|
History Of Andhra Pradesh
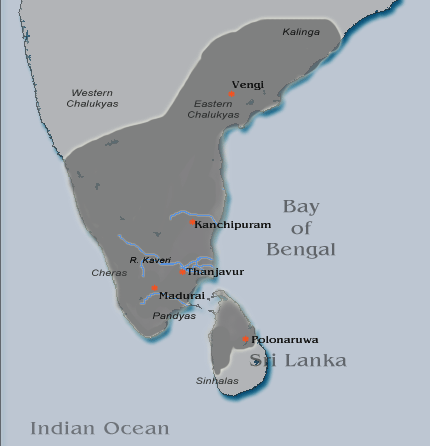
The recorded history of Andhra Pradesh, one of the 28 states of 21st-century India, begins in the Vedic period. It is mentioned in Sanskrit epics such as the Aitareya Brahmana (800 BCE). Its sixth-century BCE incarnation Assaka lay between the Godavari and Krishna Rivers, one of sixteen mahajanapadas (700–300 BCE). The Satavahanas succeeded them (230 BCE–220 CE), built Amaravati, and reached a zenith under Gautamiputra Satakarni. After the Satavahanas, the region fragmented into fiefdoms. By the late second century CE, Andhra Ikshvakus ruled along the Krishna River. In the fourth century CE, the Pallava dynasty ruled southern Andhra Pradesh and Tamilakam, and had a capital at Kanchipuram. Their power increased in the reigns of Mahendravarman I (571–630) and Narasimhavarman I (630–668), and dominated northern Tamilakam and the southern Telugu-speaking region until the end of the ninth century.Northern Andhra Pradesh was under Vengi Chalukyas starting from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and the List of states and union territories of India by population, tenth-most populous in the country. Telugu language, Telugu is the most widely spoken language in the state, as well as its official language. Amaravati is the state capital, while the largest city is Visakhapatnam. Andhra Pradesh shares borders with Odisha to the northeast, Chhattisgarh to the north, Karnataka to the southwest, Tamil Nadu to the south, Telangana to northwest and the Bay of Bengal to the east. It has the Coastline of Andhra Pradesh, third-longest coastline in India at about . Archaeological evidence indicates that Andhra Pradesh has been continuously inhabited for over 247,000 years, from early archaic Hominini, hominins to Neolithic settlements. The earliest r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahendravarman I
Mahendravarman I (600–630 CE) was a Pallava emperor who ruled over realm covering the southern portions of present-day Andhra region and northern regions of what forms present-day Tamil Nadu in India, in the early 7th century. He was a scholar, a painter, an architect and a musician. He was the son of Simhavishnu, who defeated the Kalabhras and re-established the Pallava kingdom. During his reign, the Chalukya monarch Pulakeshin II attacked the Pallava realm. The Pallavas fought a series of wars in the northern Vengi region, before Mahendra-varman decimated his chief enemies at Pullalur (according to Pallava grants at Kuram, Kasakudi and Tadantottam). Although Mahendra-varman saved his capital, he lost the northern provinces to Pulakeshin. Tamil literature flourished under his rule, with the rise in popularity of ''Tevaram'' written by Appar and Sambandhar. Mahendravarman I was the author of the play '' Mattavilasa Prahasana'' which is a Sanskrit satire. During his perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandya Dynasty
The Pandya dynasty (), also referred to as the Pandyas of Madurai, was an ancient Tamil dynasty of South India, and among the four great kingdoms of Tamilakam, the other three being the Pallavas, the Cholas and the Cheras. Existing since at least the 4th to 3rd centuries BCE, the dynasty passed through two periods of imperial dominance, the 6th to 10th centuries CE, and under the 'Later Pandyas' (13th to 14th centuries CE). Under Jatavarman Sundara Pandyan I and Maravarman Kulasekara Pandyan I, the Pandyas ruled extensive territories including regions of present-day South India and northern Sri Lanka through vassal states subject to Madurai. The Pandya dynasty is the longest ruling dynasty in the world. The rulers of the three Tamil dynasties were referred to as the " three crowned rulers (the mu-ventar) of the Tamil Region" in the southern part of India. The origin and the timeline of the Pandya dynasty are difficult to establish. The early Pandya chieftains ruled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nellore Chodas
Cholas of Nellore also known as Nellore Chodas or Nellore Cholas, were one of the branch of Telugu Chola families who ruled over parts of Andhra Pradesh in the 11th and 14th centuries. They were chieftains to Imperial Cholas, Kakatiyas and Western Chalukyas and ruled over the Nellore region. The dominance of Nellore Cholas grew towards the end of the Velanandu Chola dynasty, they claimed descent from the early Chola Tamil king Karikala Chola. Mostly their records are found in Tamil, Telugu, Sanskrit and Grantha. Rulers Twelve rulers of the line ruled for more than two centuries, and at times, their power expanded over the majority of Andhra region and beyond into the Hoysala and Imperial Chola kingdoms. * Bijjana Choda * Manumasiddharasa I * Dayabhima and Nallasiddharasa * Errasiddha * Manumasiddharasa II * Tammusiddhi * Tikka Choda I or Thirukalatti * Allutikka, Manumasiddharasa III and Vijayagandagopala * Tikka Choda II * Manumagandagopala or Nallasiddharasa III * Rajagan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jatavarman Sundara Pandyan I
Jatavarman Sundara I, also known as Sadayavarman Sundara Pandyan, was an emperor of the Pandyan dynasty who ruled regions of Tamilakam (present day South India), Northern Sri Lanka, and Southern Andhra between 1250–1268 CE.Sethuraman, p124 He is remembered for his patronage of the arts and Dravidian architecture, along with refurbishment and decoration of many Kovils (temple) in the Tamil continent. He oversaw a massive economic growth of the Pandyan empire. On the eve of his death in 1268 CE, the second Pandyan empire's power and territorial extent had risen to its zenith till Nellore and Kadapa by defeating Telugu Chola rulers Vijaya Gandagopala, Manumasiddhi III of Nellore Cholas and Ganapatideva of Kakatiyas. Accession Sundara Pandyan I acceded to the Pandyan throne in the year 1251 CE. During the middle part of the 13th century, Pandya kingdom was ruled by many princes of the royal line. This practice of shared rule with one prince asserting primacy was common in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telugu Language
Telugu (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language native to the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, where it is also the official language. Spoken by about 96 million people (2022), Telugu is the most widely spoken member of the Dravidian language family, and one of the twenty-two Languages with legal status in India, scheduled languages of the Republic of India. It is one of the few languages that has primary official status in more than one States and union territories of India, Indian state, alongside Hindi and Bengali language, Bengali. Telugu is one of the languages designated as a Classical Languages of India, classical language by the Government of India. It is the 14th most spoken native language in the world.Statistics in Modern Standard Telugu is based on the dialect of erstwhile Krishna, Guntur, East Godavari and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kurukshetra War, a war of succession between two groups of princely cousins, the Kauravas and the Pandava, Pāṇḍavas. It also contains Hindu philosophy, philosophical and devotional material, such as a discussion of the four "goals of life" or ''puruṣārtha'' (12.161). Among the principal works and stories in the ''Mahābhārata'' are the ''Bhagavad Gita'', the story of Damayanti, the story of Shakuntala, the story of Pururava and Urvashi, the story of Savitri and Satyavan, the story of Kacha (sage), Kacha and Devayani, the story of Rishyasringa and an Ramopakhyana, abbreviated version of the ''Rāmāyaṇa'', often considered as works in their own right. Traditionally, the authorship of the ''Mahābhārata'' is attributed to Vyasa, Vy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tikkana
Tikkana (1205–1288), also known as Tikkana Somayaji, was a 13th century Telugu poet. Born into a Telugu-speaking Niyogi Brahmin family . He was the second poet of the "Trinity of Poets ( Kavi Trayam)" that translated ''Mahabharata'' into Telugu. Nannaya Bhattaraka, the first, translated two and a half chapters of ''Mahabharata''. Tikkana translated the final 15 chapters, but did not undertake translating the half-finished ''Aranya Parvamu''. The Telugu people remained without this last translation for more than a century, until it was translated by Errana. Tikkana is also called Tikkana Somayaji, as he completed the Somayaga. Tikkana's titles were ''Kavibrahma'' and ''Ubhaya Kavi Mitrudu''. Religious conflict Tikkana was born in 1205 in Patur village, Kovur, Nellore district during the Golden Age of the Kakatiya dynasty. During this time conflict occurred between the two sects of Sanātana Dharma, Shaivism and Vaishnavism. Tikkana attempted to bring peace to the warr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kakatiya Dynasty
The Kakatiya dynasty (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: Kākatīya) was a Andhras, Telugu dynasty that ruled most of eastern Deccan Plateau, Deccan region in present-day India between 12th and 14th centuries. Their territory comprised much of the present day Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, and parts of eastern Karnataka, northern Tamil Nadu, and southern Odisha. Their capital was Orugallu, now known as Warangal. Early Kakatiya rulers served as feudatories to Rashtrakuta dynasty, Rashtrakutas and Western Chalukya Empire, Western Chalukyas for more than two centuries. They assumed sovereignty under Prataparudra I in 1163 CE by suppressing other Chalukya subordinates in the Telangana region. Ganapati (Kakatiya dynasty), Ganapati Deva (r. 1199–1262) significantly expanded Kakatiya lands during the 1230s and brought under Kakatiya control the Telugu-speaking lowland delta areas around the Godavari River, Godavari and Krishna River, Krishna rivers. Ganapat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telugu Chodas
The Telugu Chodas or Telugu Cholas were rulers who ruled parts of present-day Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and southern Odissa as samantas (vassals) of the Pallavas, and later as vassals of the Imperial Cholas. There are many branches like Renati Chodas, Pottapi Chodas, Velanati Chodas, Konidena Chodas, Nannuru Chodas, Nellore Chodas and Kunduru Chodas. The Telugu Chodas claimed descent from Sangam age Tamil king Karikala Chola. Language and legacy Renati Choda kingdom is mentioned by a Chinese traveller Yuan Chwang in the seventh century A.D. The Telugu Chodas contributed much to the early development and evolution of Telugu language and were the first dynasties to use Telugu as their official language in Andhra region. The oldest long Telugu inscription found so far is Kalamalla inscription dating to 575 CE put up by Renati Choda king Erikal Mutturaju Dhanunjaya. However, there exist several Telugu label inscriptions dating back to the 2nd century BCE. Renati Chodas The T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajaraja Chola I
Rajaraja I (Middle Tamil: ''Rājarāja Cōḻaṉ''; Classical Sanskrit: ''Rājarāja Śōḷa''; 3 November 947 – January/February 1014), also known as Rajaraja the Great, was a Chola Empire, Chola emperor who reigned from 985 to 1014. He was known for his conquests of South India, southern India and Anuradhapura Kingdom of Sri Lanka, as well as increasing Chola influence across the Indian Ocean. Rajaraja's birth name is variously given as Arul Mozhi Varman and Arul Moli Varman. Rajaraja's empire encompassed vast territories, including regions of the Pandya dynasty, Pandya country, the Chera dynasty, Chera country, and northern Sri Lanka. He also extended his influence over strategic islands such as Lakshadweep, Thailand, Thiladhunmadulu atoll, and parts of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean. His conquests weren't limited to the south; he also launched successful campaigns against the Western Ganga dynasty, Western Gangas and the Western Chalukya Empire, Western Chalukyas, ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Cholas
The Chola Empire, which is often referred to as the Imperial Cholas, was a medieval thalassocratic empire based in southern India that was ruled by the Chola dynasty, and comprised overseas dominions, protectorates and spheres of influence in southeast Asia. The power and the prestige the Cholas had among political powers in South, Southeast, and East Asia at its peak is evident in their expeditions to the Ganges, naval raids on cities of the Srivijaya Empire on the island of Sumatra, and their repeated embassies to China. K. A. Nilakanta Sastri, ''A History of South India'', p. 158 The Chola fleet represented the peak of ancient Indian maritime capacity. Around 1070, the Cholas began to lose almost all of their overseas territories but the later Cholas (1070–1279) continued to rule portions of southern India. The Chola empire went into decline at the beginning of the 13th century with the rise of the Pandyan dynasty, which ultimately caused the Chola's downfall. K. A. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |