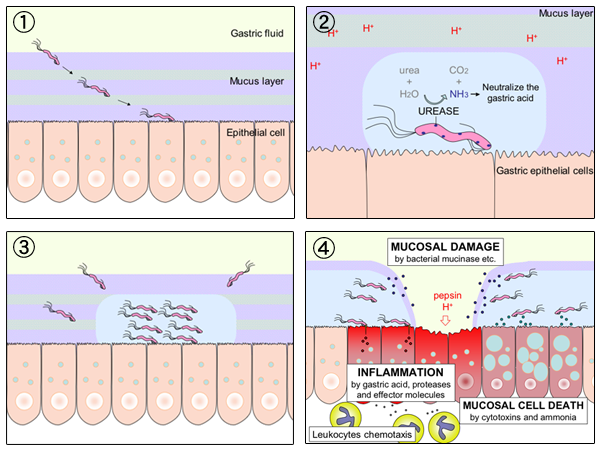
|
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, Flagellum#bacterial, flagellated, Bacterial cellular morphologies#Helical, helical bacterium. Mutants can have a rod or curved rod shape that exhibits less virulence. Its Helix, helical body (from which the genus name ''Helicobacter'' derives) is thought to have evolved to penetrate the gastric mucosa, mucous lining of the stomach, helped by its flagella, and thereby establish infection. While many earlier reports of an association between bacteria and the ulcers had existed, such as the works of John Lykoudis, it was only in 1983 when the bacterium was formally described for the first time in the English-language Western literature as the causal agent of peptic ulcer, gastric ulcers by Australian physician-scientists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. In 2005, the pair was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery. Infection of the stomach with ''H. pylori'' doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Physiology Or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's 1895 will, are awarded "to those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind". Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Medicine or Physiology, Chemistry, Literature, and Peace. The Nobel Prize is presented annually on the anniversary of Alfred Nobel's death, 10 December. As of 2024, 115 Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine have been awarded to 229 laureates, 216 men and 13 women. The first one was awarded in 1901 to the German physiologist, Emil von Behring, for his work on serum therapy and the development of a vaccine against diphtheria. The first woman to receive the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Gerty Cori, received it in 1947 for her role in elucida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. A sudden worsening of asthma symptoms sometimes called an 'asthma attack' or an 'asthma exacerbation' can occur when allergens, pollen, dust, or other particles, are inhaled into the lungs, causing the bronchioles to constrict and produce mucus, which then restricts oxygen flow to the alveoli. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to insulin's effects. Classic symptoms include polydipsia (excessive thirst), polyuria (excessive urination), polyphagia (excessive hunger), weight loss, and blurred vision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to various health complications, including disorders of the cardiovascular system, eye, kidney, and nerves. Diabetes accounts for approximately 4.2 million deaths every year, with an estimated 1.5 million caused by either untreated or poorly treated diabetes. The major types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2. The most common treatment for type 1 is insulin replacement therapy (insulin injections), while anti-diabetic medications (such as metformin and semaglutide) and lifestyle modificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have few or absent symptoms. In moderate deficiency, Fatigue, feeling tired, Headache, headaches, glossitis, soreness of the tongue, Aphthous stomatitis, mouth ulcers, breathlessness, Presyncope, feeling faint, Tachycardia, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, pallor, hair loss, decreased ability to think and severe arthralgia, joint pain and the beginning of neurological symptoms, including Paresthesia, abnormal sensations such as ''pins and needles'', numbness and tinnitus may occur. Severe deficiency may include symptoms of cardiomyopathy, reduced heart function as well as more severe neurological symptoms, including changes in reflexes, poor muscle function, memory problems, blurred vision, irritability, ataxia, decreased Anosmia, smell and Hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin available for oxygen transport, or abnormalities in hemoglobin that impair its function. The name is derived . When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague, such as Fatigue, tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, headaches, and a Exercise intolerance, reduced ability to exercise. When anemia is acute, symptoms may include confusion, lightheadedness, feeling like one is going to pass out, Syncope (medicine), loss of consciousness, and polydipsia, increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably Pallor, pale. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. Anemia can be temporary or long term and can range from mild to severe. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreased red blood cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MALT Lymphoma
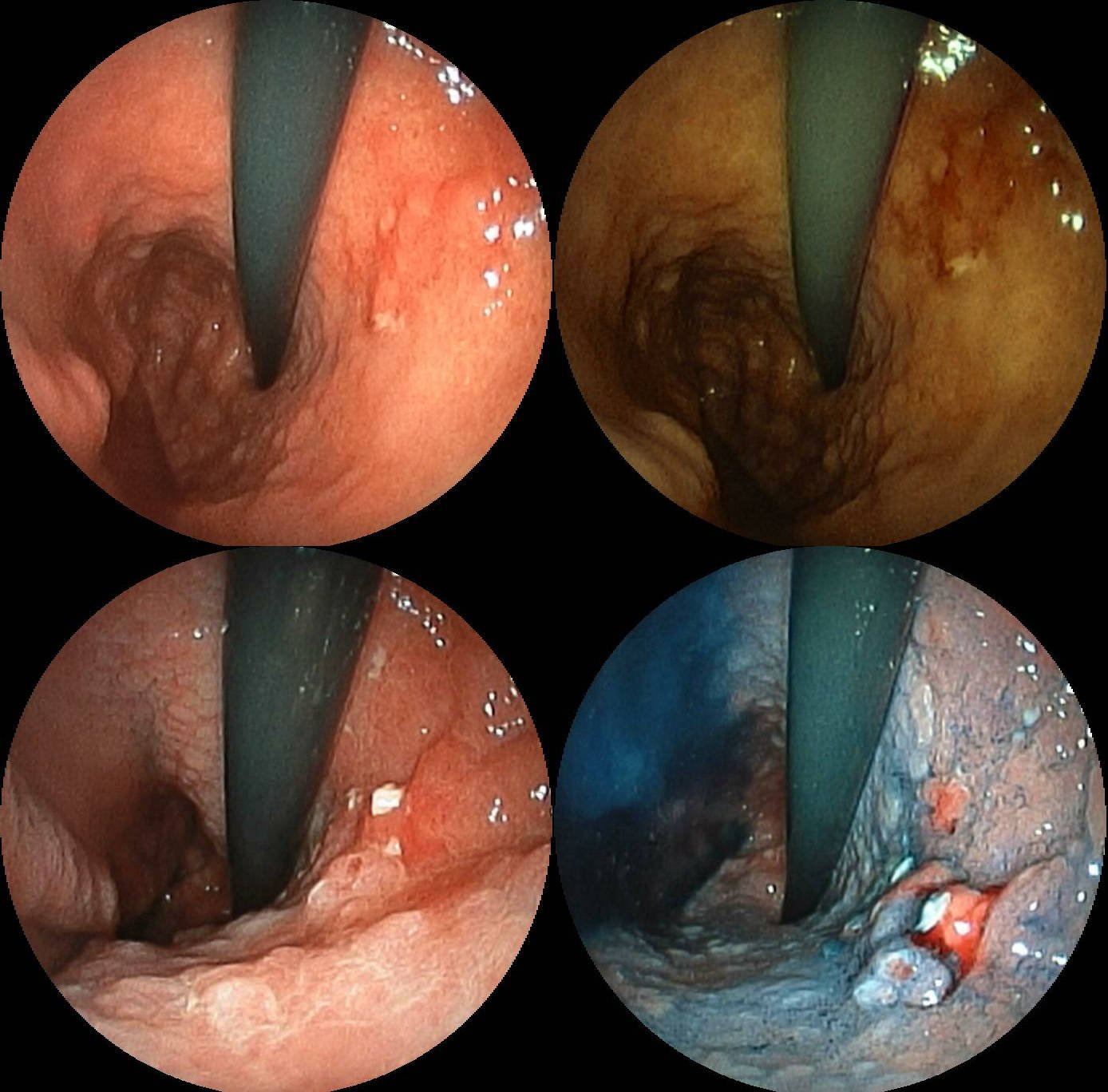
MALT lymphoma (also called MALToma) is a form of lymphoma involving the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), frequently of the stomach, but virtually any mucosal site can be affected. It is a cancer originating from B cells in the marginal zone of the MALT. Diagnosis and staging MALT lymphoma is often a multifocal disease in the organ of origin and is frequently macroscopically indistinguishable from other disease processes in the GI tract. Endoscopy is key to diagnosing MALT lymphoma, with multiple biopsies of the visible lesions required, as well as samples of macroscopically normal tissue, termed gastric mapping. Histologically, there is expansion of the marginal zone compartment with development of sheets of neoplastic small lymphoid cells. The morphology of the neoplastic cells is variable with small mature lymphocytes, cells resembling centrocytes (centrocyte like cells), or marginal zone/monocytoid B cells. Plasmacytoid or plasmacytic differentiation is frequent. Lymphoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogenic Bacteria
Cancer bacteria are bacteria infectious organisms that are known or suspected to cause cancer. While cancer-associated bacteria have long been considered to be opportunistic (i.e., infecting healthy tissues after cancer has already established itself), there is some evidence that bacteria may be directly carcinogenic. Evidence has shown that a specific stage in cancer can be associated with bacteria that is pathogenic. The strongest evidence to date involves the bacterium ''H. pylori'' and its role in gastric cancer. Oncoviruses are viral agents that are similarly suspected of causing cancer. Known to cause cancer '' Helicobacter pylori'' colonizes the human stomach and duodenum. It is described as a Class 1 carcinogen. In some cases it can cause stomach cancer and MALT lymphoma. Animal models have demonstrated Koch's third and fourth postulates for the role of ''Helicobacter pylori'' in the causation of stomach cancer. The mechanism by which ''H. pylori'' causes cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenal Ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease is when the inner part of the stomach's gastric mucosa (lining of the stomach), the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus, gets damaged. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with epigastrium, upper abdominal pain, and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a dyspepsia, burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite. About a third of older people with peptic ulcers have no symptoms. Complications may include gastrointestinal bleeding, bleeding, gastrointestinal perforation, perforation, and gastric outlet obstruction, blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include infection with ''Hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a malignant tumor of the stomach. It is a cancer that develops in the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymphomas and mesenchymal tumors may also develop in the stomach. Early symptoms may include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Later signs and symptoms may include weight loss, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and blood in the stool, among others. The cancer may spread from the stomach to other parts of the body, particularly the liver, lungs, bones, lining of the abdomen, and lymph nodes. The bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' accounts for more than 60% of cases of stomach cancer. Certain strains of ''H. pylori'' have greater risks than others. Smoking, dietary factors such as pickled vegetables and obesity are other ris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine. In humans, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about long connecting the stomach to the jejunum, the middle part of the small intestine. It begins with the duodenal bulb, and ends at the duodenojejunal flexure marked by the suspensory muscle of duodenum. The duodenum can be divided into four parts: the first (superior), the second (descending), the third (transverse) and the fourth (ascending) parts. Overview The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms ''anterior intestine'' or ''proximal intestine'' may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrophic Gastritis
Atrophic gastritis is a process of chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa of the stomach, leading to a loss of gastric gland, gastric glandular cells and their eventual replacement by Intestinal metaplasia, intestinal and fibrous tissues. As a result, the stomach's secretion of essential substances such as hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and intrinsic factor is impaired, leading to digestion, digestive problems. The most common are pernicious anemia possibly leading to vitamin B12 deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency; and malabsorption of iron, leading to iron deficiency anaemia. It can be caused by persistent infection with ''Helicobacter pylori'', or can be autoimmune in origin. Those with autoimmune atrophic gastritis (''Type A gastritis'') are statistically more likely to develop gastric carcinoma (a form of stomach cancer), Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and achlorhydria. Type A gastritis primarily affects the fundus (body) of the stomach and is more common with pernicious anemia. Ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |