|
Kabbalah
Kabbalah or Qabalah ( ; , ; ) is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal (). List of Jewish Kabbalists, Jewish Kabbalists originally developed transmissions of the primary texts of Kabbalah within the realm of Jewish tradition and often use classical Jewish scriptures to explain and demonstrate its mystical teachings. Kabbalists hold these teachings to define the inner meaning of both the Hebrew Bible and traditional rabbinic literature and their formerly concealed transmitted dimension, as well as to explain the significance of Jewish religious observances. Historically, Kabbalah emerged from earlier forms of Jewish mysticism, in 12th- to 13th-century Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain, al-Andalus (Spain) and in Hakhmei Provence, and was reinterpreted during the Jewish mystical renaissance in 16th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Mysticism
Academic study of Jewish mysticism, especially since Gershom Scholem's ''Major Trends in Jewish Mysticism'' (1941), draws distinctions between different forms of mysticism which were practiced in different eras of Jewish history. Of these, Kabbalah, which emerged in 12th-century southwestern Europe, is the most well known, but it is not the only typological form, nor was it the first form which emerged. Among the previous forms were Merkabah mysticism (c. 100 BCE – 1000 CE), and Ashkenazi Hasidim (early 13th century) around the time of the emergence of Kabbalah. Kabbalah means "received tradition", a term which was previously used in other Judaic contexts, but the Medieval Kabbalists adopted it as a term for their own doctrine in order to express the belief that they were not innovating, but were merely revealing the ancient hidden esoteric tradition of the Torah. This issue has been crystalized until today by alternative views on the origin of the Zohar, the main text of K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Meditation
Jewish meditation includes practices of settling the mind, introspection, visualization, emotional insight, contemplation of divine names, or concentration on philosophical, ethical or mystical ideas. Meditation may accompany unstructured, personal Jewish prayer, may be part of structured Jewish services, or may be separate from prayer practices. Jewish mystics have viewed meditation as leading to '' devekut'' (cleaving to God). Hebrew terms for meditation include '' hitbodedut'' (or ''hisbodedus,'' literally "self-seclusion") or ''hitbonenut/hisbonenus'' ("contemplation"). Through the centuries, meditation practices have been developed in many movements, including among Maimonideans (Moses Maimonides and Abraham Maimonides), Kabbalists ( Abraham Abulafia, Isaac the Blind, Azriel of Gerona, Moses Cordovero, Yosef Karo and Isaac Luria), Hasidic rabbis (Baal Shem Tov, Schneur Zalman of Liadi and Nachman of Breslov), Musar movement rabbis ( Israel Salanter and Simcha Zissel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Jewish Kabbalists
This article lists figures in Kabbalah according to historical chronology and schools of thought. In popular reference, Kabbalah has been used to refer to the whole history of Jewish mysticism, but more accurately, and as used in academic Jewish studies, Kabbalah refers to the doctrines, practices and Western esotericism, esoteric Exegesis#Judaism, exegetical method in Torah, that emerged in 12th-13th century Southern France and Spain, and was developed further in 16th century History of Palestine#Ottoman period, Ottoman Palestine. These formed the basis of subsequent Jewish mystical development. This is a partial list of Jewish Kabbalists; secondary literature incorporating Kabbalah is enormous, particularly in the voluminous library of Hasidic Judaism that turned esoteric Kabbalah into a popular revivalist movement. Hasidism both adapted Kabbalah to its own internalised psychological concern, and also continued the development of the Jewish mystical tradition. Therefore, only fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
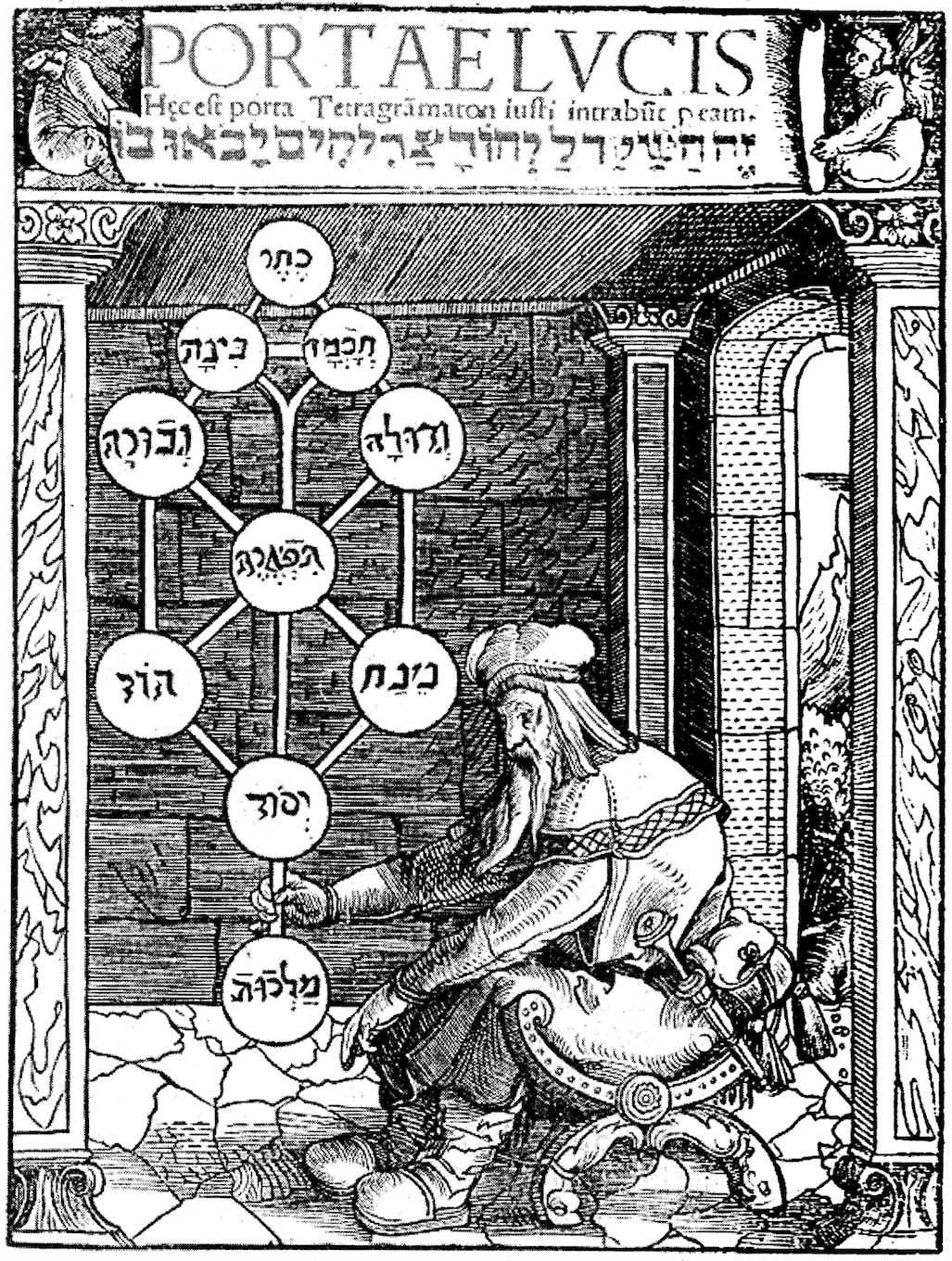
Primary Texts Of Kabbalah
The primary texts of Kabbalah were allegedly once part of an ongoing oral tradition. The written texts are obscure and difficult for readers who are unfamiliar with Jewish spirituality which assumes extensive knowledge of the Tanakh (Hebrew Bible), Midrash (Jewish hermeneutic tradition) and halakha (Jewish religious law). The Torah For kabbalists, ten utterances in Genesis with which God created the world are linked to the ten sefirot—the divine structure of all being. According to the ''Zohar'' and the ''Sefer ha-Yihud'', the Torah is synonymous with God.Kabbalah: New Perspectives, Moshe Idel, Yale University Press, 1988. More specifically, in the ''Sefer ha-Yihud'', the letters in the Torah are the forms of God. The kabbalist looks beyond the literal aspects of the text, to find the hidden mystical meaning. The text not only offers traditions and ways of thinking, but it also reveals the reality of God. One of the first Jewish philosophers, Philo of Alexandria (20BCE-40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham Abulafia
Abraham ben Samuel Abulafia () was the founder of the school of "Prophetic Kabbalah". He was born in Zaragoza, Spain, in 1240, and is assumed to have died sometime after 1291 following a stay on the small and windswept island of Comino (the smallest of the three inhabited islands that make up the Maltese archipelago). Biography Early life and travels Very early in life he was taken by his parents to Tudela, Navarre, where his aged father, Samuel Abulafia, instructed him in the Hebrew Bible and Talmud. In 1258, when Abulafia was eighteen years old, his father died, and Abulafia began a life of ceaseless wandering shortly thereafter. His first journey, in 1260, was to the Land of Israel, where he intended to begin a search for the legendary Sambation and the Ten Lost Tribes. He got no further than 'Akko, however, because of the desolation and lawlessness in the Holy Land stemming from the chaos following the recent Crusade. The battle that year between the Mongol Empire and Mam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zohar
The ''Zohar'' (, ''Zōhar'', lit. "Splendor" or "Radiance") is a foundational work of Kabbalistic literature. It is a group of books including commentary on the mystical aspects of the Torah and scriptural interpretations as well as material on mysticism, mythical cosmogony, and mystical psychology. The ''Zohar'' contains discussions of the nature of God, the origin and structure of the universe, the nature of souls, redemption, the relationship of ego to darkness and "true self" to "the light of God". The ''Zohar'' was first publicized by Moses de León (c. 1240 – 1305 CE), who claimed it was a Tannaitic work recording the teachings of Simeon ben Yochai (). This claim is universally rejected by modern scholars, most of whom believe de León, also an infamous forger of Geonic material, wrote the book himself between 1280 and 1286. Some scholars argue that the ''Zohar'' is the work of multiple medieval authors and/or contains a small amount of genuinely antique novel mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pardes (Jewish Exegesis)
Pardes () is a Kabbalistic theory of Biblical exegesis first advanced by Moses de León,ר' משה די ליאון, שו"ת לר' משה די ליאון בענייני קבלה, ישעיה תשבי, חקרי קבלה ושלוחותיה, חלק א, עמ' 64 Tishbi also published this in קבץ על יד - טו, חברת מקיצי נרדמים, which version is available on Otzar (pg. 31). adapting the popular "fourfold" method of medieval Christianity. The term, sometimes also rendered PaRDeS, means "orchard" when taken literally, but is used in this context as a Hebrew acronym formed from the initials of the following four approaches: * Peshat () – "surface" ("straight") or the literal (direct) meaning. *Remez () – "hints" or the deep (allegoric: hidden or symbolic) meaning beyond just the literal sense. In the version of the New Zohar, Re'iah. * Derash () – from Hebrew ''darash'': "inquire" ("seek") – the comparative (midrashic) meaning, as given through similar oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chasidism
Hasidism () or Hasidic Judaism is a religious movement within Judaism that arose in the 18th century as a spiritual revival movement in contemporary Western Ukraine before spreading rapidly throughout Eastern Europe. Today, most of those affiliated with the movement, known as ''hassidim'', reside in Israel and in the United States (mostly Brooklyn and the Hudson Valley). Israel Ben Eliezer, the "Baal Shem Tov", is regarded as its founding father, and his disciples developed and disseminated it. Present-day Hasidism is a sub-group within Haredi Judaism and is noted for its religious conservatism and social seclusion. Its members aim to adhere closely both to Orthodox Jewish practice – with the movement's own unique emphases – and the prewar lifestyle of Eastern European Jews. Many elements of the latter, including various special styles of dress and the use of the Yiddish language, are nowadays associated almost exclusively with Hasidism. Hasidic thought draws heavily on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasidic Judaism
Hasidism () or Hasidic Judaism is a religious movement within Judaism that arose in the 18th century as a Spirituality, spiritual revival movement in contemporary Western Ukraine before spreading rapidly throughout Eastern Europe. Today, most of those affiliated with the movement, known as ''hassidim'', reside in Israel and in the United States (mostly Brooklyn and the Hudson Valley). Israel Ben Eliezer, the "Baal Shem Tov", is regarded as its founding father, and his disciples developed and disseminated it. Present-day Hasidism is a sub-group within Haredi Judaism and is noted for its religious conservatism and social seclusion. Its members aim to adhere closely both to Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jewish practice – with the movement's own unique emphases – and the prewar lifestyle of Eastern European Jews. Many elements of the latter, including various special styles of dress and the use of the Yiddish language, are nowadays associated almost exclusively with Hasidism. Has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esoteric
Western esotericism, also known as the Western mystery tradition, is a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas and currents are united since they are largely distinct both from orthodox Judeo-Christian, Judeo-Christian religion and Age of Enlightenment rationalism. It has influenced, or contributed to, various forms of Western philosophy, mysticism, Western religions, religion, science, pseudoscience, Western art history, art, Western literature, literature, and Western culture#Music, music. The idea of grouping a wide range of Western traditions and philosophies together under the term ''esotericism'' developed in 17th-century Europe. Various academics have debated numerous definitions of Western esotericism. One view adopts a definition from certain esotericist schools of thought themselves, treating "esotericism" as a perennial philosophy, perennial hidden inner tradition. A second perspective sees esotericism as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Luria
Isaac ben Solomon Ashkenazi Luria (; #FINE_2003, Fine 2003, p24/ref>July 25, 1572), commonly known in Jewish religious circles as Ha'ari, Ha'ari Hakadosh or Arizal, was a leading rabbi and Jewish mysticism, Jewish mystic in the community of Safed in the Galilee region of Ottoman Syria, now Israel. He is considered the father of contemporary Kabbalah, his teachings being referred to as Lurianic Kabbalah. While his direct literary contribution to the Kabbalistic school of Safed was extremely minute (he wrote only a few poems), his spiritual fame led to their veneration and the acceptance of his authority. The works of his disciples compiled his oral teachings into writing. Every custom of Luria was scrutinized, and many were accepted, even against previous practice. Luria died at Safed on July 25, 1572, and is buried at the Safed Old Jewish Cemetery. The Ari Ashkenazi Synagogue, also located in Safed, was built in memory of Luria during the late 16th century. Early life Luri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysticism
Mysticism is popularly known as becoming one with God or the Absolute (philosophy), Absolute, but may refer to any kind of Religious ecstasy, ecstasy or altered state of consciousness which is given a religious or Spirituality, spiritual meaning. It may also refer to the attainment of insight in ultimate or hidden truths, and to human transformation supported by various practices and experiences. The term "mysticism" has Ancient Greek origins with various historically determined meanings. Derived from the Greek language, Greek word μύω ''múō'', meaning "to close" or "to conceal", mysticism came to refer to the biblical, liturgical (and sacramental), spiritual, and Christian contemplation, contemplative dimensions of early and medieval Christianity. During the early modern period, the definition of mysticism grew to include a broad range of beliefs and ideologies related to "extraordinary experiences and states of mind". In modern times, "mysticism" has acquired a limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |