|
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and jaundice, yellow tinged skin. The virus persists in the liver, becoming Chronic condition, chronic, in about 70% of those initially infected. Early on, chronic infection typically has no symptoms. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, hepatocellular carcinoma, liver cancer, or esophageal varices, dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and gastric varices, stomach. HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with injection drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, needlestick injuries in healthcare, and blood transfusions, transfusions. In r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or, less frequently, greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme metabolism, liver dysfunction, or biliary-tract obstruction. The prevalence of jaundice in adults is rare, while jaundice in babies is common, with an estimated 80% affected during their first week of life. The most commonly associated symptoms of jaundice are itchiness, pale feces, and dark urine. Normal levels of bilirubin in blood are below 1.0 mg/ dl (17 μmol/ L), while levels over 2–3 mg/dl (34–51 μmol/L) typically result in jaundice. High blood bilirubin is divided into two types: unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin. Causes of jaundice vary from relatively benign to potentially fatal. High unconjugated bilirubin may be due to excess red blood cell breakdown, large bruises, gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and recognize further and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylaxis, prophylactic (to prevent or alleviate the effects of a future infection by a natural or "wild" pathogen), or therapeutic vaccines, therapeutic (to fight a disease that has already occurred, such as cancer vaccine, cancer). Some vaccines offer full sterilizing immunity, in which infection is prevented. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E is inflammation of the liver caused by infection with the hepatitis E virus (HEV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Hepatitis E has mainly a fecal-oral transmission route that is similar to hepatitis A, although the viruses are unrelated. HEV is a positive-sense, single-stranded, nonenveloped, RNA icosahedral virus and one of five known human hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. Like hepatitis A, hepatitis E usually follows an acute and self-limiting course of illness (the condition is temporary and the individual recovers) with low death rates in resource-rich areas; however, it can be more severe in pregnant women and people with a weakened immune system, with substantially higher death rates. In pregnant women, especially in the third trimester, the disease is more often severe and is associated with a clinical syndrome called fulminant liver failure, with death rates around 20%. Whereas pregnant women may have a rapid and severe course, organ transpla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E. HDV is considered to be a satellite (a type of subviral agent) because it can propagate only in the presence of the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Transmission of HDV can occur either via simultaneous infection with HBV ( coinfection) or superimposed on chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis B carrier state ( superinfection). HDV infecting a person with chronic hepatitis B (superinfection) is considered the most serious type of viral hepatitis due to its severity of complications. These complications include a greater likelihood of experiencing liver failure in acute infections and a rapid progression to liver cirrhosis, with an increased risk of developing liver cancer in chronic infections. In combination with hepatitis B virus, hepatitis D has the highest fatality rate of all the hepatitis infections, at 20%. A recent estimate from 2020 su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection. Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. For others, symptoms may appear 30 to 180 days after becoming infected and can include a rapid onset of sickness with nausea, vomiting, yellowish skin, fatigue, yellow urine, and abdominal pain. Symptoms during acute infection typically last for a few weeks, though some people may feel sick for up to six months. Deaths resulting from acute stage HBV infections are rare. An HBV infection lasting longer than six months is usually considered chronic. The likelihood of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for those who are infected with HBV at a younger age. About 90% of those infected during or shortly after birth develop chronic hepatitis B, while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five develop chronic cases. Most of those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is an infectious liver disease caused by Hepatitis A virus (HAV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Many cases have few or no symptoms, especially in the young. The time between infection and symptoms, in those who develop them, is two to six weeks. When symptoms occur, they typically last eight weeks and may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, jaundice, fever, and abdominal pain. Around 10–15% of people experience a recurrence of symptoms during the six months after the initial infection. Acute liver failure may rarely occur, with this being more common in the elderly. It is usually spread by eating food or drinking water contaminated with infected feces. Undercooked or raw shellfish are relatively common sources. It may also be spread through close contact with an infectious person. While children often do not have symptoms when infected, they are still able to infect others. After a single infection, a person is immune for the rest of their life. Diagnosis req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
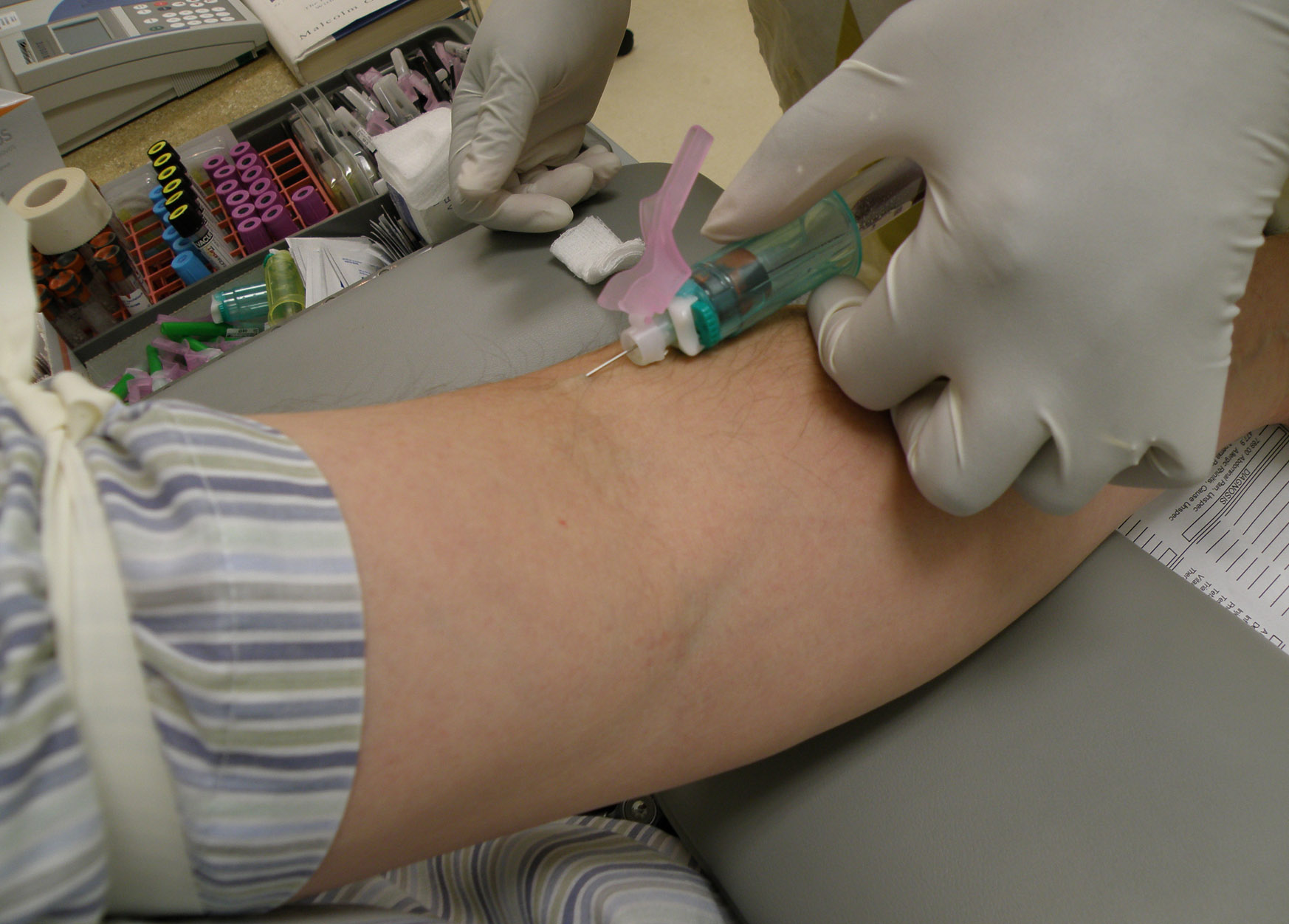
Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but modern medical practice commonly uses only components of the blood, such as red blood cells, plasma, platelets, and other clotting factors. White blood cells are transfused only in very rare circumstances, since granulocyte transfusion has limited applications. Whole blood has come back into use in the trauma setting. Red blood cells (RBC) contain hemoglobin and supply the cells of the body with oxygen. White blood cells are not commonly used during transfusions, but they are part of the immune system and also fight infections. Plasma is the "yellowish" liquid part of blood, which acts as a buffer and contains proteins and other important substances needed for the body's overall health. Platelets are involved in blood clotting, prev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needlestick Injuries
A needlestick injury is the penetration of the skin by a hypodermic needle or other sharp object that has been in contact with blood, tissue or other body fluids before the exposure. Even though the acute physiological effects of a needlestick injury are generally negligible, these injuries can lead to transmission of blood-borne diseases, placing those exposed at increased risk of infection from disease-causing pathogens, such as the hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). In healthcare and laboratory settings globally, there are over 25 distinct types of blood-borne diseases that can potentially be transmitted through needlestick injuries to workers. In addition to needlestick injuries, transmission of these viruses can also occur as a result of contamination of the mucous membranes, such as those of the eyes, with blood or body fluids, but needlestick injuries make up more than 80% of all percutaneous exposure incidents in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
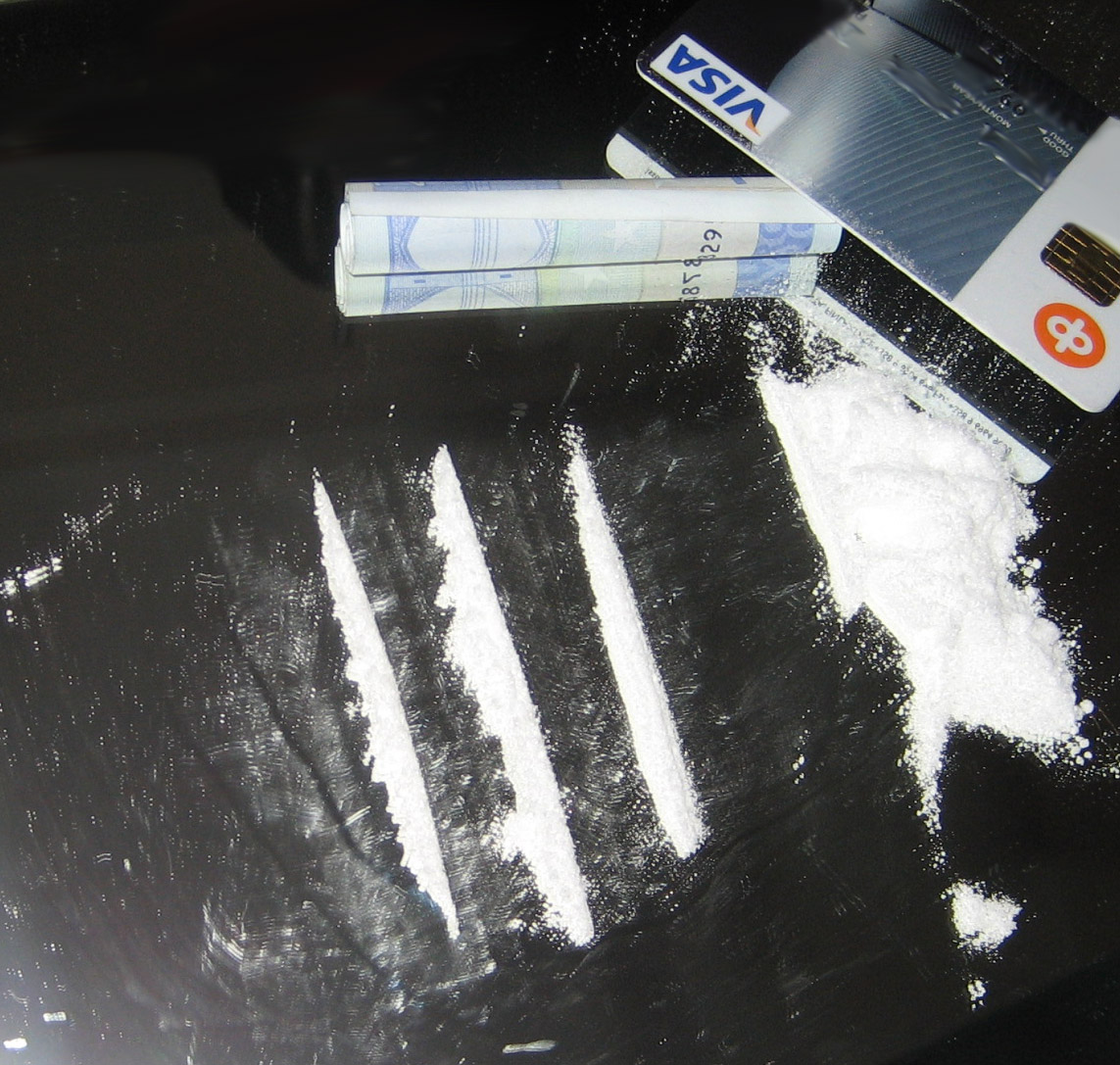
Injection Drug Use
Drug injection is a method of introducing a drug into the bloodstream via a hollow hypodermic needle, which is pierced through the skin into the body (usually intravenously, but also at an intramuscular or subcutaneous, location). Intravenous therapy, a form of drug injection, is universally practiced in modernized medical care. , there were 13.2 million people worldwide who self-administered injection drugs outside of medical supervision, of which 22% are from developed countries. A wide variety of drugs are injected, often opioids: these may include legally prescribed medicines and medication such as morphine, as well as stronger compounds often favored in recreational drug use, which are often illegal. Although there are various methods of taking drugs, injection is favoured by some people as the full effects of the drug are experienced very quickly, typically in five to ten seconds. It also bypasses first-pass metabolism in the liver, resulting in higher bioavailability and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Failure
Liver failure is the inability of the liver to perform its normal synthetic and metabolic functions as part of normal physiology. Two forms are recognised, acute and chronic (cirrhosis). Recently, a third form of liver failure known as acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is increasingly being recognized. Acute Acute liver failure is defined as "the rapid development of hepatocellular dysfunction, specifically coagulopathy and mental status changes (encephalopathy) in a patient without known prior liver disease".:1557 The disease process is associated with the development of a coagulopathy of liver aetiology, and clinically apparent altered level of consciousness due to hepatic encephalopathy. Several important measures are immediately necessary when the patient presents for medical attention. The diagnosis of acute liver failure is based on a physical exam, laboratory findings, patient history, and past medical history to establish mental status changes, coagulopathy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |