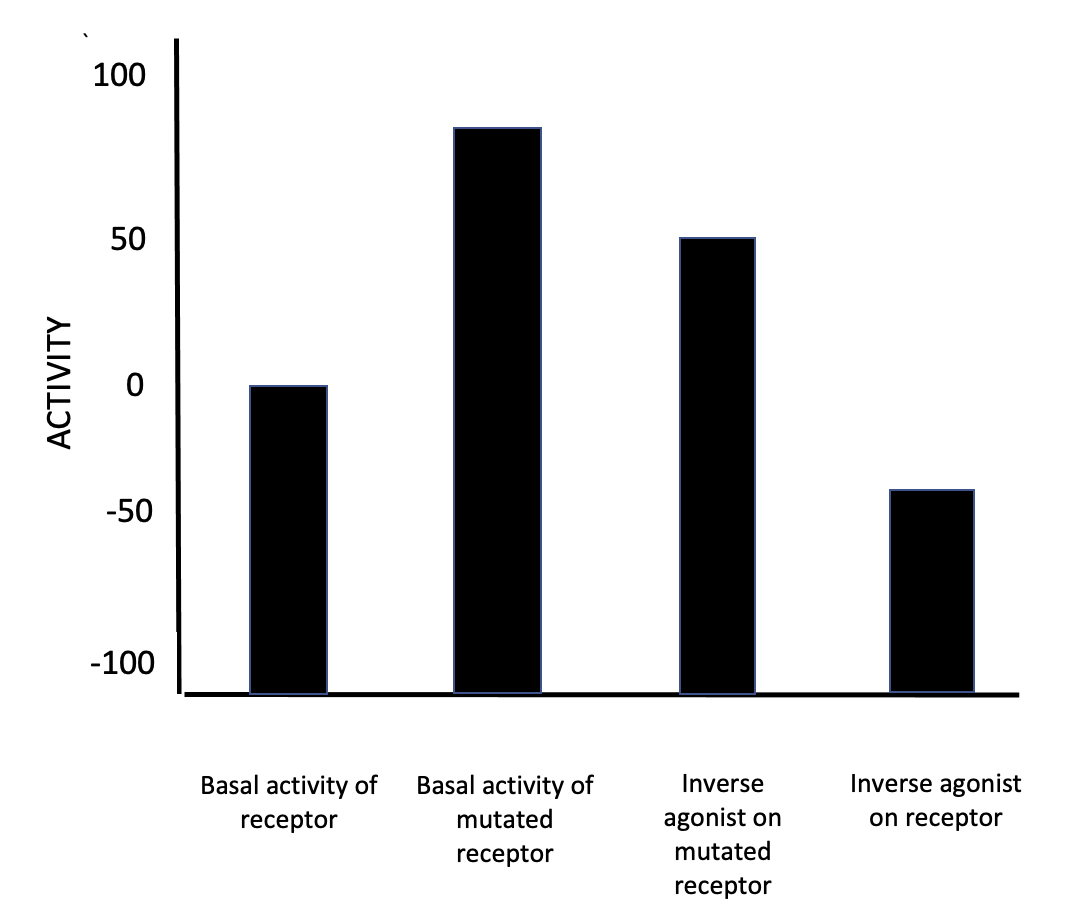
Inverse Agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agonist but can block the activity of either; they are in fact sometimes called ''blockers'' (examples include alpha blockers, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers). Inverse agonists have opposite actions to those of agonists but the effects of both of these can be blocked by antagonists. A prerequisite for an inverse agonist response is that the receptor must have a constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level of activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. The efficacy of a full agonist is by definition 100%, a neutral antagonist has 0% efficacy, and an inverse agonist has < 0% (i.e., n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbiturates
Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as well as overdose potential among other possible adverse effects. They have been used recreationally for their anti-anxiety and sedative effects, and are thus controlled in most countries due to the risks associated with such use. Barbiturates have largely been replaced by benzodiazepines and nonbenzodiazepines ("Z-drugs") in routine medical practice, particularly in the treatment of anxiety disorders and insomnia, because of the significantly lower risk of overdose, and the lack of an antidote for barbiturate overdose. Despite this, barbiturates are still in use for various purposes: in general anesthesia, epilepsy, treatment of acute migraines or cluster headaches, acute tension headaches, euthanasia, capital punishment, and assisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (drug)
Alcohol, sometimes referred to by the chemical name ethanol, is the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks such as beer, wine, and distilled spirits (hard liquor). Alcohol is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant, decreasing Action potential, electrical activity of neurons in the brain, which causes the characteristic effects of alcohol intoxication ("drunkenness"). Among other effects, alcohol produces euphoria, anxiolytic, decreased anxiety, increased sociability, sedation, and impairment of cognitive, memory, motor control, motor, and sense, sensory function. Alcohol has a variety of adverse effects. Short-term effects of alcohol consumption, Short-term adverse effects include generalized impairment of neurocognitive function, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and symptoms of hangover. Alcohol is addiction, addictive and can result in alcohol use disorder, Substance dependence, dependence, and Alcohol withdrawal syndrome, withdrawal upon cessation. The long-term effects of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |