|
Health Policy
Health policy can be defined as the "decisions, plans, and actions that are undertaken to achieve specific healthcare goals within a society".World Health Organization''Health Policy'' accessed 22 March 2011(archived 5 February 2011) According to the World Health Organization, an explicit health policy can achieve several things: it defines a vision for the future; it outlines priorities and the expected roles of different groups; and it builds consensus and informs people. Different approaches Health policy often refers to the health-related content of a policy. Understood in this sense, there are many categories of health policies, including global health policy, public health policy, mental health policy, health care services policy, insurance policy, personal healthcare policy, pharmaceutical policy, and policies related to public health such as vaccination policy, tobacco control policy or breastfeeding promotion policy. Health policy may also cover topics related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organisation Building From West
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts. In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational and critical inquiry that reflects on its methods and assumptions. Historically, many of the individual sciences, such as physics and psychology, formed part of philosophy. However, they are considered separate academic disciplines in the modern sense of the term. Influential traditions in the history of philosophy include Western philosophy, Western, Islamic philosophy, Arabic–Persian, Indian philosophy, Indian, and Chinese philosophy. Western philosophy originated in Ancient Greece and covers a wide area of philosophical subfields. A central topic in Arabic–Persian philosophy is the relation between reason and revelation. Indian philosophy combines the Spirituality, spiritual problem of how to reach Enlightenment in Buddhism, enlighten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Health Care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized around providing either all residents or only those who cannot afford on their own, with either health services or the means to acquire them, with the end goal of improving health outcomes. Some universal healthcare systems are government-funded, while others are based on a requirement that all citizens purchase private health insurance. Universal healthcare can be determined by three critical dimensions: who is covered, what services are covered, and how much of the cost is covered. It is described by the World Health Organization as a situation where citizens can access health services without incurring financial hardship. Then-Director General of the WHO Margaret Chan described universal health coverage as the "single most powerful conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Human Resources
Health human resources (HHR) – also known as human resources for health (HRH) or health workforce – is defined as "all people engaged in actions whose primary intent is to enhance positive health outcomes", according to World Health Organization's ''World Health Report 2006''. Human resources for health are identified as one of the six core building blocks of a health system. They include physicians, nursing professionals, pharmacists, midwives, dentists, allied health professions, community health workers, and other social service and health care providers. Health human resources are further composed of health management and support personnel: those who do not provide direct patient care but add important value to enhance health system efficiency, effectiveness and equity. They include health services managers, medical records and health information technicians, health economists, health supply chain managers, medical secretaries, facility maintenance workers, and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry is a medical industry that discovers, develops, produces, and markets pharmaceutical goods such as medications and medical devices. Medications are then administered to (or self-administered by) patients for curing or preventing disease or for alleviating symptoms of illness or injury. Pharmaceutical companies may deal in generic drugs, branded drugs, or both, in different contexts. Generic materials are without the involvement of intellectual property, whereas branded materials are protected by chemical patents. The industry's various subdivisions include distinct areas, such as manufacturing biologics and total synthesis. The industry is subject to a variety of laws and regulations that govern the patenting, efficacy testing, safety evaluation, and marketing of these drugs. The global pharmaceutical market produced treatments worth a total of $1,228.45 billion in 2020. The sector showed a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1.8% in 2021, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Out-of-pocket Expenses
An out-of-pocket expense, or out-of-pocket cost (OOP), is the direct payment of money that may or may not be later reimbursed from a third-party source. For example, when operating a vehicle, gasoline, parking fees and tolls are considered out-of-pocket expenses for a trip. Car insurance, oil changes, and interest are not, since the outlay of cash covers expenses accrued over a longer period of time. The services rendered and other in-kind expenses are not considered out-of-pocket expenses; the same goes for depreciation of capital goods or depletion. Organizations often reimburse out-of-pocket expenses incurred on their behalf, especially expenses incurred by employees on their employers' behalf. In the United States, out-of-pocket expenses for such things as charity, medical bills, and education may be deductions on US income taxes, according to IRS regulations. To be out of pocket is to have expended personal resources, often unexpectedly or unfairly, at the end of some en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Services Research
Health services research (HSR) became a burgeoning field in North America in the 1960s, when scientific information and policy deliberation began to coalesce. Sometimes also referred to as health systems research or health policy and systems research (HPSR), HSR is a multidisciplinary scientific field that examines how people get access to health care practitioners and health care services, how much care costs, and what happens to patients as a result of this care. HSR utilizes all qualitative and quantitative methods across the board to ask questions of the healthcare system. It focuses on performance, quality, effectiveness and efficiency of health care services as they relate to health problems of individuals and populations, as well as health care systems and addresses wide-ranging topics of structure, processes, and organization of health care services; their use and people's access to services; efficiency and effectiveness of health care services; the quality of healthcare ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Research
Medical research (or biomedical research), also known as health research, refers to the process of using scientific methods with the aim to produce knowledge about human diseases, the prevention and treatment of illness, and the promotion of health. Medical research encompasses a wide array of research, extending from " basic research" (also called ''bench science'' or ''bench research''), – involving fundamental scientific principles that may apply to a ''preclinical'' understanding – to clinical research, which involves studies of people who may be subjects in clinical trials. Within this spectrum is applied research, or translational research, conducted to expand knowledge in the field of medicine. Both clinical and preclinical research phases exist in the pharmaceutical industry's drug development pipelines, where the clinical phase is denoted by the term ''clinical trial''. However, only part of the clinical or preclinical research is oriented towards a specif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
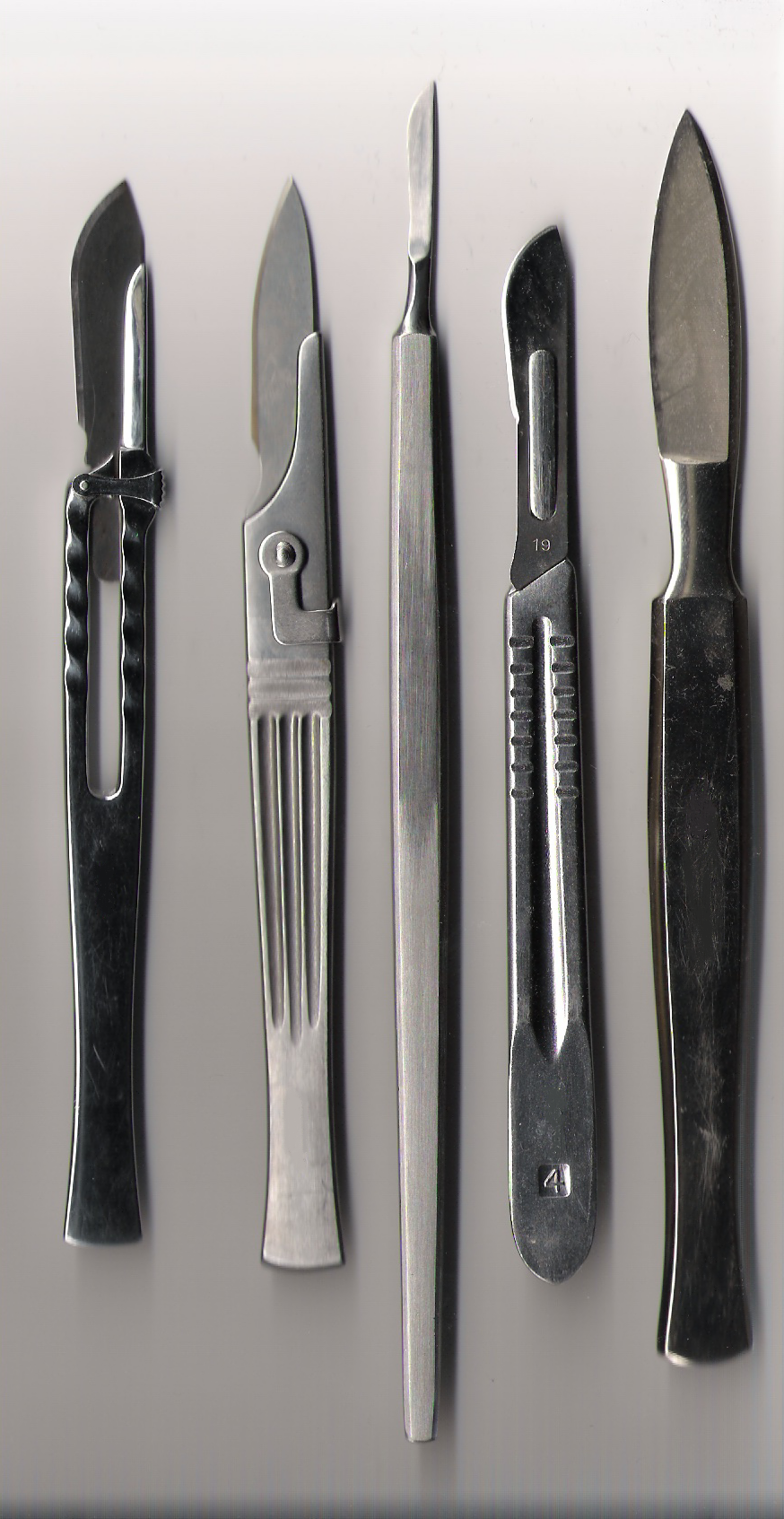
Surgical Instrument
A surgical instrument is a medical device for performing specific actions or carrying out desired effects during a surgery or operation, such as modifying biological tissue, or to provide access for viewing it. Over time, many different kinds of surgical instruments and tools have been invented. Some surgical instruments are designed for general use in all sorts of surgeries, while others are designed for only certain specialties or specific procedures. Classification of surgical instruments helps surgeons to understand the functions and purposes of the instruments. With the goal of optimizing surgical results and performing more difficult operations, more instruments continue to be invented in the modern era. History Many different kinds of surgical instruments and tools have been invented and some have been repurposed as medical knowledge and surgical practices have developed. As surgery practice diversified, some tools are advanced for higher accuracy and stability while so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medicine, medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are Drug class, classified in many ways. One of the key divisions is by level of controlled substance, control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the medical prescription) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Medicines may be classified by mode of action, route of administration, biological system affected, or therapeutic effects. The World Health Organization keeps a list of essential medicines. Drug discovery and drug development are complex and expensive endeavors undertake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Technology
Health technology is defined by the World Health Organization as the "application of organized knowledge and skills in the form of devices, medicines, vaccines, procedures, and systems developed to solve a health problem and improve quality of lives". This includes pharmaceuticals, devices, procedures, and organizational systems used in the healthcare industry, as well as computer-supported information systems. In the United States, these technologies involve standardized physical objects, as well as traditional and designed social means and methods to treat or care for patients. Development Pre-digital era During the pre-digital era, patients suffered from inefficient and faulty clinical systems, processes, and conditions. Many medical errors happened in the past due to undeveloped health technologies. Some examples of these medical errors included adverse drug events and alarm fatigue. When many alarms are repeatedly triggered or activated, especially for unimportant events ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Care Provider
A health care provider is an individual health professional or a health facility organization licensed to provide health care diagnosis and treatment services including medication, surgery and medical devices. Health care providers often receive payments for their services rendered from health insurance providers. In the United States, the Department of Health and Human Services defines a health care provider as any "person or organization who furnishes, bills, or is paid for health care in the normal course of business." Individual providers In the United States, the law defines a healthcare provider as a "doctor of medicine or osteopathy who is authorized to practice medicine or surgery" by the state, or anyone else designated by the United States Secretary of Labor as being able to provide health care services. In general, this is seen to include: * Physician, a professional who practices medicine * Advanced practice provider, a trained health worker who has a defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |