|
History Of The Republic Of Artsakh
Nagorno-Karabakh is located in the southern part of the Lesser Caucasus range, at the eastern edge of the Armenian Highlands, encompassing the highland part of the wider geographical region known as Karabakh. Under Russian and Soviet rule, the region came to be known as ''Nagorno-Karabakh'', meaning "Mountainous Karabakh" in Russian. The name Karabakh itself (derived from Persian and Turkic, and meaning "black vineyard") was first encountered in Georgian and Persian sources from the 13th and 14th centuries to refer to lowlands between the Kura and Aras rivers and the adjacent mountainous territory. Following the collapse of Soviet Union, most of this area came under the control of the Artsakh Republic, which had economic, political, and military support from Armenia but has been internationally recognized as a part of Azerbaijan. As a result of the 2020 war, all surrounding territories and some areas within Nagorno-Karabakh were taken back by Azerbaijan. On 1 January 2024, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagorno-Karabakh
Nagorno-Karabakh (, ; ) is a region in Azerbaijan, covering the southeastern stretch of the Lesser Caucasus mountain range. Part of the greater region of Karabakh, it spans the area between Lower Karabakh and Syunik Province, Syunik. Its terrain mostly consists of mountains and forestland. Most of Nagorno-Karabakh was governed by Armenian people, ethnic Armenians under the breakaway Republic of Artsakh — also known as the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic (NKR) — from the end of the first Nagorno-Karabakh War between Armenia and Azerbaijan in 1994 to the announcement of the dissolution of the republic in September 2023. Representatives from the two sides held numerous inconclusive peace talks mediated by the OSCE Minsk Group regarding the region's disputed status, with its majority-Armenian population over time variously advocating either for Artsakh's independence from both states or for its integration into Armenia. The region is usually equated with the administrative borders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adad-nirari III
Adad-nīrārī III (also Adad-nārārī, meaning "Adad (the storm god) is my help") was a King of Assyria from 811 to 783 BC. Family Adad-nīrārī was a son and successor of king Shamshi-Adad V, and was apparently quite young at the time of his accession, because for the first five years of his reign, his mother Shammuramat was highly influential, which has given rise to the legend of Semiramis. It is widely rejected that his mother acted as regent, but she was surprisingly influential for the time period.''Ancient Near Eastern History and Culture'' by William H. Stiebing Jr. He was the father of kings Ashur-nirari V, Shalmaneser IV, and Ashur-dan III. Tiglath-Pileser III described himself as a son of Adad-nīrārī in his inscriptions, but it is uncertain if this is true. Biography Adad-nīrārī's youth, and the struggles his father had faced early in his reign, caused a serious weakening of Assyrian rulership over their indigenous Mesopotamia, and made way for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
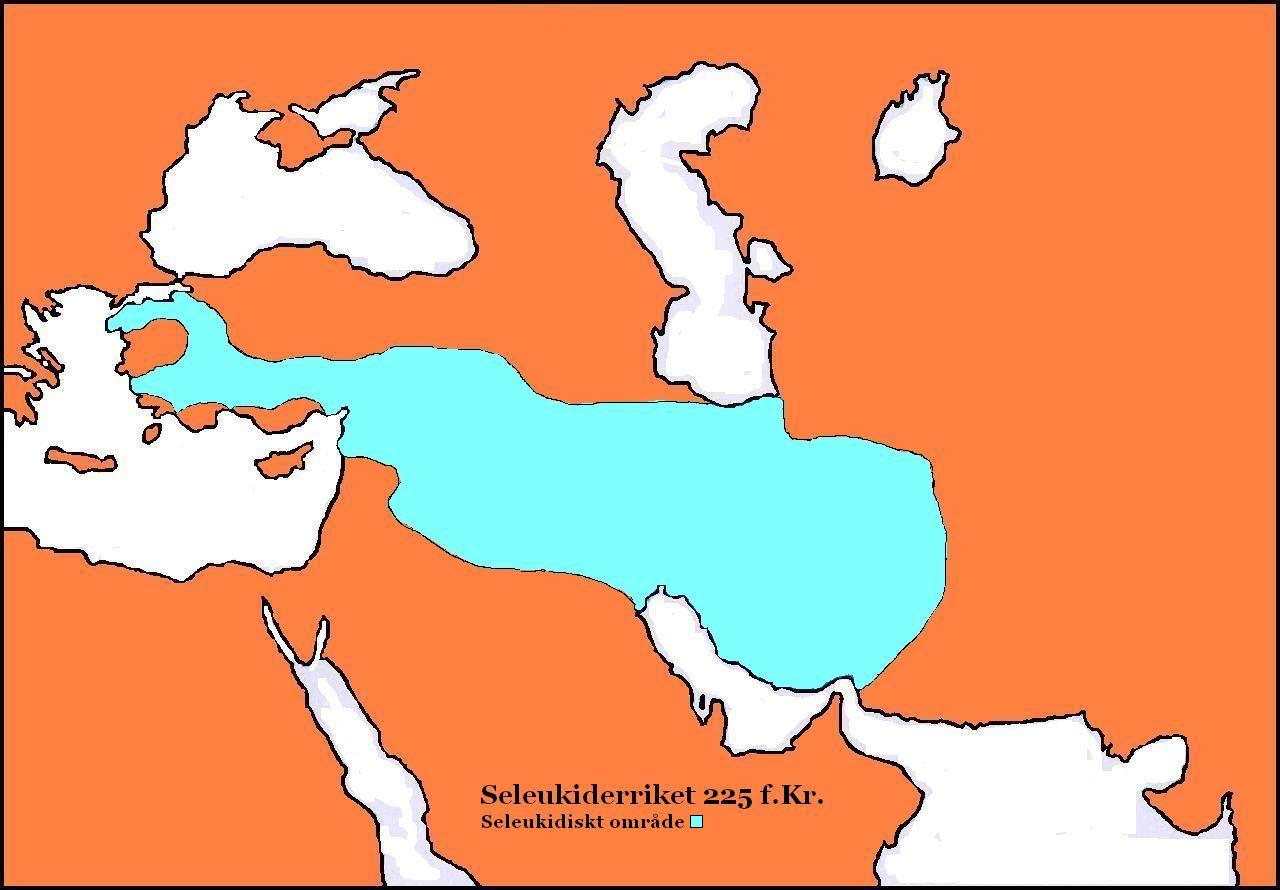
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great, and ruled by the Seleucid dynasty until its annexation by the Roman Republic under Pompey in 63 BC. After receiving the Mesopotamian regions of Babylonia and Assyria in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, and Lebanon, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, and what are now modern Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus III The Great
Antiochus III the Great (; , ; 3 July 187 BC) was the sixth ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 223 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of West Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in April/June 223 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for ' Great King'), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against the Roman Republic. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domination", he waged a four-year war against Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
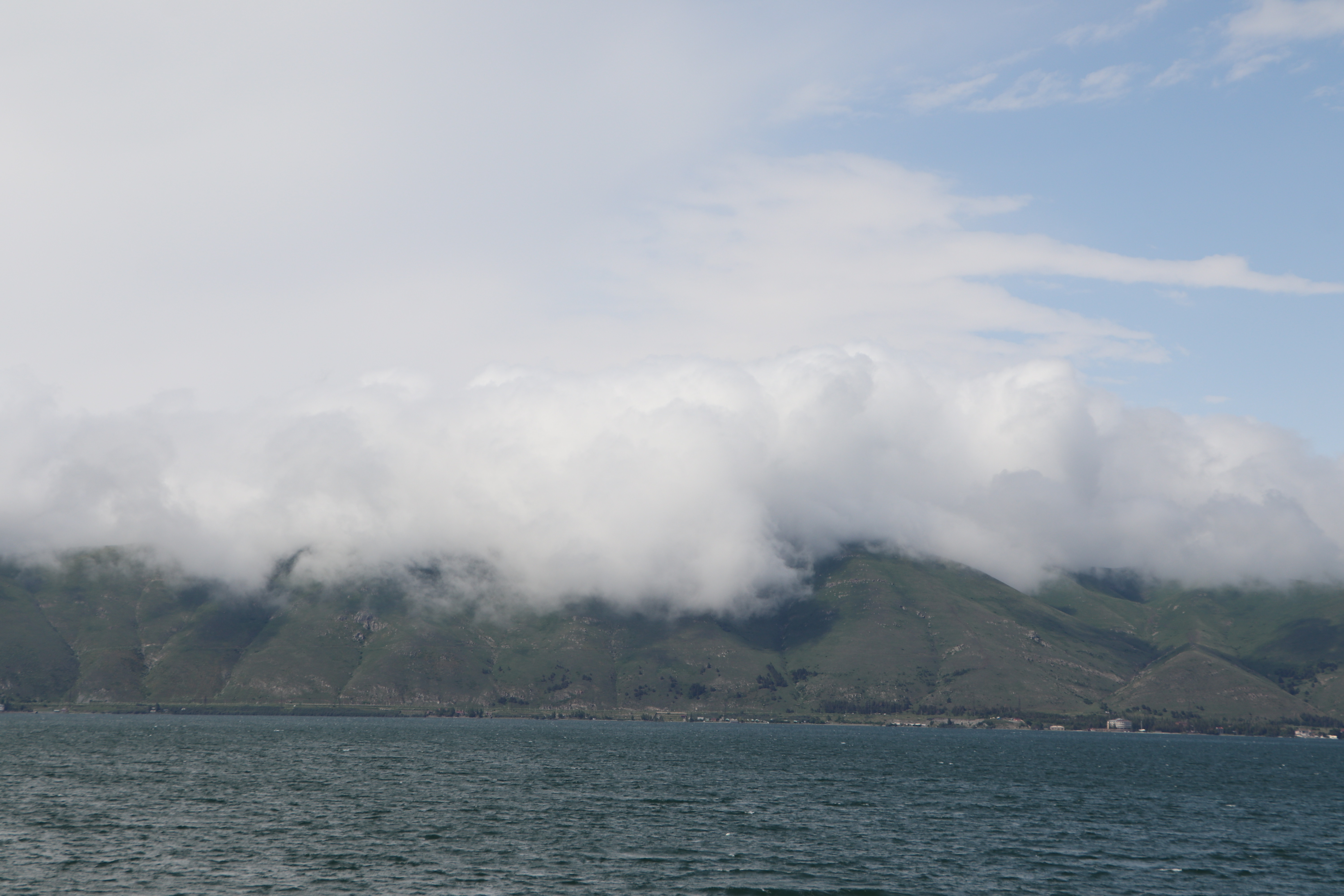
Lake Sevan
Lake Sevan () is the largest body of water in both Armenia and the Caucasus region. It is one of the largest freshwater Alpine lake, high-altitude (alpine) lakes in Eurasia. The lake is situated in Gegharkunik Province, at an altitude of above sea level. The total surface area of its basin is about , which makes up of Armenia's territory. The lake itself is , and the volume is . It is fed by 28 rivers and streams. Only 10% of the incoming water is drained by the Hrazdan River, while the remaining 90% evaporates. Sevan has significant economic, cultural, and recreational value. Its sole major island (now a peninsula) is home to a Sevanavank, medieval monastery. The lake provides some 90% of the fish and 80% of the crayfish catch of Armenia. Sevan was heavily exploited for irrigation of the Ararat plain and hydroelectric power generation during the Soviet period. Consequently, its water level decreased by around and its volume reduced by more than 40%. Later, two Water tunne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orontid Dynasty
The Orontid dynasty, also known as the Eruandids or Eruandunis, ruled the Satrapy of Armenia until 330 BC and the Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia from 321 BC to 200 BC. The Orontids ruled first as client kings or satraps of the Achaemenid Empire and after the collapse of the Achaemenid Empire established an independent kingdom. Later, a branch of the Orontids ruled as kings of Kingdom of Sophene, Sophene and Commagene. They are the first of the three royal dynasties that successively ruled the ancient Kingdom of Armenia (321 BC–428 AD). Although the overthrow of Orontes IV and the accession of Artaxias I to the throne of Armenia in the early 2nd century BC is traditionally treated as the start of a Artaxiad dynasty, new dynasty, Artaxias probably belonged to a branch of the Orontid dynasty. His descendants ruled Armenia until the 1st century AD. Historical background Some historians state that the Orontids were of Iranian peoples, Iranian origin, and sugges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Hewsen
Robert H. Hewsen (born Hewsenian; May 20, 1934 – November 17, 2018) was an American historian and professor of history at Rowan University. He was an expert on the ancient history of the South Caucasus. Hewsen is the author of ''Armenia: A Historical Atlas'' (2001), a major reference book, acclaimed as an important achievement in Armenian studies. Biography Hewsen was born Robert H. Hewsenian in New York City in 1934. His Armenian father came to the U.S. from Smyrna (now Izmir). He spent seven years in Europe with the US Air Force and studying. He received his B.A. in history from the University of Maryland and his Ph.D. from Georgetown University in 1967. The same year he joined the history department of Rowan University, where he taught Byzantine and Russian history for more than 30 years. After retiring from Rowan University in July 1999, Professor Hewsen lectured at University of Chicago, Columbia University, California State University, Fresno and University of Californ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e.g., Tajikistan and Afghanistan), Armenia, and areas of southern India. Historically, Indo-European languages were also spoken in Anatolia. Some European languages of this family—English language, English, French language, French, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Russian language, Russian, Spanish language, Spanish, and Dutch language, Dutch—have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, including Albanian language, Albanian, Armenian language, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic languages, Celtic, Germanic languages, Germanic, Hellenic languages, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian, and Italic languages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic Period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the Roman conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year, which eliminated the last major Hellenistic kingdom. Its name stems from the Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás''), which was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the modern historiographical term ''Hellenistic'' was derived. The term "Hellenistic" is to be distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all the ancient territories of the period that had come under significant Greek influence, particularly the Hellenized Middle East, after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian conquest of the Achaemenid Empire in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran and the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, Nakhchivan to the south. Yerevan is the Capital city, capital, largest city and Economy of Armenia, financial center. The Armenian Highlands has been home to the Hayasa-Azzi, Shupria and Nairi. By at least 600 BC, an archaic form of Proto-Armenian language, Proto-Armenian, an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, had diffused into the Armenian Highlands.Robert Drews (2017). ''Militarism and the Indo-Europeanizing of Europe''. Routledge. . p. 228: "The vernacular of the Great Kingdom of Biainili was quite certainly Armenian. The Armenian language was obviously the region's vernacular in the fifth century BC, when Persian commanders and Greek writers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |