|
Hindu Pilgrimage Sites In India
In Hinduism, the yatra (pilgrimage) to the tirthas (sacred places) has special significance for earning the punya (spiritual merit) needed to attain the moksha (salvation) by performing the darśana (viewing of deity), the parikrama (circumambulation), the yajna (sacrificial fire offering), the Dhyana (spiritual contemplation), the puja (worship), the prarthana (prayer, which could be in the form of mantra - sacred chants, bhajan - prayer singing, or kirtan - collective musical prayer performance), the dakshina (alms and donation for worthy cause), the seva (selfless service towards community, devotees or temple), the bhandara (running volunteer community kitchen for pilgrims), etc. These sacred places are usually located on the banks of sacred waters, such as sacred rivers or their tributaries (among the rigvedic rivers of sapta sindhu the trio ganges-yamuna-saraswati are considered most sacred), the kundas (pond or lake, among these the Lake Manasarovar is considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified by adherence to the concept of ''dharma'', a Ṛta, cosmic order maintained by its followers through rituals and righteous living, as expounded in the Vedas. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, it has also been described by the modern term ''Sanātana Dharma'' () emphasizing its eternal nature. ''Vaidika Dharma'' () and ''Arya dharma'' are historical endonyms for Hinduism. Hinduism entails diverse systems of thought, marked by a range of shared Glossary of Hinduism terms, concepts that discuss God in Hinduism, theology, Hindu mythology, mythology, among other topics in Hindu texts, textual sources. Hindu texts have been classified into Śruti () and Smṛti (). The major Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kedarnath Temple In Uttarakhand
Kedarnath is a town and Nagar Panchayat in Rudraprayag district of Uttarakhand, India, known primarily for the Kedarnath Temple. It is approximately 86.5 kilometres from Rudraprayag, the district headquarters. Kedarnath is the most remote of the four Chota Char Dham pilgrimage sites. It is located in the Himalayas, about above sea level near the Chorabari Glacier, which is the source of the Mandakini River. The town is flanked by snow-capped peaks, most prominently the Kedarnath Mountain. The nearest road head is at Gaurikund about 16 km away. The town suffered extensive destruction during June 2013 from the flash floods caused by torrential rains in Uttarakhand. Etymology The name "Kedarnath" means "the Lord of the Field". It is derived from the Sanskrit words ''kedara'' ("field") and ''natha'' ("lord"). The text ''Kashi Kedara Mahatmya'' states that it is so-called because "the crop of liberation" grows here. History Kedarnath is a pilgrimage site or '' tirtha'' d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seva (Indian Religions)
Seva may refer to: * Seva (Indian religions), volunteer work offered to God (in Indian religions) * Seva (Puerto Rico), a fictional town described in the novel ''Seva'' by Luis López Nieves * Seva (short story), "Seva" (short story), by Puerto Rican author Luis López Nieves * Seva, Barcelona, a municipality in the comarca of Osona, Catalonia, Spain * Seva, Ghana, an island in the Volta Region of Ghana * Seva Canada Society, a Vancouver-based non-profit organization that fights blindness in the developing world * Seva Foundation, an American non-profit foundation that fights blindness and poverty * Ševa, a principal character in the Croatian "anti-show" ''Nightmare Stage'' * Seva, a nickname for the East Slavic name Vsevolod * Stand-up Extravehicular activity, an activity in which an astronaut partially emerges into space See also * Seva Sadan (other) * Sewa (other) * Sevak (other) * Sewak (other) * Ceva (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghats In Varanasi
Ghats in Varanasi are riverfront steps leading to the banks of the Ganges river. The city has 84 ghats. Most of the ghats are bathing and puja ceremonial ghats, while two ghats, Manikarnika and Harishchandra, are used exclusively as cremation sites. Most of the ghats in Varanasi were rebuilt in the 18th century under the maratha patronage. The patrons of current ghats are Maharajas of Benares, Marathas, Shindes (Scindias), Holkars, Bhonsles and Peshwes (Peshwas). Many ghats are associated with legends or mythologies while other ghats have private histories and users. A morning boat ride on the Ganges along the ghats is a popular visitor attraction. Etymology It is derived from Sanskrit, "" (Sanskrit: ). It means an embankment or a landing place. ''Ghat'', a term used in the Indian subcontinent, depending on the context could either refer to a range of stepped-hill such as Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats; or the series of steps leading down to a body of water or wharf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghat
Ghat (), a term used in the Indian subcontinent, to refer to the series of steps leading down to a body of water or wharf, such as a bathing or cremation place along the banks of a river or pond, the Ghats in Varanasi, Dhobi Ghat or the Aapravasi Ghat.Sunithi L. Narayan, Revathy Nagaswami, 1992Discover sublime India: handbook for tourists Page 5.Ghat definition Cambridge dictionary. Etymology The origin of the English 'ghat' is , ' and is normally translated as ghaṭ, quay, landing or bathing place, as well as, steps by a river-side. The word 'ghat' has also been derived from Dravidian etymons such as Telugu ''kaṭṭa '' and ''gaṭṭu'' (dam and embankment) derived from ''kaṭṭu'' meaning "to ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Manasarovar
Lake Manasarovar also called Mapam Yumtso (; ) locally, is a high altitude freshwater lake near Mount Kailash in Burang County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region, China. It is located at an elevation of , near the western trijunction between China, India and Nepal. It overflows into the adjacent salt-water lake of Rakshastal via the Ganga Chhu. The sources of four rivers: Indus, Sutlej, Brahmaputra, and Karnali lie in the vicinity of the region. The lake is sacred in Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Bon religion. People from India, China, Nepal and other countries in the region undertake a pilgrimage to the region. The pilgrimage generally involves trekking towards Lake Manasarovar and a circumambulation of the nearby Mount Kailash. Etymology The Sanskrit word "Manasarovar" (मानसरोवर) is a combination of two Sanskrit words, ''Mānas'' (मानस्) meaning "mind" (generally denotes the mental powers associated including intellect, perceptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johad
A johad, also known as a pokhar or a percolation pond, is a community-owned traditional harvested rainwater storage wetland principally used for effectively harnessing water resources in the states of Haryana, Rajasthan, Punjab, Delhi and western Uttar Pradesh of North India, that collects and stores water throughout the year, to be used for the purpose of recharging the groundwater in the nearby water wells, washing, bathing and drinking by humans and cattle.Haruka Yanagisawa, 2015Community, Commons and Natural Resource Management in Asia:/ref>Video: How India's 'Water Man' first revived a river and a village in Rajasthan Scroll.in, 23 Mar 2015.Amanda Suutari and Gerry Marten [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saraswati
Saraswati (, ), also spelled as Sarasvati, is one of the principal Devi, goddesses in Hinduism, revered as the goddess of knowledge, education, learning, arts, speech, poetry, music, purification, language and culture. Together with the goddesses Lakshmi and Parvati, she forms the trinity of chief goddesses, known as the Tridevi. Sarasvati is a pan-Indian deity, venerated not only in Hinduism but also in Jainism and Buddhism.Ludvik (2007), pp. 1, 11. She is one of the prominent goddesses in the Historical Vedic religion, Vedic tradition (1500 to 500 BCE) who retains her significance in later Hinduism. In the Vedas, her characteristics and attributes are closely connected with the Sarasvati River, making her one of the earliest examples of a Rivers in Hinduism, river goddess in Indian tradition. As a deity associated with a river, Sarasvati is revered for her dual abilities to purify and to nurture fertility. In later Vedic literature, particularly the Brahmanas, Sarasvati is i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamuna
The Yamuna (; ) is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Lower Himalaya in Uttarakhand, it travels and has a drainage system of , 40.2% of the entire Ganges Basin. It merges with the Ganges at Triveni Sangam, Prayagraj, which is a site of the Kumbh Mela, a Hindu festival held every 12 years. Like the Ganges, the Yamuna is highly venerated in Hinduism and worshipped as the goddess Yamuna. In Hinduism, she is believed to be the daughter of the sun god, Surya, and the sister of Yama, the god of death, and so she is also known as Yami. According to popular Hindu legends, bathing in Yamuna's sacred waters frees one from the torments of death. The river crosses several states such as Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Delhi. It also meets several tributaries along the way, including Ton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain, Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly River. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma River, Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna, the lower str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
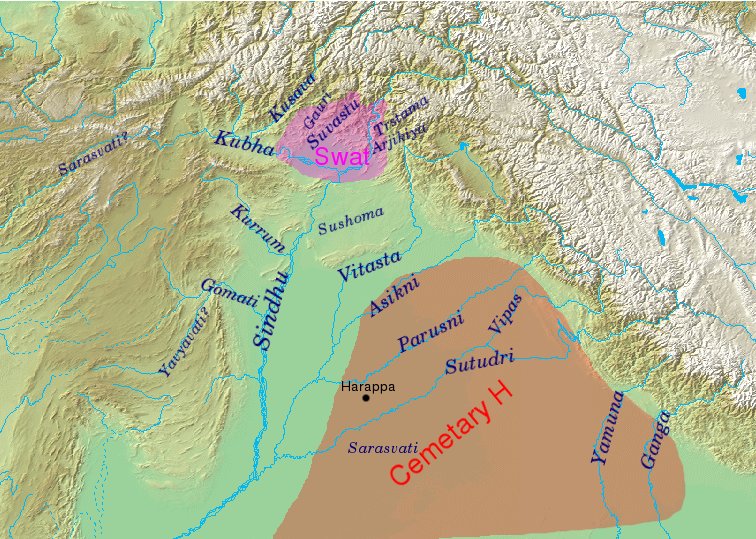
Sapta Sindhu
The Rigveda refers to a number of rivers located in the northwestern Indian subcontinent, from Gandhara to Kurukshetra. Rigvedic geography Identification of Rigvedic hydronyms has engaged multiple historians; it is the single most important way of establishing the geography and chronology of the early Vedic period. Rivers with certain identifications stretch from eastern Afghanistan to the western Gangetic plain, clustering in the Punjab. The Rigveda mentions the ''sapta-sindhavaḥ'' (, seven rivers), along with other rivers: ''Sapta-sindhavaḥ'' is cognate with Avestan ''hapta həndu'', and is interpreted as referring to Punjab. The region's name comes from پنج, ''panj'', 'five' and آب, ''āb'', 'water' thus " five waters", a Persian calque of the Indo-Aryan ''Pancha-nada'' meaning "five rivers". The same names were often imposed on different rivers as the Vedic culture migrated eastward from around Afghanistan (where they stayed for a considerable time) to the subco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigvedic Rivers
The Rigveda refers to a number of rivers located in the northwestern Indian subcontinent, from Gandhara to Kurukshetra. Rigvedic geography Identification of Rigvedic hydronyms has engaged multiple historians; it is the single most important way of establishing the geography and chronology of the early Vedic period. Rivers with certain identifications stretch from eastern Afghanistan to the western Gangetic plain, clustering in the Punjab. The Rigveda mentions the ''sapta-sindhavaḥ'' (, seven rivers), along with other rivers: ''Sapta-sindhavaḥ'' is cognate with Avestan ''hapta həndu'', and is interpreted as referring to Punjab. The region's name comes from پنج, ''panj'', 'five' and آب, ''āb'', 'water' thus " five waters", a Persian calque of the Indo-Aryan ''Pancha-nada'' meaning "five rivers". The same names were often imposed on different rivers as the Vedic culture migrated eastward from around Afghanistan (where they stayed for a considerable time) to the subc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |