|
Gustav Kirchhoff
Gustav Robert Kirchhoff (; 12 March 1824 – 17 October 1887) was a German chemist, mathematician, physicist, and spectroscopist who contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy and the emission of black-body radiation by heated objects. He also coined the term ''black body'' in 1860. Several different sets of concepts are named "Kirchhoff's laws" after him, which include Kirchhoff's circuit laws, Kirchhoff's law of thermal radiation, and Kirchhoff's law of thermochemistry. The Bunsen–Kirchhoff Award for spectroscopy is named after Kirchhoff and his colleague, Robert Bunsen. Life and work Gustav Kirchhoff was born on 12 March 1824 in Königsberg, Prussia, the son of Friedrich Kirchhoff, a lawyer, and Johanna Henriette Wittke. His family were Lutheranism, Lutherans in the Evangelical Church of Prussia. He graduated from the Albertus University of Königsberg in 1847 where he attended the mathematico-physical seminar directed by Carl Gusta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, Baltic Crusades. It was named in honour of King Ottokar II of Bohemia, who led a campaign against the pagan Old Prussians, a Baltic tribe. A Baltic Sea, Baltic port city, it successively became the capital of the State of the Teutonic Order, the Duchy of Prussia and the provinces of East Prussia and Province of Prussia, Prussia. Königsberg remained the coronation city of the Prussian monarchy from 1701 onwards, though the capital was Berlin. From the thirteenth to the twentieth centuries on, the inhabitants spoke predominantly German language, German, although the city also had a profound influence upon the Lithuanian and Polish cultures. It was a publishing center of Lutheranism, Lutheran literatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Arthur Schuster
Sir Franz Arthur Friedrich Schuster (12 September 1851 – 14 October 1934) was a German-born British physicist known for his work in spectroscopy, electrochemistry, optics, X-radiography and the application of harmonic analysis to physics. Schuster's integral is named after him. He contributed to making the University of Manchester a centre for the study of physics. Early years Arthur Schuster was born in Frankfurt am Main, Germany the son of Francis Joseph Schuster, a cotton merchant and banker, and his wife Marie Pfeiffer. Schuster's parents were married in 1849, converted from Judaism to Christianity, and brought up their children in that faith. In 1869, his father moved to Manchester where the family textile business was based. Arthur, who had been to school in Frankfurt and was studying in Geneva, joined his parents in 1870 and he and the other children became British citizens in 1875. From his childhood, Schuster had been interested in science and after working for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
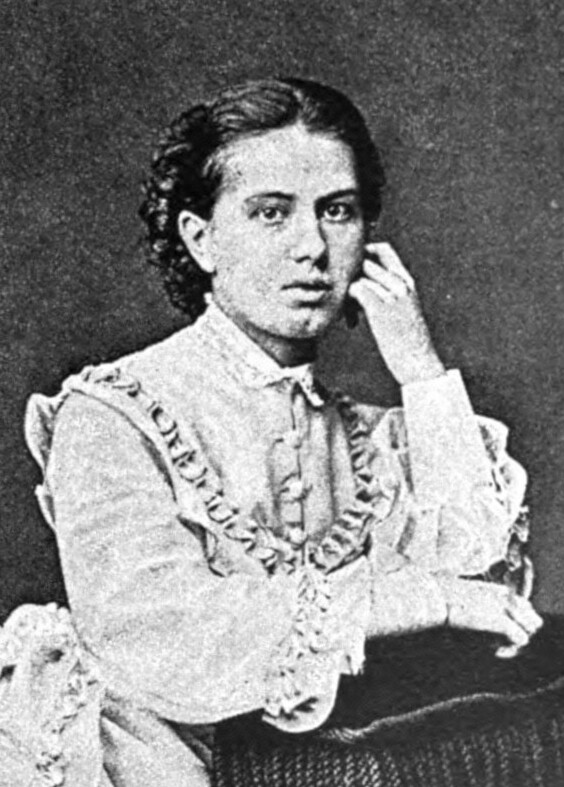 |
Sofia Kovalevskaya
Sofya Vasilyevna Kovalevskaya (; born Korvin-Krukovskaya; – 10 February 1891) was a Russian mathematician who made noteworthy contributions to analysis, partial differential equations and mechanics. She was a pioneer for women in mathematics around the world – the first woman to earn a doctorate (in the modern sense) in mathematics, the first woman appointed to a full professorship in northern Europe and one of the first women to work for a scientific journal as an editor. According to historian of science Ann Hibner Koblitz, Kovalevskaya was "the greatest known woman scientist before the twentieth century". Historian of mathematics Roger Cooke writes: Her sister was the socialist Anne Jaclard. There are several alternative transliterations of her name. She herself used Sophie Kowalevski (or occasionally Kowalevsky) in her academic publications. In Sweden she was known as Sonja Kovalevsky; Sonja (Russian ) is her Russian nickname. Background and early education Sofya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Heinrich Hertz
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (; ; 22 February 1857 – 1 January 1894) was a German physicist who first conclusively proved the existence of the electromagnetic waves predicted by James Clerk Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. Biography Heinrich Rudolf Hertz was born in 1857 in Hamburg, then a sovereign state of the German Confederation, into a prosperous and cultured Hanseatic family. His father was Gustav Ferdinand Hertz. His mother was Anna Elisabeth Pfefferkorn. While studying at the Gelehrtenschule des Johanneums in Hamburg, Hertz showed an aptitude for sciences as well as languages, learning Arabic. He studied sciences and engineering in the German cities of Dresden, Munich and Berlin, where he studied under Gustav R. Kirchhoff and Hermann von Helmholtz. In 1880, Hertz obtained his PhD from the University of Berlin, and for the next three years remained for post-doctoral study under Helmholtz, serving as his assistant. In 1883, Hertz took a post as a lecturer in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Gabriel Lippmann
Gabriel Lippmann ( ; 16 August 1845 – 12 July 1921) was a French physicist who received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1908 "for his method of reproducing colours photographically based on the phenomenon of interference". Early life and education Gabriel Lippmann was born in Bonnevoie, Luxembourg (Luxembourgish: Bouneweg), on 16 August 1845. At the time, Bonnevoie was part of the commune of Hollerich (Luxembourgish: Hollerech), which is often given as his place of birth. (Both places, Bonnevoie and Hollerich, are now districts of Luxembourg City.) His father, Isaïe, a French Jew born in Ennery near Metz, managed the family glove-making business at the former convent in Bonnevoie. In 1848, the family moved to Paris, where Lippmann was initially tutored by his mother, Miriam Rose (Lévy), before attending the Lycée Napoléon (now Lycée Henri-IV). He was said to have been a rather inattentive but thoughtful pupil with a special interest in mathematics. In 1868, he was admit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Friedrich Julius Richelot
Friedrich Julius Richelot (6 November 1808 – 31 March 1875) was a German mathematician, born in Königsberg. He was a student of Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi. He was promoted in 1831 at the Philosophical Faculty of the University of Königsberg with a dissertation on the division of the circle into 257 equal parts (see references) and was a professor there. Richelot authored numerous publications in German, French and Latin, among them — with his 1832 dissertation — the first known guide to the Euclidean construction of the regular 257-gon with compass and straightedge In geometry, straightedge-and-compass construction – also known as ruler-and-compass construction, Euclidean construction, or classical construction – is the construction of lengths, angles, and other geometric figures using only an Idealiz .... In 1825, he joined the Corps Masovia.Kösener Korps-Listen 1910, 141, 8 He died in Königsberg in 1875. See also * Timeline of abelian varieties References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Franz Ernst Neumann
Franz Ernst Neumann (11 September 1798 – 23 May 1895) was a German mineralogist and physicist. He devised the first formulas to calculate inductance. He also formulated Neumann's law for molecular heat. In electromagnetism, he is credited for introducing the magnetic vector potential. Biography Early life Franz Ernst Neumann was born in Joachimsthal, Margraviate of Brandenburg (near Berlin), the son of Ernst Neumann, a farmer who became a state agent. His mother was a Countess who was not allowed to marry Ernst, and Neumann did not meet her mother until he was 10 years old. Neumann attended a Gymnasium in Berlin, where he excelled in mathematics. However his studies were interrupted by the war with France. In 1815 he paused his education at Berlin to serve as a volunteer in the Hundred Days against Napoleon, and was wounded in the Battle of Ligny. He later returned to finish his studies in Berlin. Subsequently, he enrolled at Berlin University in 1818 as a student of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi
Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi (; ; 10 December 1804 – 18 February 1851) was a German mathematician who made fundamental contributions to elliptic functions, dynamics, differential equations, determinants and number theory. Biography Jacobi was born of Ashkenazi Jewish parentage in Potsdam on 10 December 1804. He was the second of four children of a banker, Simon Jacobi. His elder brother, Moritz, would also become known later as an engineer and physicist. He was initially home schooled by his uncle Lehman, who instructed him in the classical languages and elements of mathematics. In 1816, the twelve-year-old Jacobi went to the Potsdam Gymnasium, where students were taught all the standard subjects: classical languages, history, philology, mathematics, sciences, etc. As a result of the good education he had received from his uncle, as well as his own remarkable abilities, after less than half a year Jacobi was moved to the senior year despite his young age. However, as the Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
University Of Heidelberg
Heidelberg University, officially the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg (; ), is a public university, public research university in Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Founded in 1386 on instruction of Pope Urban VI, Heidelberg is List of universities in Germany#Universities by date of establishment, Germany's oldest university and one of the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, world's oldest surviving universities; it was the third university established in the Holy Roman Empire after Charles University, Prague (1347) and University of Vienna, Vienna (1365). Since 1899, it has been a coeducational institution. Heidelberg is one of the most prestigious universities in Germany. It is a German Excellence Universities, German Excellence University, part of the U15 (German universities), U15, as well as a founding member of the League of European Research Universities and the Coimbra Group. The university consists of twelve Faculty (division), faculties and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
University Of Breslau
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate education, undergraduate and postgraduate education, postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church, Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
University Of Berlin
The Humboldt University of Berlin (, abbreviated HU Berlin) is a public research university in the central borough of Mitte in Berlin, Germany. The university was established by Frederick William III on the initiative of Wilhelm von Humboldt, Johann Gottlieb Fichte and Friedrich Daniel Ernst Schleiermacher as the University of Berlin () in 1809, and opened in 1810. From 1828 until its closure in 1945, it was named the (Royal) Friedrich Wilhelm University of Berlin (FWU Berlin; ). During the Cold War, the university found itself in East Berlin and was ''de facto'' split in two when the Free University of Berlin opened in West Berlin. The university received its current name in honour of Alexander and Wilhelm von Humboldt in 1949. The university is divided into nine faculties including its medical school shared with the Freie Universität Berlin. The university has a student enrollment of around 35,000 students, and offers degree programs in some 171 disciplines from und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |