|
Interborough Rapid Transit Company
The Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT) was the private operator of New York City's original underground subway line that opened in 1904, as well as earlier elevated railways and additional rapid transit lines in New York City. The IRT was purchased by the city on June 12, 1940, along with the younger BMT and IND systems, to form the modern New York City Subway. The former IRT lines (the numbered routes in the current subway system) are now the A Division or IRT Division of the Subway. History The first IRT subway ran between City Hall and 145th Street at Broadway, opening on October 27, 1904. It opened following more than twenty years of public debate on the merits of subways versus the existing elevated rail system and on various proposed routes. Founded on May 6, 1902, by August Belmont, Jr., the IRT's mission was to operate New York City's initial underground rapid transit system after Belmont's and John B. McDonald's Rapid Transit Construction Company w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Transit Museum
The New York Transit Museum (also called the NYC Transit Museum) is a museum that displays historical artifacts of the New York City Subway, MTA Regional Bus Operations, bus, and commuter rail systems in the greater New York City metropolitan region. The main museum is located in the decommissioned Court Street metro station, subway station in Downtown Brooklyn and Brooklyn Heights in the New York City borough (New York City), borough of Brooklyn. There is a smaller satellite Museum Annex in Grand Central Terminal in Midtown Manhattan. The museum is a self-supporting division of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority. __TOC__ Historic use as station The museum is located in an actual subway station, which was originally called Court Street. The Court Street station was built as a terminus for local trains of the IND Fulton Street Line and opened on April 9, 1936, along with a long section of the Fulton Street Line and the Rutgers Street Tunnel. The station has one center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R142 (NYCS Car)
The R142 is the first mass-produced model class of the newest generation or new technology (NTT) A Division cars for the New York City Subway. It was built by Bombardier Transportation in La Pocatière, Quebec, Canada and Barre, Vermont, U.S. with final assembly performed at Plattsburgh, New York, from 1999 to 2003. There are 880 cars numbered 6301–7180 and another 150 cars numbered 1101–1250, for a total of 1,030 cars, all arranged as five-car sets. Together with the R142As, they replaced the Redbird trains, including the R26, R28, R29, R33, R33S, and R36. The R142s and R142As are the first New York City Subway cars to feature recorded announcements. The first R142s were delivered on November 16, 1999, though they initially experienced minor issues that were reported while undergoing testing. Following the completion of non-revenue service testing, the R142s were placed into revenue service on July 10, 2000 as part of its 30-day revenue acceptance test. After suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
145th Street (IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line)
145th Street may refer to: New York * 145th Street (Manhattan), a street in Manhattan, New York City * 145th Street (IRT Broadway – Seventh Avenue Line), a station at Broadway serving the train * 145th Street (IND Eighth Avenue Line), a station at Saint Nicholas Avenue serving the trains * 145th Street (IRT Lenox Avenue Line), a station at Lenox Avenue serving the train * 145th Street (IRT Ninth Avenue Line), a demolished Interborough Rapid Transit Company station * 145th Street Bridge, a bridge over the Harlem River * 145th Street Shuttle, a former service of the Interborough Rapid Transit Company and New York City Subway Washington * Washington State Route 523, which is named 145th Street, and forms part of the northern border of Seattle ** Shoreline South/148th station, a light rail station in Shoreline, Washington {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Hall (IRT Lexington Avenue Line)
The City Hall station, also known as City Hall Loop station, is a closed station on the IRT Lexington Avenue Line of the New York City Subway. It is located under City Hall Park, next to New York City Hall, in the Civic Center neighborhood of Manhattan in New York City. The station was constructed for the Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT) as the southern terminal of the city's first subway line, which was approved in 1900. Construction of the segment of the line that includes the City Hall station started on September 12 of the same year. The station opened on October 27, 1904, as one of the original 28 stations of the New York City Subway. As ridership grew, it was deemed infeasible to lengthen the original platform to accommodate ten-car trains. The station was closed on December 31, 1945, because of its proximity to the Brooklyn Bridge station. The City Hall station, with its single track and curved side platform, was the showpiece of the original IRT subway. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The IRT Subway Before 1918
The first regularly operated line of the New York City Subway was opened on October 27, 1904, and was operated by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT). The early IRT system consisted of a single trunk line running south from 96th Street in Manhattan (running under Broadway, 42nd Street, Park Avenue, and Lafayette Street), with a southern branch to Brooklyn. North of 96th Street, the line had three northern branches in Upper Manhattan and the Bronx. The system had four tracks between Brooklyn Bridge–City Hall and 96th Street, allowing for local and express service. The original line and early extensions consisted of: * The IRT Eastern Parkway Line from Atlantic Avenue–Barclays Center to Borough Hall * The IRT Lexington Avenue Line from Borough Hall to Grand Central–42nd Street * The IRT 42nd Street Shuttle from Grand Central–42nd Street to Times Square * The IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line from Times Square to Van Cortlandt Park–242nd Street * The IRT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Division (New York City Subway)
The A Division, also known as the IRT Division, is a division of the New York City Subway, consisting of the lines operated with services designated by numbers ( 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) and the 42nd Street Shuttle. These lines and services were operated by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company before the 1940 city takeover. A Division cars are narrower, shorter, and lighter than those of the B Division, measuring . List of lines The following lines are part of the A Division (services shown in parentheses; lines with colors next to them are trunk lines): * IRT 42nd Street Shuttle () * IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line () * IRT Dyre Avenue Line () *IRT Eastern Parkway Line () * IRT Flushing Line () * IRT Jerome Avenue Line () * IRT Lenox Avenue Line () * IRT Lexington Avenue Line () * IRT New Lots Line () *IRT Nostrand Avenue Line () *IRT Pelham Line () * IRT White Plains Road Line () Service history Numbers were assigned to subway services in 1948: The 42nd Street Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
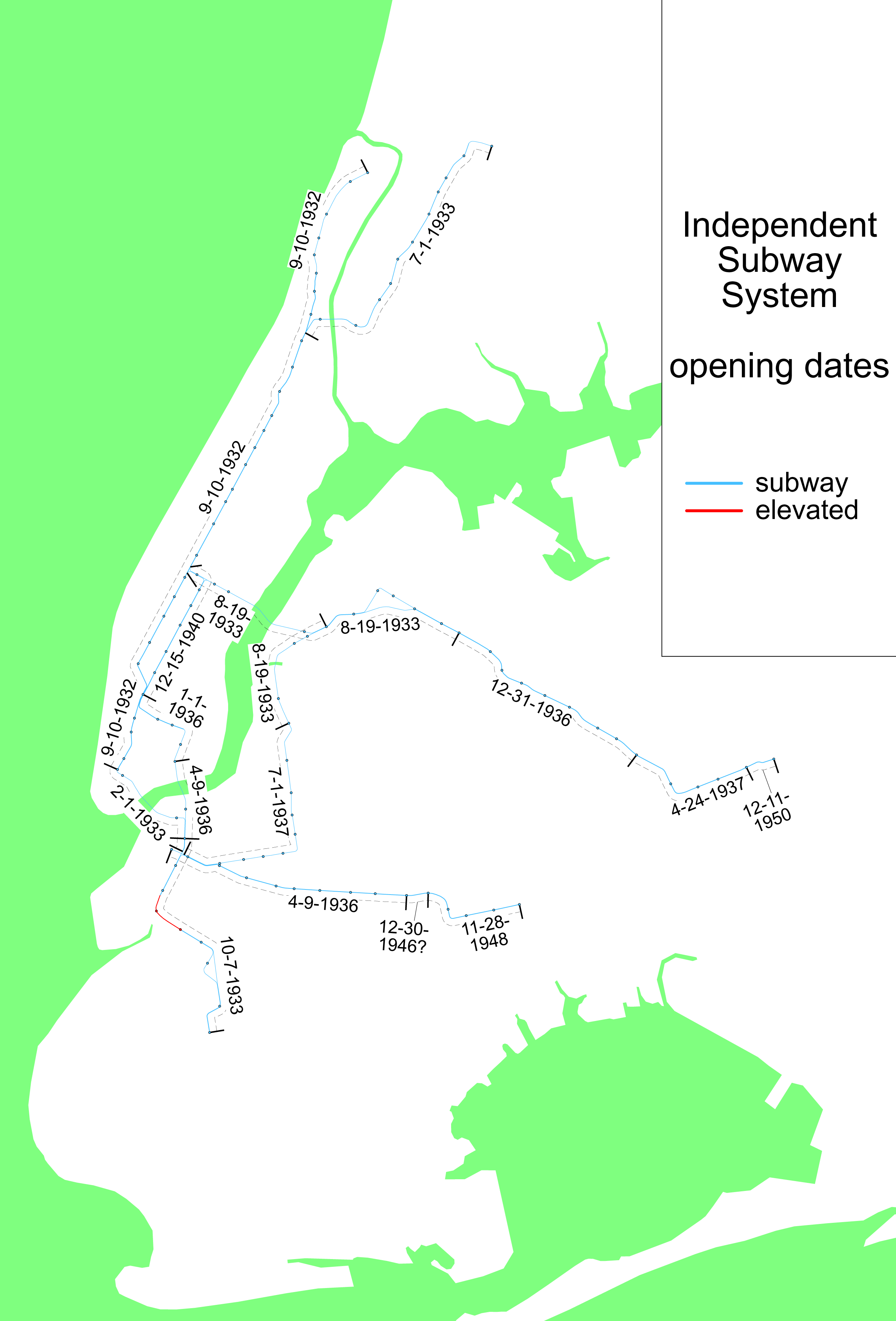
Independent Subway System
The Independent Subway System (IND; formerly the ISS) was a rapid transit rail system in New York City that is now part of the New York City Subway. It was first constructed as the IND Eighth Avenue Line, Eighth Avenue Line in Manhattan in 1932. It was originally also known as the Independent City-Owned Subway System (ICOSS) or the Independent City-Owned Rapid Transit Railroad (ICORTR). One of three subway networks that became part of the modern New York City Subway, the IND was intended to be fully owned and operated by the municipal government, in contrast to the privately operated or jointly funded Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT) and Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation (BMT) companies. It was merged with these two networks when the subway system was History of the New York City Subway#Unification, unified in 1940. The original IND services are the modern subway's A (New York City Subway service), A, C (New York City Subway service), C, E (New York City Subway ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation
The Brooklyn–Manhattan Transit Corporation (BMT) was an urban transit holding company, based in Brooklyn, New York City, United States, and incorporated in 1923. The system was sold to the city in 1940. Today, together with the IND subway system, it forms the B Division of the modern New York City Subway. The original BMT routes form the , , , , , and trains, as well as the Franklin Avenue Shuttle, with the IND and using BMT trackage in Brooklyn. The train enters the IND via the Chrystie Street Connection after crossing the Williamsburg Bridge. The , along with some rush-hour trains enter the IND from the BMT 63rd Street Line. The train enters the IND via the 60th Street Tunnel Connection. The train supplements the in the peak direction during rush hours only. Prior to city ownership, the BMT services were designed with numbers, and the current letter scheme was developed as a continuation of the IND nomenclature as the IND and BMT systems were integrated. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapid Transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT) or heavy rail, commonly referred to as metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport that is generally built in urban areas. A grade separation, grade separated rapid transit line below ground surface through a tunnel can be regionally called a subway, tube, metro or underground. They are sometimes grade-separated on elevated railways, in which case some are referred to as el trains – short for "elevated" – or skytrains. Rapid transit systems are usually electric railway, electric railways, that unlike buses or trams operate on an exclusive right-of-way (transportation), right-of-way, which cannot be accessed by pedestrians or other vehicles. Modern services on rapid transit systems are provided on designated lines between metro station, stations typically using electric multiple units on railway tracks. Some systems use rubber-tyred metro, guided rubber tires, magnetic levitation (''maglev''), or monorail. The stations typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevated Railways
An elevated railway or elevated train (also known as an el train or el for short) is a railway with the tracks above street level on a viaduct or other elevated structure (usually constructed from steel, cast iron, concrete, or bricks). The railway may be a broad-gauge, standard-gauge or narrow-gauge railway, light rail, monorail, or a suspension railway. Elevated railways are normally found in urban areas that would otherwise require impracticably many level crossings. Usually, the tracks of elevated railways that run on steel viaducts can be seen from street level. History The earliest elevated railway was the London and Greenwich Railway on a brick viaduct of 878 arches, built between 1836 and 1838. The first of the London and Blackwall Railway (1840) was also built on a viaduct. During the 1840s there were other plans for elevated railways in London that never came to fruition. From the late 1860s onward, elevated railways became popular in US cities. New York's West S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Company
A privately held company (or simply a private company) is a company whose Stock, shares and related rights or obligations are not offered for public subscription or publicly negotiated in their respective listed markets. Instead, the Private equity, company's stock is offered, owned, traded or exchanged privately, also known as "over-the-counter (finance), over-the-counter". Related terms are unlisted organisation, unquoted company and private equity. Private companies are often less well-known than their public company, publicly traded counterparts but still have major importance in the world's economy. For example, in 2008, the 441 list of largest private non-governmental companies by revenue, largest private companies in the United States accounted for $1.8 trillion in revenues and employed 6.2 million people, according to ''Forbes''. In general, all companies that are not owned by the government are classified as private enterprises. This definition encompasses both publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wall Street IRT Subway Sign
A wall is a structure and a surface that defines an area; carries a load; provides security, shelter, or soundproofing; or serves a decorative purpose. There are various types of walls, including border barriers between countries, brick walls, defensive walls in fortifications, and retaining walls that hold back dirt, stone, water, or noise. Walls can also be found in buildings, where they support roofs, floors, and ceilings, enclose spaces, and provide shelter and security. The construction of walls can be categorized into framed walls and mass-walls. Framed walls transfer the load to the foundation through posts, columns, or studs and typically consist of structural elements, insulation, and finish elements. Mass-walls are made of solid materials such as masonry, concrete, adobe, or rammed earth. Walls may also house utilities like electrical wiring or plumbing and must conform to local building and fire codes. Walls have historically served defensive purposes, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |