|
Indian Council Of Medical Research
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the apex body in India for the formulation, coordination and promotion of biomedical research, is one of the oldest and largest medical research bodies in the world. The ICMR is funded by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. In 2007, the organization established the Clinical Trials Registry - India, which is India's national registry for clinical trials. ICMR's 26 national institutes address themselves to research on specific health topics like tuberculosis, leprosy, cholera and diarrhoeal diseases, viral diseases including AIDS, malaria, kala-azar, vector control, nutrition, food & drug toxicology, reproduction, immuno-haematology, oncology, medical statistics, etc. Its 6 regional medical research centres address themselves to regional health problems, and also aim to strengthen or generate research capabilities in different geographic areas of the country. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajiv Bahl
Dr. Rajiv Bahl is an Indian paediatrician and public health researcher known for his research on maternal and child health research and health policy. He was the Head of Research on Maternal, Newborn, Child and Adolescent Health at the World Health Organization (WHO) from 2013 to 2022 and is currently the Director-General of the Indian Council of Medical Research The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the apex body in India for the formulation, coordination and promotion of biomedical research, is one of the oldest and largest medical research bodies in the world. The ICMR is funded by the Gove .... Early life and education Rajiv Bahl received an M.B.B.S. from the University of Delhi and a PhD in public health from AIIMS, Delhi. References External links Profile from official website of Indian Council of Medical Research{{India-academic-bio-stub All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi alumni Indian Council of Medical Research Indian paediatr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maternal
A mother is the female parent of a child. A woman may be considered a mother by virtue of having given birth, by raising a child who may or may not be her biological offspring, or by supplying her ovum for fertilisation in the case of gestational surrogacy. A biological mother is the female genetic contributor to the creation of the infant, through sexual intercourse or egg donation. A biological mother may have legal obligations to a child not raised by her, such as an obligation of monetary support. An adoptive mother is a female who has become the child's parent through the legal process of adoption. A putative mother is a female whose biological relationship to a child is alleged but has not been established. A stepmother is a non-biological female parent married to a child's preexisting parent, and may form a family unit but generally does not have the legal rights and responsibilities of a parent in relation to the child. A father is the male counterpart of a mother. Wom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating exposures to toxins and toxicants. The relationship between dose and its effects on the exposed organism is of high significance in toxicology. Factors that influence chemical toxicity include the dosage, duration of exposure (whether it is acute or chronic), route of exposure, species, age, sex, and environment. Toxicologists are experts on poisons and poisoning. There is a movement for evidence-based toxicology as part of the larger movement towards evidence-based practices. Toxicology is currently contributing to the field of cancer research, since some toxins can be used as drugs for killing tumor cells. One prime example of this is ribosome-inactivating proteins, tested in the treatment of leukemia. The word ''toxicology'' () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis (JE) is an infection of the brain caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). While most infections result in little or no symptoms, occasional inflammation of the brain occurs. In these cases, symptoms may include headache, vomiting, fever, confusion and seizures. This occurs about 5 to 15 days after infection. JEV is generally spread by mosquitoes, specifically those of the '' Culex'' type. Pigs and wild birds serve as a reservoir for the virus. The disease occurs mostly outside of cities. Diagnosis is based on blood or cerebrospinal fluid testing. Prevention is generally achieved with the Japanese encephalitis vaccine, which is both safe and effective. Other measures include avoiding mosquito bites. Once infected, there is no specific treatment, with care being supportive. This is generally carried out in a hospital. Permanent problems occur in up to half of people who recover from JE. The disease primarily occurs in East and Southeast Asia as w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms begin one to four (typically two) days after exposure to the virus and last for about two to eight days. Diarrhea and vomiting can occur, particularly in children. Influenza may progress to pneumonia from the virus or a subsequent bacterial infection. Other complications include acute respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, encephalitis, and worsening of pre-existing health problems such as asthma and cardiovascular disease. There are four types of influenza virus: types A, B, C, and D. Aquatic birds are the primary source of influenza A virus (IAV), which is also widespread in various mammals, including humans and pigs. Influenza B virus (IBV) and influenza C virus (ICV) primarily infect humans, and influenza D virus (IDV) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebolavirus
The genus ''Ebolavirus'' (- or ; - or ) is a International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses, virological taxon included in the family ''Filoviridae'' (filament-shaped viruses), order ''Mononegavirales''. The members of this genus are called ebolaviruses, and encode their genome in the form of RNA virus#Group V—negative-sense ssRNA viruses, single-stranded negative-sense RNA. The six known virus International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses, species are named for the region where each was originally identified: ''Bundibugyo ebolavirus'', ''Reston ebolavirus'', ''Sudan ebolavirus'', ''Taï Forest ebolavirus'' (originally ''Côte d'Ivoire ebolavirus''), ''Zaire ebolavirus'', and ''Bombali ebolavirus''. The last is the most recent species to be named and was isolated from Angolan free-tailed bats in Sierra Leone. Each species of the genus ''Ebolavirus'' has one member virus, and four of these cause Ebola virus disease (EVD) in humans, a type of Viral hemorrhagic fever, hemorrhagic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dengue
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus, prevalent in tropical and subtropical areas. Asymptomatic infections are uncommon, mild cases happen frequently; if symptoms appear, they typically begin 3 to 14 days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic skin itching and skin rash. Recovery generally takes two to seven days. In a small proportion of cases, the disease develops into severe dengue (previously known as dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome) with bleeding, low levels of blood platelets, blood plasma leakage, and dangerously low blood pressure. Dengue virus has four confirmed serotypes; infection with one type usually gives lifelong immunity to that type, but only short-term immunity to the others. Subsequent infection with a different type increases the risk of severe complications, so-called Antibody-Dependent Enhancement (ADE). The symptoms of dengu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
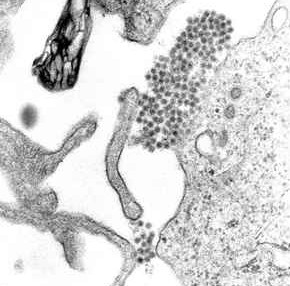
Rotavirus
Rotaviruses are the most common cause of diarrhea, diarrhoeal disease among infants and young children. Nearly every child in the world is infected with a rotavirus at least once by the age of five. Immunity (medical), Immunity develops with each infection, so subsequent infections are less severe. Adults are rarely affected. The virus is transmitted by the fecal–oral route, faecal–oral route. It infects and damages the enterocyte, cells that line the small intestine and causes gastroenteritis (which is often called "stomach flu" despite having no relation to influenza). Although rotavirus was discovered in 1973 by Ruth Bishop and her colleagues by electron micrograph images and accounts for approximately one third of hospitalisations for severe diarrhoea in infants and children, its importance has historically been underestimated within the public health community, particularly in developing country, developing countries. In addition to its impact on human health, rotavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. What is diarrhea? How is it caused, treated and prevented? (see also script)The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic. The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever, fatigue, cough, breathing difficulties, anosmia, loss of smell, and ageusia, loss of taste. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days incubation period, after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected asymptomatic, do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia (medical), hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock (circulatory), shock, or organ dysfunction, multiorgan dysfunction). Older people have a higher risk of developing severe symptoms. Some complicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-communicable Disease
A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmission (medicine), transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, heart diseases, cancers, Diabetes mellitus, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's disease, cataracts, and others. NCDs may be chronic condition, chronic or acute (medicine), acute. Most are non-infection, infectious, although there are some non-communicable infectious diseases, such as parasitic diseases in which the parasite's biological life cycle, life cycle does not include direct host-to-host transmission. The four main NCDs that are the leading causes of death globally are cardiovascular disease, cancer, Respiratory disease, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes. NCDs account for seven out of the ten leading causes of death worldwide. Figures given for 2019 are 41 million deaths due to NCDs worldwide. Of these 17.9 million were due to car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |