|
Huilliche
The Huilliche (), Huiliche or Huilliche-Mapuche are the southern partiality of the Mapuche macroethnic group in Chile and Argentina. Located in the Zona Sur, they inhabit both Futahuillimapu ("great land of the south") and, as the Cunco or Veliche subgroup, the northern half of Chiloé Island. The Huilliche are the principal Indigenous people of those regions.Villalobos ''et al''. 1974, p. 49. According to Ricardo E. Latcham the term Huilliche started to be used in Spanish after the second founding of Valdivia in 1645, adopting the usage of the Mapuches of Araucanía for the southern Mapuche tribes. Huilliche means 'southerners' (Mapudungun ''willi'' 'south' and ''che'' 'people'.) A genetic study showed significant affinities between Huilliches and Indigenous peoples east of the Andes, which suggests but does not prove a partial origin in present-day Argentina. During the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries, the mainland Huilliche were generally successful at resisting Spanish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veliche People
Huilliche (which can also be found spelt Williche, Huiliche or Veliche) is a moribund branch of the Araucanian language family. In 1982 it was spoken by about 2,000 ethnic Huilliche people in Chile, but now hen?it is only spoken by a few elderly speakers. It is spoken in the nation's Los Lagos and Los Ríos regions; and mountain valleys, between the city of Valdivia and south toward the Chiloé Archipelago. Huilliche is composed of at least two varieties, called Huillichesungun and Tsesungun by their speakers. Huillichesungun is spoken in Wequetrumao, on the island of Chiloé, and Tsesungun is spoken in Choroy Traiguen, on the coast of Osorno province. Huilliche is closely related to Mapudungun, the language of the Mapuche, though more research is needed to determine the degree of mutual intelligibility between the two. The "Enduring Voices" project of National Geographic reports the following:"They are to some degree hidden within the broader Mapuche ethnic group, yet con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunco People
Cuncos, Juncos or Cunches is a poorly known subgroup of Huilliche people native to coastal areas of southern Chile and the nearby hinterland. Mostly a historic term, Cuncos are chiefly known for their long-running conflict with the Spanish during the colonial era of Chilean history. Cuncos cultivated maize, potatoes and quinoa and raised chilihueques.Urbina 2009, p. 44. Their economy was complemented by travels during spring and summer to the coast where they gathered shellfish and hunted sea lions. They were said to live in large rukas.Alcamán 1997, p. 32. Cuncos were organized in small local chiefdoms forming a complex system of intermarried families or clans with local allegiance.Alcamán 1997, p. 47. Ethnicity and identity The details of the identity of the Cuncos is not fully clear. José Bengoa defines "Cunco" as a category of Indigenous Mapuche-Huilliche people in southern Chile used by the Spanish in colonial times.Bengoa 2000, p. 122. The Spanish referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huilliche Uprising Of 1792
The Huilliche uprising of 1792 was an indigenous uprising against the Spanish penetration into Futahuillimapu, territory in southern Chile that had been ''de facto'' free of Spanish rule since 1602. The first part of the conflict was a series of Huilliche attacks on Spanish settlers and the mission in the frontier next to Bueno River. Following this a militia in charge of Tomás de Figueroa departed from Valdivia ravaging Huilliche territory in a quest to subdue anti-Spanish elements in Futahuillimapu. Background Beginning in the mid-18th century the Spanish enclave of Valdivia started a period of agricultural expansion. The expansion was mainly directed to the south and was done mostly by pacific means, but hostilities with indigenous Huilliches did occur. In 1758 Huilliche chief Huarán requested Spanish soldiers to defend his lands against his Cunco enemies.Rumian Cisterna 2000, p. 103. The Governor of Valdivia Ambrosio Sáes de Bustamante responded to this call leading to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
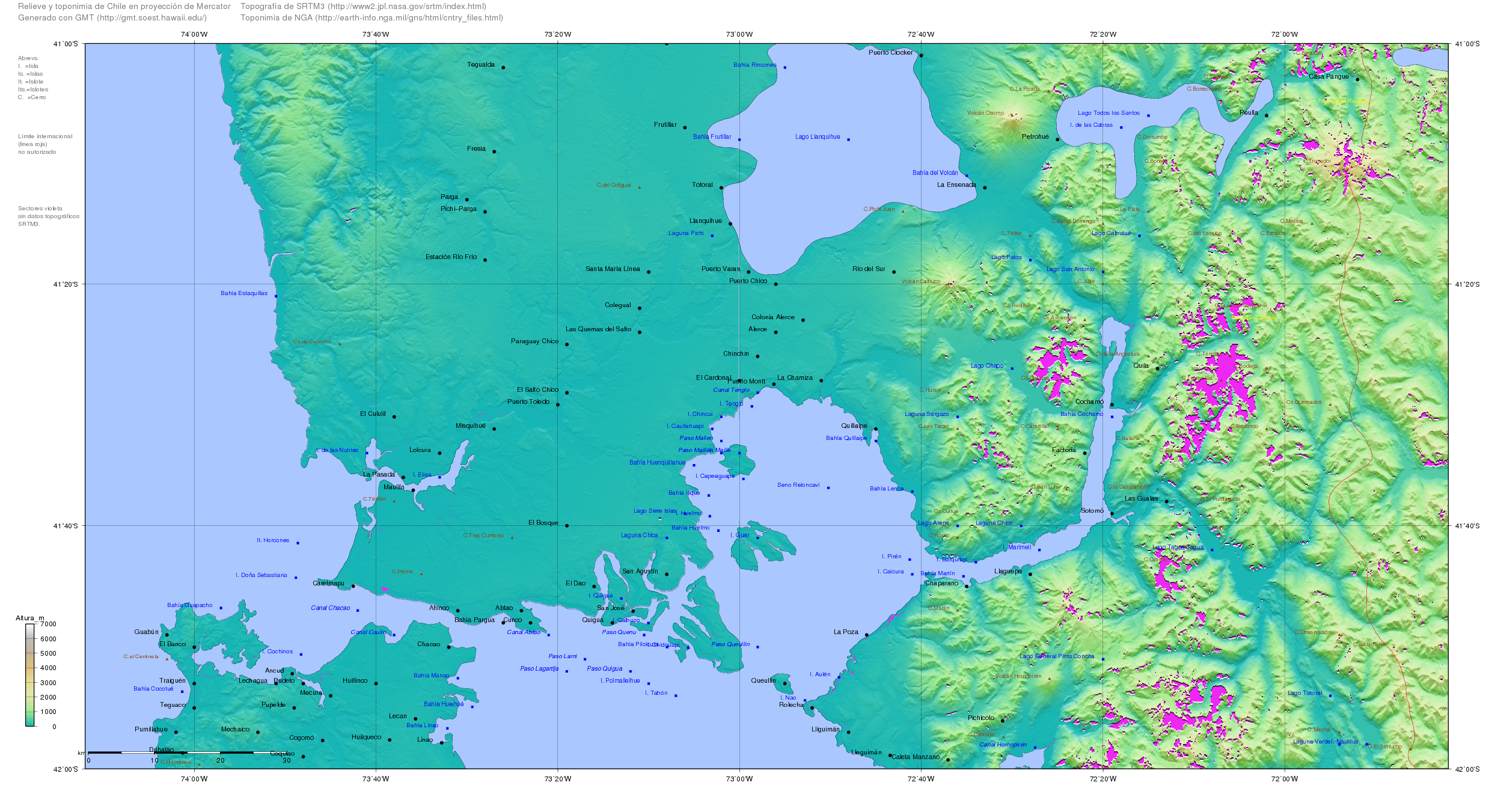
Chiloé Archipelago
The Chiloé Archipelago (, , ) is a group of islands lying off the coast of Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. It is separated from mainland Chile by the Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and the Gulf of Corcovado in the southeast. All islands except the Desertores Islands form Chiloé Province. The main island is Chiloé Island. Of roughly rectangular shape, the southwestern half of this island is a wilderness of contiguous forests, wetlands and, in some places, Chilean Coast Range, mountains. The landscape of the northeastern sectors of Chiloé Island and the islands to the east is dominated by rolling hills, with a mosaic of pastures, forests and cultivated fields. The archipelago is known within Chile for its distinctive folklore, chilote mythology, mythology, potatoes of Chiloé, potatoes, cuisine of Chiloé, cuisine and unique Chilotan architecture, architecture. The culture of Chiloé is the result of mixing of Huilliche people, Huilliche, Culture of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Futahuillimapu
Futahuillimapu, or Fütawillimapu, is a traditional territory of the Huilliche people. Futahuillimapu spans the land between Bueno River and Reloncaví Sound. Futahuillimapu means "great land of the south". Back in the 18th century when this territory was free of foreign rule its western part, corresponding to the Chilean Coast Range and its foothills was inhabited by so-called Cuncos while proper Huilliches lived in the flatlands of the eastern portion corresponding to the Central Valley. After the destruction of Osorno in 1602 Futahuillimapu and the whole area between Valdivia and the settlements of Calbuco and Carelmapu remained independent indigenous territory closed to the Spanish. The Spanish had thus little information on this territory and had to rely on hearsay. This lack of concrete knowledge of the territory fueled speculations about the mythical City of the Caesars. The territory was ravaged by a Spanish militia in 1792. The next year the Spanish-Huilliche Parl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of Las Canoas
The Parliament of Las Canoas () was a diplomatic meeting between Mapuche-Huilliches and Spanish authorities in 1793 held at the confluence of Rahue River and Damas River near what is today the city of Osorno. The parliament was summoned by the Royal Governor of Chile Ambrosio O'Higgins after the Spanish had suppressed an uprising by the Mapuche-Huilliches of Ranco and Río Bueno in 1792. The parliament is historically relevant since the treaty signed at the end of the meeting allowed the Spanish to reestablish the city of Osorno and secure the transit rights between Valdivia and the Spanish mainland settlements near Chiloé Archipelago. The indigenous signatories recognized the king of Spain as their sovereign but they kept considerable autonomy in the lands they did not cede. The treaty is unique in that it was the first time Mapuches formally ceded territory to the Spanish. The Mapuche-Huilliche leaders summoned by the Spanish to the parliament were those whose lands were aff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valdivia
Valdivia (; Mapuche: Ainil) is a city and commune in southern Chile, administered by the Municipality of Valdivia. The city is named after its founder, Pedro de Valdivia, and is located at the confluence of the Calle-Calle, Valdivia, and Cau-Cau Rivers, approximately east of the coastal towns of Corral and Niebla. Since October 2007, Valdivia has been the capital of Los Ríos Region and is also the capital of Valdivia Province. The national census of 2017 recorded the commune of Valdivia as having 166,080 inhabitants (''Valdivianos''), of whom 150,048 were living in the city. The main economic activities of Valdivia include tourism, wood pulp manufacturing, forestry, metallurgy, and beer production. The city is also the home of the Austral University of Chile, founded in 1954 and the Centro de Estudios Científicos. The city of Valdivia and the Chiloé Archipelago were once the two southernmost outliers of the Spanish Empire. From 1645 to 1740, the city depended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapuche
The Mapuche ( , ) also known as Araucanians are a group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who share a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their homelands once extended from Choapa River, Choapa Valley to the Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Pampas, Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the Indigenous peoples in Chile and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are concentrated in the Araucanía (historic region), Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities, more than 92% of the Mapuches are from Chile. The Mapuche traditional e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapuche People
The Mapuche ( , ) also known as Araucanians are a group of Indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who share a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their homelands once extended from Choapa Valley to the Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the Indigenous peoples in Chile and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are concentrated in the Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities, more than 92% of the Mapuches are from Chile. The Mapuche traditional economy is based on agriculture; their traditional social organization consists of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiloé Island
Chiloé Island (, , ), also known as Greater Island of Chiloé (''Isla Grande de Chiloé''), is the largest island of the Chiloé Archipelago off the west coast of Chile, in the Pacific Ocean. The island is located in southern Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. The island is roughly rectangular. Its southwestern half is a wilderness of contiguous forests and swamps. Mountains form a belt running from the northwestern to the southeastern corner of the island. Cordillera del Piuchén make up the northern mountains and the more subdued Cordillera de Pirulil gathers the southern mountains. The landscape of the northeastern sectors of Chiloé Island is dominated by rolling hills with a mosaic of pastures, forests and cultivated fields. While the western shores are rocky and relatively straight, the eastern and northern shores contain many inlets, bays and peninsulas, and it is here where all towns and cities lie. Geographically, the bulk of the island is a continuation of the Chilean C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |