|
Iranian Archaeologists
This is a list of archaeologists – people who study or practise archaeology, the study of the human past through material remains. A * Charles Conrad Abbott (1843–1919) American; advocate of early occupation of Americas * Kamyar Abdi (born 1969) Iranian; Iran, Neolithic to the Bronze Age * Aziz Ab'Saber (1924–2012) Brazilian; Brazil * Johann Michael Ackner (1783–1862) Transylvanian; Roman Dacia * Dinu Adameșteanu (1913–2004) Romanian-Italian; aerial photography, survey of sites * James M. Adovasio (born 1944) U.S.; New World (esp. Pre-Clovis), perishable technologies * Anagnostis Agelarakis (born 1956) Greek; archaeological and physical anthropology * Yohanan Aharoni (1919–1976) Israeli; Israel Bronze Age * Julius Ailio (1872–1933) Finnish; Karelian Isthmus * Ekrem Akurgal (1911–2002) Turkish; Anatolia * Jorge de Alarcão (born 1934) Portuguese; Roman Portugal * Umberto Albarella (born 19??) Italian-British; zooarchaeology * William F. Albright (1891–1971) U. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susan E
Susan is a feminine given name, the usual English version of Susanna or Susannah. All are versions of the Hebrew name Shoshana, which is derived from the Hebrew ''shoshan'', meaning ''lotus flower'' in Egyptian, original derivation, and several other languages. Variations * Susana, Susanna (or Suzanna), Susannah, Suzana, Suzannah * Susann, Sussan, Suzan, Suzann * Susanne, Suzanne * Susanne * Suzan * Suzanne * Suzette * Susie, Suzy Nicknames Common nicknames for Susan include: * Sue, Susie, Susi (German), Suzi, Suzy, Suzie, Suze, Sanna, Suzie, Sookie, Sukie Sukie are an English four piece indie band from Kettering, Northamptonshire, England, who formed in March 2006. They had a number one on the UK Indie Chart in 2008 with the double a-side "Pink-A-Pade" / "Fairies". Following the split of the band, ..., Sukey, Subo, Suus (Dutch), Shanti In other languages * Albanian and * * , or * * , or * * , or * Catalan, Estonian and * ** * Czech and * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruth Amiran
Ruth Amiran (; ; December 8, 1914 – December 14, 2005) was an Israeli archaeologist whose book ''Ancient Pottery of the Holy Land: From Its Beginnings in the Neolithic Period to the End of the Iron Age'' which was published in 1970 is a standard reference for archaeologists working in Israel. Ruth Amiran was born in the moshava Yavne'el in the Galilee area of the Ottoman Empire. In 1908 her father Yehezkel Brandshteter had immigrated from Tarnów in Poland (Galicia) to the area, where he married her mother Devora in 1913. She went to school in Haifa and became later in 1933 one of the first students of Archeology at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. She excavated alongside Judith Marquet-Krause at et-Tell. Awards Amiran received the Israel Prize in 1982. Further reading * * * * See also *List of Israel Prize recipients This is an incomplete list of recipients of the Israel Prize from the inception of the Prize in 1953 - 2025. List For each year, the recipients a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedat Alp
Prof. Ord. Sedat Alp (January 1, 1913 in Veroia – October 9, 2006 in Ankara) was the first Turkish archaeologist, historian and academic with a specialization in Hittitology, and was among the foremost names in the field. He was the president of the Turkish Historical Association from 1982 to 1983. Biography Sedat Alp was born in Veroia, Greece. His family moved to Turkey as a result of the exchange of populations between Greece and Turkey in 1923. In 1932, he earned a state scholarship opened under the personal auspices of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk and was sent to the University of Leipzig (he later transferred to the University of Berlin) to study prehistory, history, Hittitology, Sumerology, Assyriology, ancient Anatolian languages and cultures, as well as archaeology in general. Having earned his doctorate in the University of Berlin, he returned to Turkey in 1940 and started to teach Hittitology within Ankara University's Faculty of Languages, History and Geography (DTCF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penelope Allison
Penelope Mary "Pim" Allison (born 1954) is a New Zealand academic archaeologist specialising in the Roman Empire. Since 2015, she has been professor of archaeology at the University of Leicester. She is also a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries and an Honorary Fellow of the Australian Academy of the Humanities. Life Allison is originally from North Canterbury, New Zealand. She grew up on a sheep farm. Career Allison received an undergraduate degree in pure mathematics from the University of Canterbury, and her MA Honours and her doctorate in archaeology from the University of Sydney. She was a scholar at the British School in Rome, and has taught archaeology and ancient history at the University of Sydney, the Australian National University and the University of Sheffield. She has held several research fellowships, including a fellowship in the Classics faculty at the University of Cambridge and fellowships at the University of Sydney. She joined the School of Archaeol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesians
Polynesians are an ethnolinguistic group comprising closely related ethnic groups native to Polynesia, which encompasses the islands within the Polynesian Triangle in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Southeast Asia and are part of the larger Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, with an Urheimat in Taiwan. They speak the Polynesian languages, a branch of the Oceanic subfamily within the Austronesian language family. The Indigenous Māori people form the largest Polynesian population, followed by Samoans, Native Hawaiians, Tahitians, Tongans, and Cook Islands Māori. , there were an estimated 2 million ethnic Polynesians (both full and part) worldwide. The vast majority either inhabit independent Polynesian nation-states (Samoa, Niue, Cook Islands, Tonga, and Tuvalu) or form minorities in countries such as Australia, Chile (Easter Island), New Zealand, France (French Polynesia and Wallis and Futuna), and the United States (Hawaii and Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapita
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their distinct material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. The Lapita people are believed to have originated from the northern Philippines, either directly, via the Mariana Islands, or both. They were notable for their distinctive geometric designs on dentate-stamped pottery, which closely resemble the pottery recovered from the Nagsabaran archaeological site in northern Luzon. The Lapita intermarried with the Papuan populations to various degrees, and are the direct ancestors of the Austronesian peoples of Polynesia, eastern Micronesia, and Island Melanesia. Etymology The term "Lapita" was coined by archaeologists after mishearing a word in the local Haveke language, ''xapeta'a'', which means "to dig a hole" or "the place where one digs", during the 1952 excavation in New Caledonia. The Lapita archaeological culture is named after the type site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Essington
Port Essington is an inlet and historic site located on the Cobourg Peninsula in the Garig Gunak Barlu National Park in Australia's Northern Territory. It was the site of an early attempt at British settlement, but now exists only as a remote series of ruins. Settlement In August 1618 Lenaert Jacobszoon, the captain of the Dutch East India Company vessel ''Mauritius (1618 ship), Mauritius'', marked the point on the entrance to what was later called Port Essington, on the Dutch charts as Kape Schildpad (Cape Turtle). In the early 19th century, the United Kingdom, British government became interested in establishing a settlement on Australia's northern coastline in order to facilitate trade with Asia. Port Essington was named on 23 April 1818 by Phillip Parker King in 'as a tribute of my respect for the memory of my lamented friend, Vice-Admiral Sir William Essington', who was in command of ''HMS Triumph (1764), Triumph'' at the battle of Camperdown in October 1797. Sir J.G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its continental landmass. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, at the centre of the land and water hemispheres, water hemisphere, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of about and a population of around 46.3 million as of 2024. Oceania is the smallest continent in land area and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, second-least populated after Antarctica. Oceania has a diverse mix of economies from the developed country, highly developed and globally competitive market economy, financial markets of Australia, French Polynesia, Hawaii, New Caledonia, and New Zealand, which rank high in quality of life and Human Development Index, to the much least developed countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jim Allen (archaeologist)
Jim Allen is an Australian archaeologist specialising in the archaeology of the South Pacific. Allen led the first professional excavation of a European site in Australia, the 1840s military settlement of Victoria, which was established at Port Essington at the northernmost point of the Northern Territory. He also worked on the Lapita culture, tracing the expansion of Polynesian settlement through its distinctive pottery style. In the 1990s, he played a prominent role in the debate over the forced repatriation of Aboriginal remains.Kathy Laster. Law as Culture'. Federation Press; 2001. . p. 230. Allen was the Foundation Professor of Department of Archaeology at La Trobe University from 1985 to 1993. Prior to that, he taught in the department of prehistory at the Australian National University. From 1993, he was a professorial fellow of the Australian Research Council and research associate at La Trobe. In 2012 he was elected a foreign associate of the United States National Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbas Alizadeh
Abbas Alizadeh (born 1951) is an Iranologist and Persian archaeologist. Alizadeh is a senior research associate at the Institute for the Study of Ancient Cultures of The University of Chicago The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, or UChi) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Its main campus is in the Hyde Park neighborhood on Chicago's South Side, near the shore of Lake Michigan about fr ..., who works with the Iranian Prehistoric Project. He has supervised foreign teams of archaeologists working throughout Iran. He is known for his investigations of Chogha Bonut.Mullen, WilliamPERSIAN CITY'S RUINS, RICHES FIND A HOME IN CHICAGO ''Chicago Tribune'', September 9, 2000 References *- by Abbas Alizadeh, with contributions by N. F. Miller, A. M. Rosen, and R. W. Redding External links Iranian Prehistoric Project {{DEFAULTSORT:Alizadeh, Abbas Iranian archaeologists American Iranologists Iranian Iranologists American people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
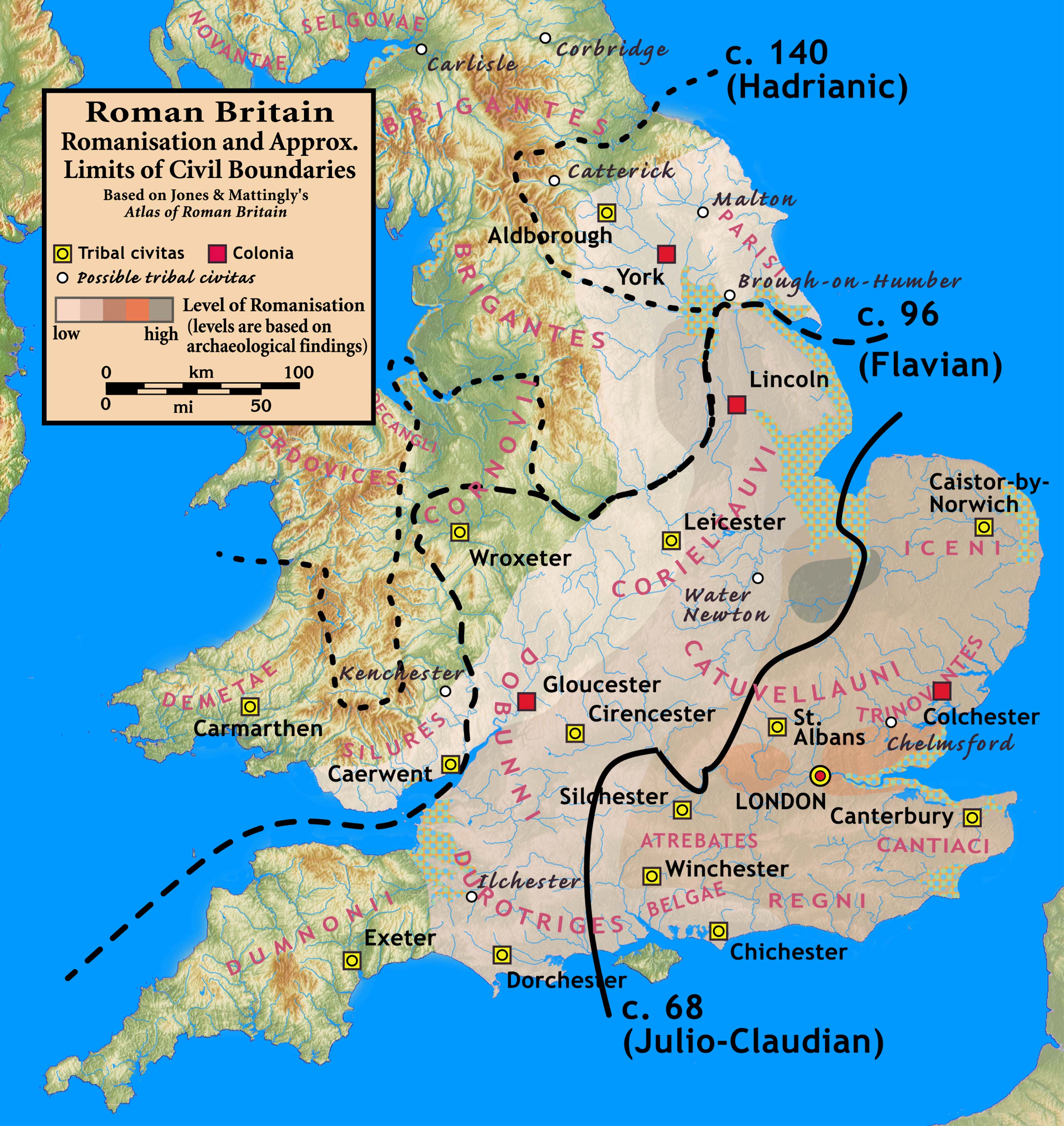
Romano-British Culture
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, a people of Celtic language and custom. Scholars such as Christopher Snyder believe that during the 5th and 6th centuries – approximately from 410 when the Roman legions withdrew, to 597 when St Augustine of Canterbury arrived – southern Britain preserved an active sub-Roman culture that survived the attacks from the Anglo-Saxons and even used a vernacular Latin when writing. Arrival of the Romans Roman troops, mainly from nearby provinces, invaded in AD 43, in what is now part of England, during the reign of Emperor Claudius. Over the next few years the province of Britannia was formed, eventually including the whole of what later became England and Wales and parts of Scotland.Kinder, H. & Hilgemann W. ''The Penguin Atlas of Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |