|
Jenin Governorate
The Jenin Governorate () is one of 16 Governorates of Palestine. It covers the northern extremity of the West Bank, including the area around the city of Jenin, which is the district capital or ''muhfaza'' of the district. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics 2017 Census, the governorate had a population of 314,866. This is an increase from the reported population of 256,619 in the 2007 Census2007 Locality Population Statistics living in 47,437 households. 100,701 inhabitants (or 39%) were under the age of 63 (or 31%) were re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governorates Of Palestine
Palestine is a unitary state, but is divided into sixteen governorates for administrative purposes. After the signing of the Oslo Accords, the West Bank and Gaza Strip were placed under the jurisdiction of the Palestinian National Authority, which divided the territories into governorates. The governorates are subdivided in turn into Municipality (Palestinian Authority), municipalities. List Notes See also * ISO 3166-2:PS * List of regions of Palestine by Human Development Index References {{DEFAULTSORT:Governorates of Palestine Governorates of Palestine, Subdivisions of Palestine Lists of administrative divisions, Palestine, Governorates Administrative divisions in Asia, Palestine 1 First-level administrative divisions by country, Governorates, Palestine Palestine geography-related lists Governorates, Palestine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samaria
Samaria (), the Hellenized form of the Hebrew name Shomron (), is used as a historical and Hebrew Bible, biblical name for the central region of the Land of Israel. It is bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The region is known to the Palestinians in Arabic under two names, Samirah (, ''as-Sāmira''), and Mount Nablus (جَبَل نَابُلُس, ''Jabal Nābulus''). The first-century historian Josephus set the Mediterranean Sea as its limit to the west, and the Jordan Rift Valley, Jordan River as its limit to the east. Its territory largely corresponds to the Hebrew Bible, biblical allotments of the tribe of Ephraim and the western half of Tribe of Manasseh, Manasseh. It includes most of the region of the ancient Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel, which was north of the Kingdom of Judah. The border between Samaria and Judea is set at the latitude of Ramallah. The name "Samaria" is derived from the Samaria (ancient city), ancient city of Sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
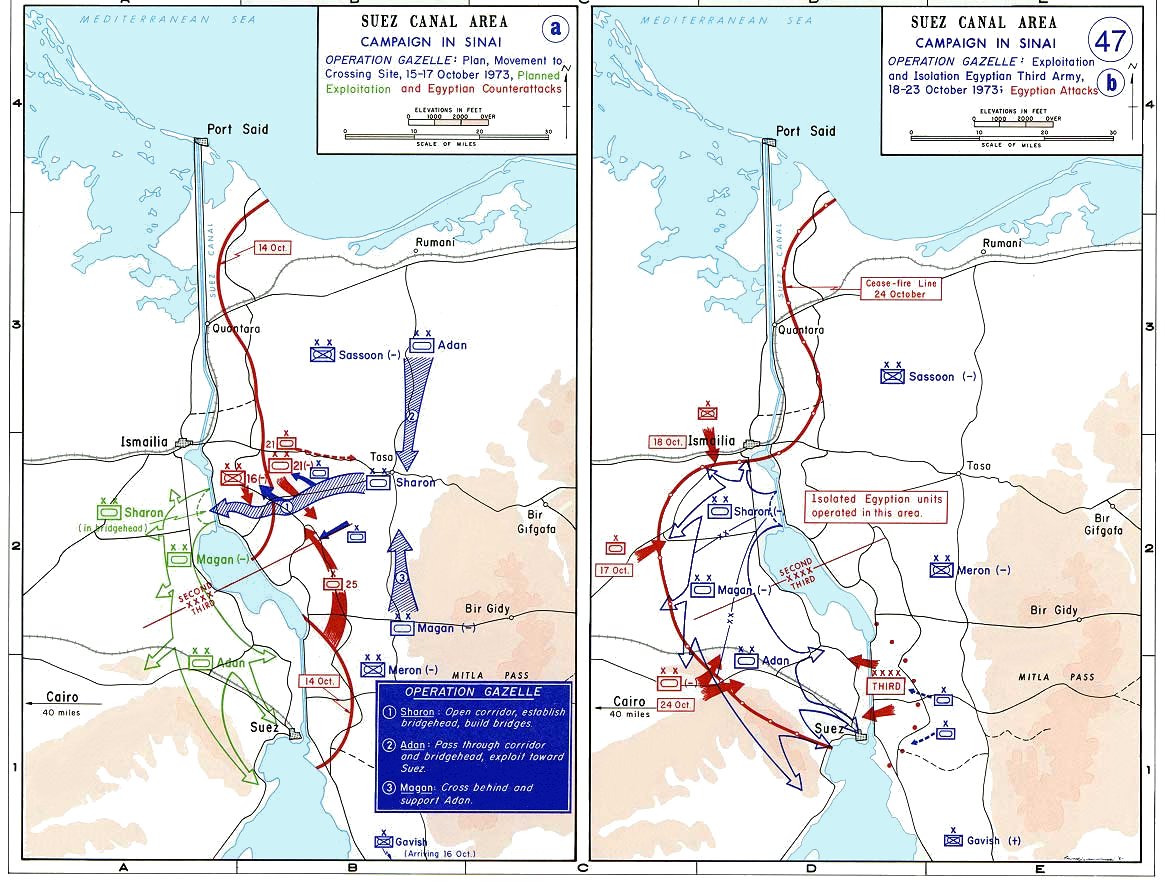
Israeli Army
The Israeli Ground Forces () are the Army, ground forces of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF). The commander is the GOC Army Headquarters, General Officer Commanding with the rank of major general, the ''Mazi'', subordinate to the Chief of the General Staff (Israel), Chief of General Staff. An order from Defense Minister David Ben-Gurion on 26 May 1948 officially set up the Israel Defense Forces as a conscription, conscript army formed out of the paramilitary group Haganah, incorporating the militant (word), militant groups Irgun and Lehi (group), Lehi. The Ground Forces have served in all the country's major military operations—including the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, 1956 Suez Crisis, 1967 Six-Day War, 1973 Yom Kippur War, 1976 Operation Entebbe, 1982 Lebanon War, 1987–1993 First Intifada, 2000–2005 Second Intifada, 2006 Lebanon War, and the Gaza War (2008–09). While originally the IDF operated on three fronts—against Lebanon and Syria in the north, Jordan and Iraq in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Intifada
The First Intifada (), also known as the First Palestinian Intifada, was a sustained series of Nonviolent resistance, non-violent protests, acts of civil disobedience, Riot, riots, and Terrorism, terrorist attacks carried out by Palestinians and Palestinian political violence, Palestinian militant groups in the Israeli-occupied territories, Israeli-occupied Palestinian territories and Israel. It was motivated by collective Palestinian frustration over Israel's military occupation of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip as it approached a twenty-year mark, having begun in the wake of the Six-Day War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War.#LockmanBeinin1989, Lockman; Beinin (1989), p.&nbs5./ref> The uprising lasted from December 1987 until the Madrid Conference of 1991, though some date its conclusion to 1993, the year the Oslo Accords were signed. The Intifada began on 9 December 1987 in the Jabalia refugee camp after an Israeli truck driver collided with parked civilian vehicles, killing four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodities
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that specifically has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them. The price of a commodity good is typically determined as a function of its market as a whole: well-established physical commodities have actively traded spot and derivative markets. The wide availability of commodities typically leads to smaller profit margins and diminishes the importance of factors (such as brand name) other than price. Most commodities are raw materials, basic resources, agricultural, or mining products, such as iron ore, sugar, or grains like rice and wheat. Commodities can also be mass-produced unspecialized products such as chemicals and computer memory. Popular commodities include crude oil, corn, and gold. Other definitions of commodity include something useful or valued and an alternative term for an econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market (economics)
In economics, a market is a composition of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations or infrastructures whereby parties engage in Exchange (economics), exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services (including labour power) to buyers in exchange for money. It can be said that a market is the process by which the value of goods and services are established. Markets facilitate trade and enable the distribution and allocation of resources in a society. Markets allow any tradeable item to be evaluated and priced. A market emergence, emerges more or less spontaneous order, spontaneously or may be constructed deliberately by human interaction in order to enable the exchange of rights (cf. ownership) of services and goods. Markets generally supplant Gift economy, gift economies and are often held in place through rules and customs, such as a booth fee, competitive pricing, and source of goods for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finished Goods
Finished goods are goods that have completed the manufacturing process but have not yet been sold or distributed to the end user. Manufacturing Manufacturing has three classes of inventory: # Raw material # Work in process # Finished goods A good purchased as a "raw material" goes into the manufacture of a product. A good only partially completed during the manufacturing process is called "work in process". When the good is completed as to manufacturing but not yet sold or distributed to the end-user, it is called a "finished good". This is the last stage for the processing of goods. The goods are ready to be consumed or distributed. There is no processing required in term of the goods after this stage by the seller. Though there may be instance that seller finished goods become buyer's raw materials Finished goods is a relative term. In a Supply chain management flow, the finished goods of a supplier can constitute the raw material of a buyer Procurement is the proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cash Crop
A cash crop, also called profit crop, is an Agriculture, agricultural crop which is grown to sell for profit. It is typically purchased by parties separate from a farm. The term is used to differentiate a marketed crop from a staple crop ("subsistence crop") in subsistence agriculture, which is one fed to the producer's own livestock or grown as food for the producer's family. In earlier times, cash crops were usually only a small (but vital) part of a farm's total yield, while today, especially in Developed country, developed countries and among Smallholding, smallholders almost all crops are mainly grown for revenue. In the Least developed country, least developed countries, cash crops are usually crops which attract demand in more developed nations, and hence have some export value. Prices for major cash crops are set in international trade markets with global markets, global scope, with some local variation (termed as "basis") based on Cargo, freight costs and local supply a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autarky
Autarky is the characteristic of self-sufficiency, usually applied to societies, communities, states, and their economic systems. Autarky as an ideology or economic approach has been attempted by a range of political ideologies and movements, particularly leftist ones like African socialism, mutualism, war communism, communalism, swadeshi, syndicalism (especially anarcho-syndicalism), and left-wing populism, generally in an effort to build alternative economic structures or to control resources against structures a particular movement views as hostile. However, some right-wing ones, like nationalism, conservatism, and anti-globalism, along with even some centrist movements, have also adopted autarky, generally on a more limited scale, to develop a particular industry, to gain independence from other national entities or to preserve part of an existing social order. Proponents of autarky have argued for national self-sufficiency to reduce foreign economic, polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce a particular thing, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise prices or exclude competitors. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. In law, a monopoly is a business entity that has significant market power, that is, the power to charge Monopoly price, overly high prices, which is associated with unfair price raises. Although monopolies may be big businesses, size is not a characteristic of a monopoly. A small business may still have the power to raise prices in a small industry (or market). A monopoly may als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rural Notables (Palestine)
Rural notables, as individuals, or the rural notability as a collective, was a social class of local notables (known in Arabic as ''a'yan-'', ''wujaha'-'', ''zu'ama- rifiyya, qarawiyya, mahaliyya'') in late Ottoman and British Mandate Palestine, with equivalent groups developing throughout the Levant. Most rural notables originated in, and belonged to, the fellahin/peasantry class, forming a lower-echelon land-owning gentry in Palestine's post-Tanzimat countryside and emergent towns. Numerically, rural notables form the majority of Palestinian elites, although certainly not the richest. In contrast to urban elites traditionally made of city-dwelling merchants (''tujjar''), clerics (ulema''), ashraf, military officers, and governmental functionaries, the rural notability was composed of rural sheikhs, village or clan mukhtars. Rural notables took advantage of changing legal, administrative and political conditions, and global economic realities, to achieve socio-economic and po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nablus Sanjak
The Nablus Sanjak (; ) was an administrative area that existed throughout Ottoman Empire, Ottoman rule in the Ottoman Syria, Levant (1517–1917). It was administratively part of the Damascus Eyalet until 1864 when it became part of Syria Vilayet and then the Beirut Vilayet in 1888. History Early Ottoman rule In the 1596- daftar, the Sanjak of Nablus contained the following subdivisions and villages/towns: Nahiya Jabal Shami *Tayasir, 'Aqqaba, Tammun, Tubas (city), Tubas, Sir, Jenin, Sir, Talluza, Fandaqumiya, Jaba, Jenin, Jaba, Burqa, Nablus, Burqa, Zawata,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 125 Ijnisinya, Rama, Jenin, Rama, Ajjah, Attil, Kafr Rumman, Shufa, Tulkarm, Shufa, Beit Lid, Saffarin, YasidHütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 126 Kufeir, Baqa al-Gharbiyye, Ramin, Tulkarm, Ramin, Zemer, Anabta, Bal'a, Qabatiya, Al-Judeida,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 127 Arraba, Jenin, Arraba, Yabad, Kufeirit, Burqin, Palestine, Burqin, Asira ash-Shamaliya, Kafr Qud, Mirka, Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |