|
History Of Surgery
Surgery is the branch of medicine that deals with the physical manipulation of a bodily structure to diagnose, prevent, or cure an ailment. Ambroise Paré, a 16th-century French surgeon, stated that to perform surgery is, "To eliminate that which is superfluous, restore that which has been dislocated, separate that which has been united, join that which has been divided and repair the defects of nature." Since humans first learned how to make and handle tools, they have employed these skills to develop increasingly sophisticated surgical techniques. However, until the Industrial Revolution, surgeons were incapable of overcoming the three principal obstacles which had plagued the medical profession from its infancy—bleeding, pain and infection. Advances in these fields have transformed surgery from a risky art into a scientific discipline capable of treating many diseases and conditions. Origins The first surgical techniques were developed to treat injuries and traumas. A comb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraction Of The Stone Hieronymus Bosch
Extraction may refer to: Science and technology Biology and medicine * Comedo extraction, a method of acne treatment * Dental extraction, the surgical removal of a tooth from the mouth Computing and information science * Data extraction, the process of retrieving data out of data sources * Information extraction * Knowledge extraction * The process of reversing data compression, a.k.a. decompression * The process of choosing elements from a source document, in linguistics Other uses in science and technology * Root extraction, in mathematics, the computation of a th root * Extraction (chemistry), the separation of a substance from a matrix * Primary extraction, the act of removing a spent cartridge from the chamber of a firearm * Fragrance extraction, the process of obtaining fragrant oils and compounds from raw materials * Resource extraction, the process of locating, acquiring and selling any resource ** Petroleum extraction, the process of recovering petroleum from the gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnieper River
The Dnieper or Dnepr ( ), also called Dnipro ( ), is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Approximately long, with a drainage basin of , it is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth- longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers. In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing what is now Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat River, a tributary of the Dnieper, just upstream from its confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erasistratus
Erasistratus (; ; c. 304 – c. 250 BC) was a Greek anatomist and royal physician under Seleucus I Nicator of Syria. Along with fellow physician Herophilus, he founded a school of anatomy in Alexandria, where they carried out anatomical research. As well, he is credited with helping to found the methodic school of teachings of medicine in Alexandria whilst opposing traditional humoral theories of Hippocratic ideologies. Together with Herophilus, he is credited by historians as the potential founder of neuroscience due to his acknowledgements of nerves and their roles in motor control through the brain and skeletal muscles.Wills, Adrian, and A Wills. “Herophilus, Erasistratus, and the Birth of Neuroscience.” ''Lancet'' 354, no. 9191 (November 13, 1999): 1719–20. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(99)02081-4. Furthermore, Erasistratus is seen as one of the first physicians/scientists to conduct recorded dissections and potential vivisections alongside Herophilus.Ferngren, Gary. “Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayan Civilization
The Maya civilization () was a Mesoamerican civilization that existed from Ancient history, antiquity to the early modern period. It is known by Maya architecture#Pyramids and temples, its ancient temples and glyphs (script). The Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian Americas. The civilization is also noted for Maya art, its art, Maya architecture, architecture, Maya numerals, mathematics, Maya calendar, calendar, and Maya astronomy, astronomical system. The Maya civilization developed in the Maya Region, an area that today comprises southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador. It includes the Mayan Lowlands, northern lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula and the Guatemalan Highlands of the Sierra Madre de Chiapas, Sierra Madre, the Mexican state of Chiapas, southern Guatemala, El Salvador, and the southern lowlands of the Pacific littoral plain. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of the modern Middle East. Just beyond it lies southwestern Iran, where the region transitions into the Iranian plateau, Persian plateau, marking the shift from the Arab world to Iran. In the broader sense, the historical region of Mesopotamia also includes parts of present-day Iran (southwest), Turkey (southeast), Syria (northeast), and Kuwait. Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10,000 BC. It has been identified as having "inspired some of the most important developments in human history, including the invention of the wheel, the planting of the first cereal crops, the development of cursive script, mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture". It is recognised as the cradle of some of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
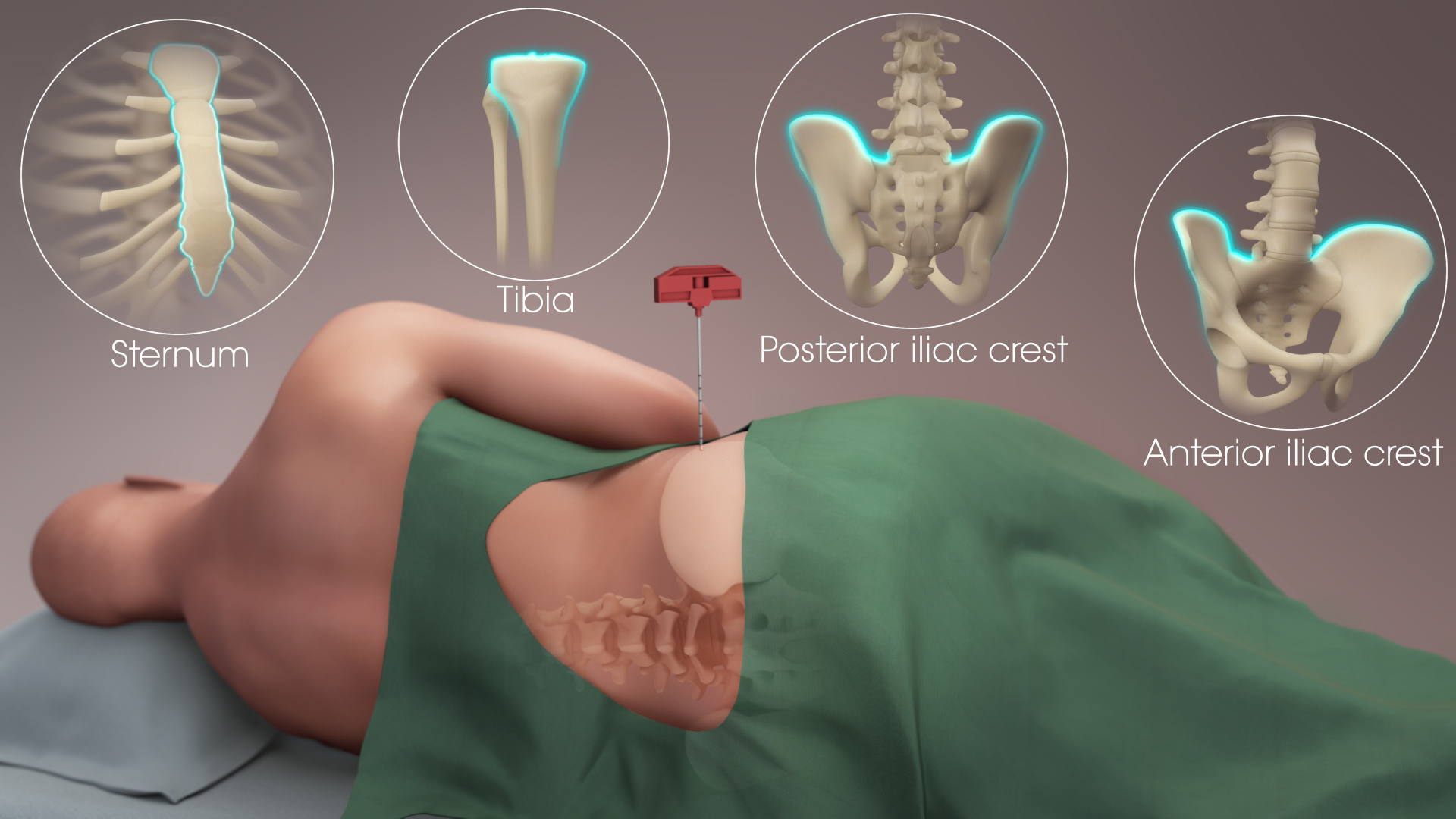
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of Blood cell, hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the Rib cage, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and Pelvis, bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a person weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the Circulatory system, systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of Hematopoietic cell, hematopoietic cells, including both Myeloid tissue, myeloid and Lymphocyte, lymphoid lineages, are create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztecs
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states ('' altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, the capital city of the Mexica or Tenochca, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era, as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521–1821). The definitions of Azt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and sedentism, settlement, making an increasingly large population possible. These settled communities permitted humans to observe and experiment with plants, learning how they grew and developed. This new knowledge led to the domestication of plants into crops. Archaeological data indicate that the domestication of various types of plants and animals happened in separate locations worldwide, starting in the Geologic time scale, geological epoch of the Holocene 11,700 years ago, after the end of the last Ice Age. It was humankind's first historically verifiable transition to agriculture. The Neolithic Revolution greatly narrowed the diversity of foods available, resulting in a decrease in the quality of human nutrition compared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borneo
Borneo () is the List of islands by area, third-largest island in the world, with an area of , and population of 23,053,723 (2020 national censuses). Situated at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, it is one of the Greater Sunda Islands, located north of Java Island, Java, west of Sulawesi, and east of Sumatra. The island is crossed by the equator, which divides it roughly in half. The list of divided islands, island is politically divided among three states. The sovereign state of Brunei in the north makes up 1% of the territory. Approximately 73% of Borneo is Indonesian territory, and in the north, the East Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak make up about 26% of the island. The Malaysian federal territory of Labuan is situated on a small island just off the coast of Borneo. Etymology When the sixteenth-century Portuguese explorer Jorge de Menezes made contact with the indigenous people of Borneo, they referred to their island as ''Pulu K'lemantang'', which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Disorder
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness, a mental health condition, or a psychiatric disability, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. A mental disorder is also characterized by a clinically significant disturbance in an individual's cognition, emotional regulation, or behavior, often in a society, social context. Such disturbances may occur as single episodes, may be persistent, or may be relapsing–remitting. There are many different types of mental disorders, with signs and symptoms that vary widely between specific disorders. A mental disorder is one aspect of mental health. The causes of mental disorders are often unclear. Theories incorporate findings from a range of fields. Disorders may be associated with particular regions or functions of the brain. Disorders are usually Medical diagnosis, diagnosed or assessed by a mental health professional, such as a Clinical psychology#Profes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |