|
History Of Wisconsin
The history of Wisconsin includes the story of the people who have lived in Wisconsin since it became a state of the U.S., but also that of the Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribes who made their homeland in Wisconsin, the French and British colonists who were the first Europeans to live there, and the American settlers who lived in Wisconsin when it was a territory. Since its admission to the Union on May 29, 1848, as the 30th state, Wisconsin has been ethnically heterogeneous, with Yankees being among the first to arrive from New York and New England. They dominated the state's heavy industry, finance, politics and education. Large numbers of European immigrants followed them, including German Americans, mostly between 1850 and 1900, Scandinavians (the largest group being Norwegian Americans) and smaller groups of Belgian Americans, Dutch Americans, Swiss Americans, Finnish Americans, Irish Americans and others; in the 20th century, large numbers of Polis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. With a population of about 6 million and an area of about 65,500 square miles, Wisconsin is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 20th-largest state by population and the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 23rd-largest by area. It has List of counties in Wisconsin, 72 counties. Its List of municipalities in Wisconsin by population, most populous city is Milwaukee; its List of capitals in the United States, capital and second-most populous city is Madison, Wisconsin, Madison. Other urban areas include Green Bay, Wisconsin, Green Bay, Kenosha, Wisconsin, Kenosha, Racine, Wisconsin, Racine, Eau Claire, Wisconsin, Eau Claire, and the Fox Cities. Geography of Wiscon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
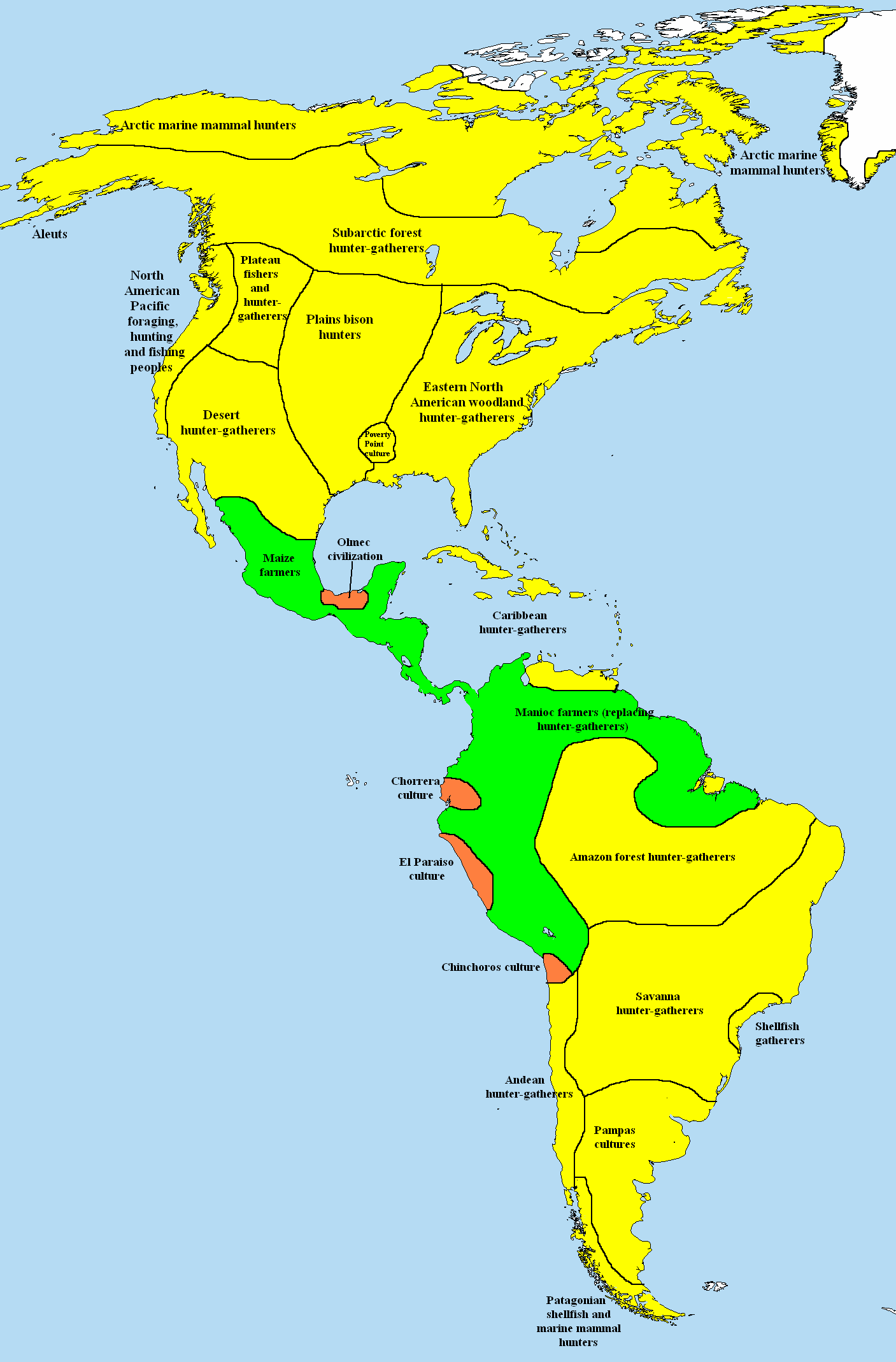
Paleo-Indians
Paleo-Indians were the first peoples who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas towards the end of the Late Pleistocene period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in the Western Hemisphere and is distinct from the term ''Paleolithic''.''Paleolithic'' specifically refers to the period between million years ago and the end of the Pleistocene in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is not used in New World archaeology. Traditional theories suggest that big-animal hunters crossed the Bering Strait from North Asia into the Americas over a land bridge ( Beringia). This bridge existed from 45,000 to 12,000 BCE (47,000–14,000 BP). Small isolated groups of hunter-gatherers migrated alongside herds of large herbivores far into Alaska. From BCE ( BP), ice-free corridors developed along the Pacific coast and valleys of North America. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
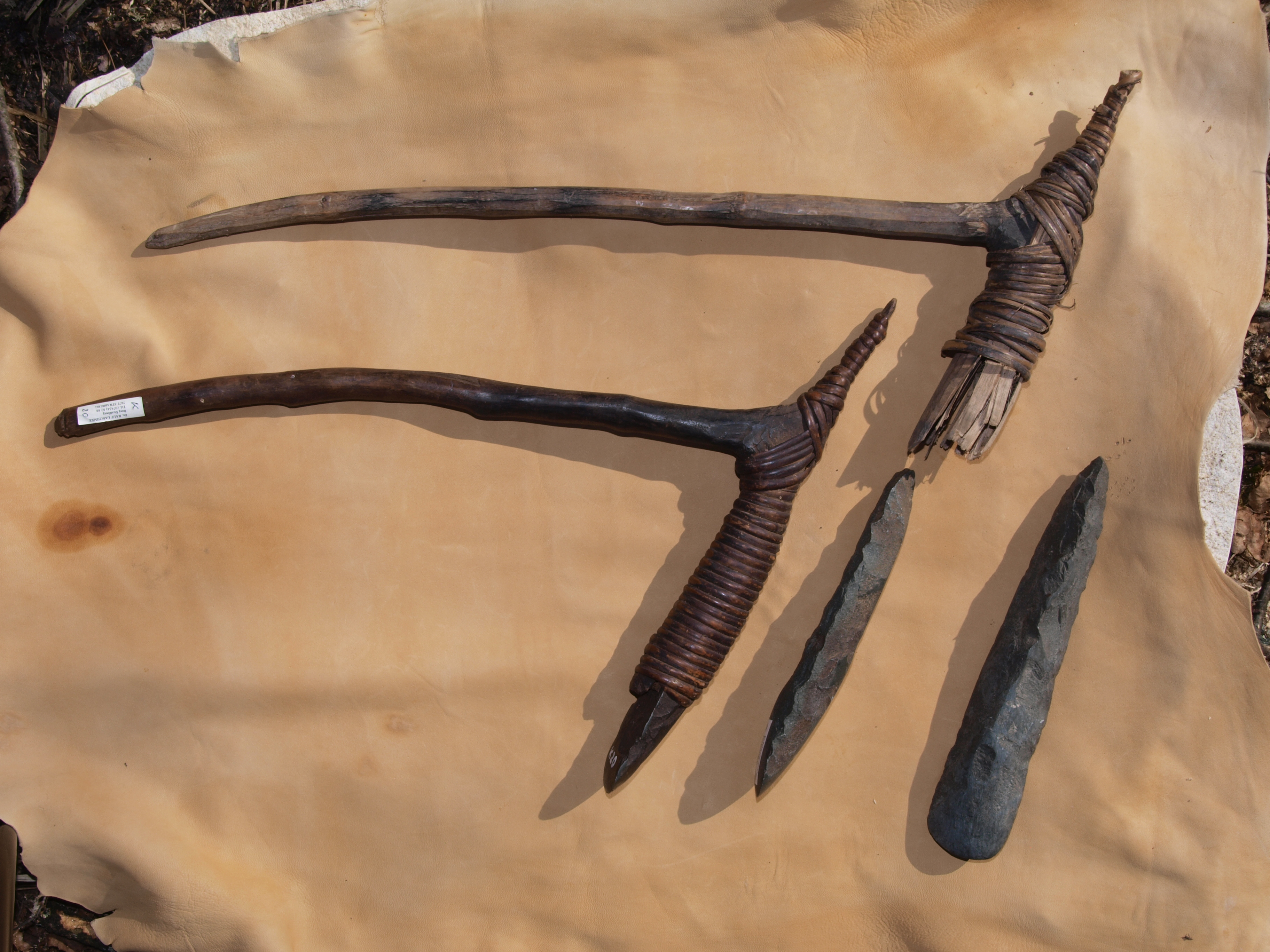
Adze
An adze () or adz is an ancient and versatile cutting tool similar to an axe but with the cutting edge perpendicular to the handle rather than parallel. Adzes have been used since the Stone Age. They are used for smoothing or carving wood in hand woodworking, and as a Hoe (tool), hoe for agriculture and horticulture. Two basic forms of an adze are the hand adze (short hoe)—a short-handled tool swung with one hand—and the foot adze (hoe)—a long-handled tool capable of powerful swings using both hands, the cutting edge usually striking at foot or shin level. A similar tool is called a mattock, which differs by having two blades, one perpendicular to the handle and one parallel. History Africa The adze is depicted in ancient Egyptian art from the Old Kingdom onward. Originally the adze blades were made of stone, but already in the Predynastic Egypt, Predynastic Period copper adzes had all but replaced those made of flint. Stone blades were fastened to the handle by tying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Copper Complex
The Old Copper complex or Old Copper culture is an archaeological culture from the Archaic period of North America's Great Lakes region. Artifacts from some of these sites have been dated from 6500 to 1580 BCE. It is characterized by widespread copper artifacts, including tools and weapons, as well as ornamental objects. The archeological evidence of smelting or alloying is subject to some dispute, and it is commonly believed that objects were cold-worked into shape. Furthermore, some archaeologists are convinced by the artifactual and structural evidence for metal casting by Hopewellian and Mississippian peoples. Western Great Lakes The Old Copper complex of the Western Great Lakes is the best known, and can be dated as far back as 9,500 years ago. Great Lakes natives of the Archaic period located 99% pure copper near Lake Superior, in veins touching the surface and in nuggets from gravel beds. Major quarries were located on Isle Royale, the Keweenaw Peninsula, and the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spear-thrower
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever, or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Classical Nahuatl, Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in Dart (missile), dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a Plain bearing, bearing surface that allows the user to store energy during the throw. It may consist of a shaft with a cup or a spur at the end that supports and propels the butt of the spear. It's usually about as long as the user's arm or forearm. The user holds the spear-thrower in one hand, gripping near the end farthest from the cup. The user puts the butt end of the spear, or dart, in the cup, or grabs the spur with the end of the spear. The spear is much longer than the thrower. The user holds the thrower at the grip end, with the spear resting on the thrower and the butt end of the spear resting in the thrower's cup. The user can hold the spear, with the index and thumb, with the same hand as the thrower, with the other fingers. The user reaches b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaic Period In The Americas
In the classification of the archaeological cultures of North America, the Archaic period in North America, taken to last from around 8000 to 1000 BC in the sequence of North American pre-Columbian cultural stages, is a period defined by the ''archaic stage'' of cultural development. The Archaic stage is characterized by subsistence economies supported through the exploitation of nuts, seeds, and shellfish. As its ending is defined by the adoption of sedentary farming, this date can vary significantly across the Americas. The rest of the Americas also have an Archaic Period. Classifications This classification system was first proposed by Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips in the widely accepted 1958 book ''Method and Theory in American Archaeology''. In the organization of the system, the Archaic period followed the Lithic stage and is superseded by the Formative stage. # The Lithic stage # The Archaic stage # The Formative stage # The Classic stage # The Post-Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boaz, Wisconsin
Boaz is a village in Richland County, Wisconsin, United States. According to the 2020 census, the population of the village was 129. Geography Boaz is located at (43.330793, -90.527280). According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of , all of it land. History Boaz was the boyhood home of Richard M. Brewer, the first leader of the Regulators in the Lincoln County (New Mexico) War. A skeleton of a mastodon, the Boaz mastodon, was found in 1897, near Boaz. Demographics 2010 census As of the census of 2010, there were 156 people, 67 households, and 40 families living in the village. The population density was . There were 68 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the village was 98.7% White and 1.3% Asian. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 0.6% of the population. There were 67 households, of which 20.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 50.7% were married couples living together, 4.5% had a female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clovis Culture
The Clovis culture is an archaeological culture from the Paleoindian period of North America, spanning around 13,050 to 12,750 years Before Present (BP). The type site is Blackwater Draw locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, where stone tools were found alongside the remains of Columbian mammoths in 1929. Clovis sites have been found across North America. The most distinctive part of the Clovis culture toolkit are Clovis points, which are projectile points with a fluted, lanceolate shape.Fluted: Having a flake removed from the base, either on one or both sides.Lanceolate: Tapering to a point at one end, like the head of a lance. Clovis points are typically large, sometimes exceeding in length. These points were multifunctional, also serving as cutting tools. Other stone tools used by the Clovis culture include knives, scrapers, and bifacial tools, with bone tools including beveled rods and shaft wrenches, with possible ivory points also being identified. Hides, wood, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boaz Mastodon
The Boaz mastodon is the skeleton of a mastodon found near Boaz, Wisconsin, USA, in 1897. A fluted quartzite spear point found near the Boaz mastodon suggests that humans hunted mastodons in southwestern Wisconsin. It is currently on display at the University of Wisconsin Geology Museum. Although the mastodon on display at the Geology Museum has long been presented as a complete individual, it was uncovered in 2015 that two bones from the Boaz mastodon were combined with many bones from a different individual, the Anderson Mills mastodon, to form a composite skeleton. History Following a heavy rainfall on July 10, 1897, the sons (Harry, Chris, Verne, and Clyde) of farmer John Dosch were checking for flood damage along the eastern branch of Mill Creek near the village of Boaz when they discovered some unusual bones sticking out of the creek bank where it had been partially washed away. The boys excavated the bones and displayed them by a hitching post near the road. The local mailm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muskox
The muskox (''Ovibos moschatus'') is a hoofed mammal of the family Bovidae. Native to the Arctic, it is noted for its thick coat and for the strong odor emitted by males during the seasonal rut, from which its name derives. This musky odor has the effect of attracting females during mating season. Its Inuktitut name "umingmak" translates to "the bearded one". Its Woods Cree names "mâthi-môs" and "mâthi-mostos" translate to "ugly moose" and "ugly bison", respectively. In historic times, muskoxen primarily lived in Greenland and the Canadian Arctic of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut. They were formerly present in Eurasia, with their youngest natural records in the region dating to around 2,700 years ago, with reintroduced populations in the American state of Alaska, the Canadian territory of Yukon, and Siberia, and an introduced population in Norway, part of which emigrated to Sweden, where a small population now lives. Evolution Extant relatives The muskox i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castoroides
''Castoroides'' (from Latin ''castor'' (beaver) and -''oides'' (like)), or the giant beaver, is an extinct genus of enormous, bear-sized beavers that lived in North America during the Pleistocene. Two species are currently recognized, ''C. dilophidus'' in the Southeastern United States and ''C. ohioensis'' in most of North America. ''C. leiseyorum'' was previously described from the Irvingtonian age but is now regarded as an invalid name. All specimens previously described as ''C. leiseyorum'' are considered to belong to ''C. dilophidus''. Description ''Castoroides'' species were much larger than modern beavers. Their average length was approximately , and they could grow as large as . The weight of the giant beaver could vary from to . This makes it the largest known rodent in North America during the Pleistocene and the largest known beaver. Recent analyses suggest that they weighed less, closer to , but this is disputable. The hind feet of the giant beaver were much larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bison
A bison (: bison) is a large bovine in the genus ''Bison'' (from Greek, meaning 'wild ox') within the tribe Bovini. Two extant taxon, extant and numerous extinction, extinct species are recognised. Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North America, is the more numerous. Although colloquially referred to as a buffalo in the United States and Canada, it is only distantly related to the true buffalo. The North American species is composed of two subspecies, the Plains bison, ''B. b. bison'', and the generally more northern wood bison, ''B. b. athabascae''. A third subspecies, the eastern bison (''B. b. pennsylvanicus'') is no longer considered a valid taxon, being a junior synonym of ''B. b. bison''. Historical references to "woods bison" or "wood bison" from the Eastern United States refer to this synonym animal (and to their eastern woodland habitat), not to ''B. b. athabascae'', wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |