|
Gunpowder Mills
A powder mill was a mill where gunpowder is made from sulfur, saltpeter and charcoal. Milling steps Crude grinding and mixing operations such as the Frankford Powder-Mill of Philadelphia were a cottage industry until the Industrial Revolution brought improved product quality through the following procedures: * Charcoal was often manufactured nearby from locally available trees, but the heating retorts were typically separated from the other buildings to minimize fire danger. Trees with low value as sources of lumber were debarked, dried, and cut to uniform length to fit into iron retorts with cast iron doors. The retorts were carefully packed to leave as little air space as possible, and the retort doors were closed and sealed with clay to prevent entry of air as the retorts were heated by external fires. Volatile gas generated by the heating process was vented through a small flue at the top of each retort. After the external fires were extinguished, the retorts were allowed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
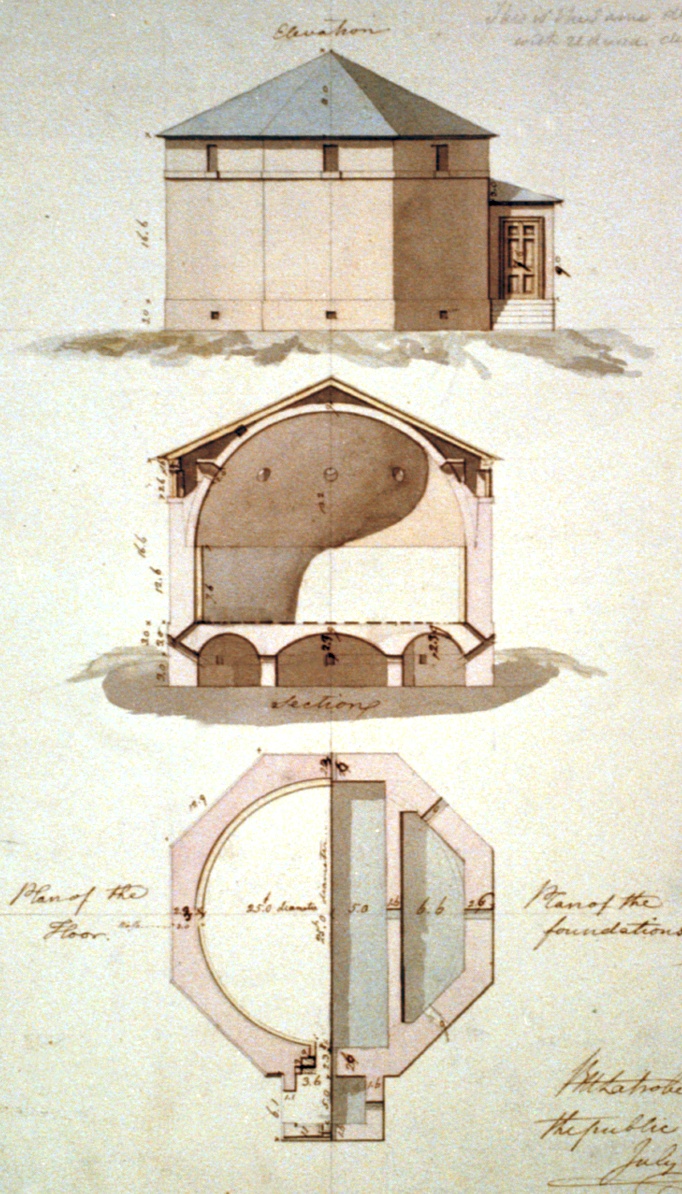
Encyclopédie - Illustration Of A Powder-mill (18th Century)
, better known as ''Encyclopédie'' (), was a general encyclopedia published in France between 1751 and 1772, with later supplements, revised editions, and translations. It had many writers, known as the Encyclopédistes. It was edited by Denis Diderot and, until 1759, co-edited by Jean le Rond d'Alembert. The ''Encyclopédie'' is most famous for representing the thought of the Enlightenment. According to Denis Diderot in the article "Encyclopédie", the ''Encyclopédie'' aim was "to change the way people think" and for people to be able to inform themselves and to know things. He and the other contributors advocated for the secularization of learning away from the Jesuits. Diderot wanted to incorporate all of the world's knowledge into the ''Encyclopédie'' and hoped that the text could disseminate all this information to the public and future generations. Thus, it is an example of democratization of knowledge. It was also the first encyclopedia to include contributions from m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
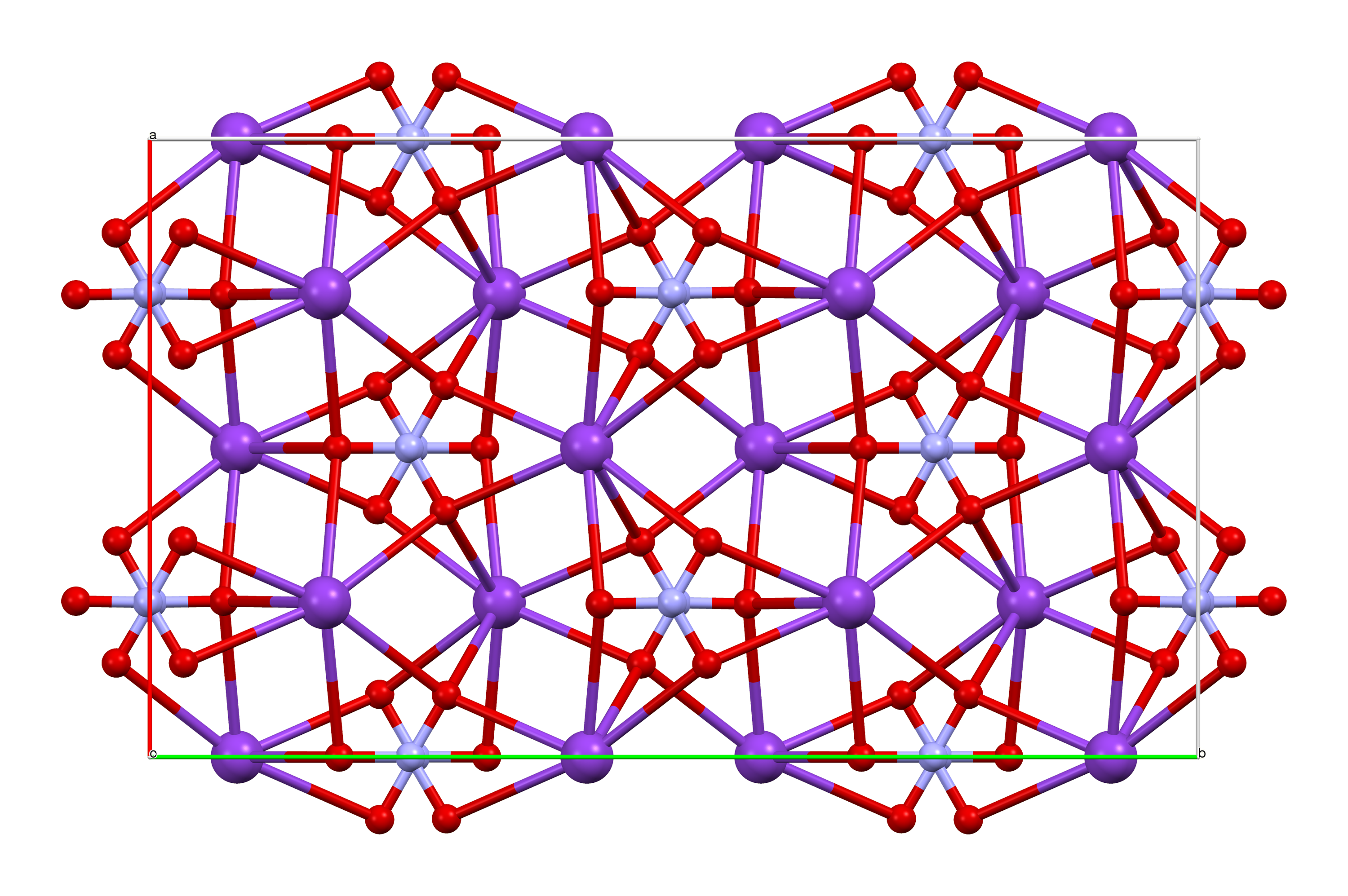
Potassium Nitrate
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with a sharp, salty, bitter taste and the chemical formula . It is a potassium salt of nitric acid. This salt consists of potassium cations and nitrate anions , and is therefore an alkali metal nitrate. It occurs in nature as a mineral, niter (or ''nitre'' outside the United States). It is a source of nitrogen, and nitrogen was named after niter. Potassium nitrate is one of several nitrogen-containing compounds collectively referred to as saltpetre (or saltpeter in the United States). Major uses of potassium nitrate are in fertilizers, tree stump removal, rocket propellants and fireworks. It is one of the major constituents of traditional gunpowder (black powder). In processed meats, potassium nitrate reacts with hemoglobin and myoglobin generating a red color. Etymology Nitre, or potassium nitrate, because of its early and global use and production, has many names. As for nitrate, Egyptian and Hebrew words for it had the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightning Strike
A lightning strike or lightning bolt is a lightning event in which an electric discharge takes place between the atmosphere and the ground. Most originate in a cumulonimbus cloud and terminate on the ground, called cloud-to-ground (CG) lightning. A less common type of strike, ground-to-cloud (GC) lightning, is upward-propagating lightning initiated from a tall grounded object and reaching into the clouds. About 25% of all lightning events worldwide are strikes between the atmosphere and earth-bound objects. Most are intracloud (IC) lightning and cloud-to-cloud (CC), where discharges only occur high in the atmosphere.Cooray, Vernon. (2014). Lightning Flash (2nd Edition) - 1. Charge Structure and Geographical Variation of Thunderclouds. Page 4. Institution of Engineering and Technology. Lightning strikes the average commercial aircraft at least once a year, but modern engineering and design means this is rarely a problem. The movement of aircraft through clouds can even cause lightn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Electricity
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it can move away by an electric current or electrical discharge. The word "static" is used to differentiate it from electric current, current electricity, where an electric charge flows through an electrical conductor. A static electric charge can be created whenever two surfaces contact and/or slide against each other and then separate. The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because they can feel, hear, and even see sparks if the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to an electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shockmore specifically, an electrostatic dischargeis caused by the neutralization of a charge. Causes Materials are made of atoms that are normally electrically neutral because they contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orange Powder Mill Ruins
Orange most often refers to: *Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis'' ** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower ** Orange juice *Orange (colour), the color of an orange fruit, occurs between red and yellow in the visible light spectrum *Some other citrus or citrus-like fruit, see ''list of plants known as orange'' * ''Orange'' (word), both a noun and an adjective in the English language Orange may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Game of Life'' (film), a 2007 film originally known as ''Oranges'' * ''Orange'' (2010 film), a Telugu-language film * ''The Oranges'' (film), a 2011 American romantic comedy starring Hugh Laurie * ''Orange'' (2012 film), a Malayalam-language film * ''Orange'' (2015 film), a Japanese film * ''Orange'' (2018 film), a Kannada-language film Music Groups and labels * Orange (band) Orange is an American-British pop punk/punk band from Los Angeles, California, formed in 2002. The band were firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunpowder Magazine
A gunpowder magazine is a magazine (building) designed to store the explosive gunpowder in wooden barrels for safety. Gunpowder, until superseded, was a universal explosive used in the military and for civil engineering: both applications required storage magazines. Most magazines were purely functional and tended to be in remote and secure locations. They are the successor to the earlier powder towers and powder houses. In Australia Historic magazines were at the following locations, among others: * Jack's Magazine, Saltwater River, Victoria * Goat Island, Sydney * Spectacle Island (Port Jackson) * North Arm Powder Magazine * Dry Creek explosives depot In Canada There are magazines at: * Citadel Hill (Fort George) * Citadel of Quebec, Quebec City, Quebec *Parc de l'Esplanade, Quebec City, Quebec *Cole Island, Esquimalt, British Columbia * Fort Lennox, Île-aux-Noix, Quebec * Fort William Historical Park, Thunder Bay, Ontario *Fort York, Toronto In Ireland Ballincollig, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on a large scale (1.3million metric tons per year in 2022) for uses in many critical industries including refractories (50%), lithium-ion batteries (18%), foundries (10%), and lubricants (5%), among others (17%). Graphite converts to diamond under extremely high pressure and temperature. Graphite's low cost, thermal and chemical inertness and characteristic conductivity of heat and electricity finds numerous applications in high energy and high temperature processes. Types and varieties Graphite can occur naturally or be produced synthetically. Natural graphite is obtained from naturally occurring geologic deposits and synthetic graphite is produced t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sieve
A sieve (), fine mesh strainer, or sift is a tool used for separating wanted elements from unwanted material or for controlling the particle size distribution of a sample, using a screen such as a woven mesh or net or perforated sheet material. The word ''sift'' derives from ''sieve''. In cooking, a sifter is used to separate and break up clumps in dry ingredients such as flour, as well as to aerate and combine them. A strainer (see colander), meanwhile, is a form of sieve used to separate suspended solids from a liquid by filtration. Sieving Sieving is a simple technique for separating particles of different sizes. A sieve such as used for sifting flour has very small holes. Coarse particles are separated or broken up by grinding against one another and the screen openings. Depending upon the types of particles to be separated, sieves with different types of holes are used. Sieves are also used to separate stones from sand. Sieving plays an important role in food ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It is the second most abundant trace metal in humans after iron, an import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloids (such as arsenic or silicon). These additions produce a range of alloys some of which are harder than copper alone or have other useful properties, such as strength, ductility, or machinability. The archaeological period during which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age, which started about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in modern times. Because historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
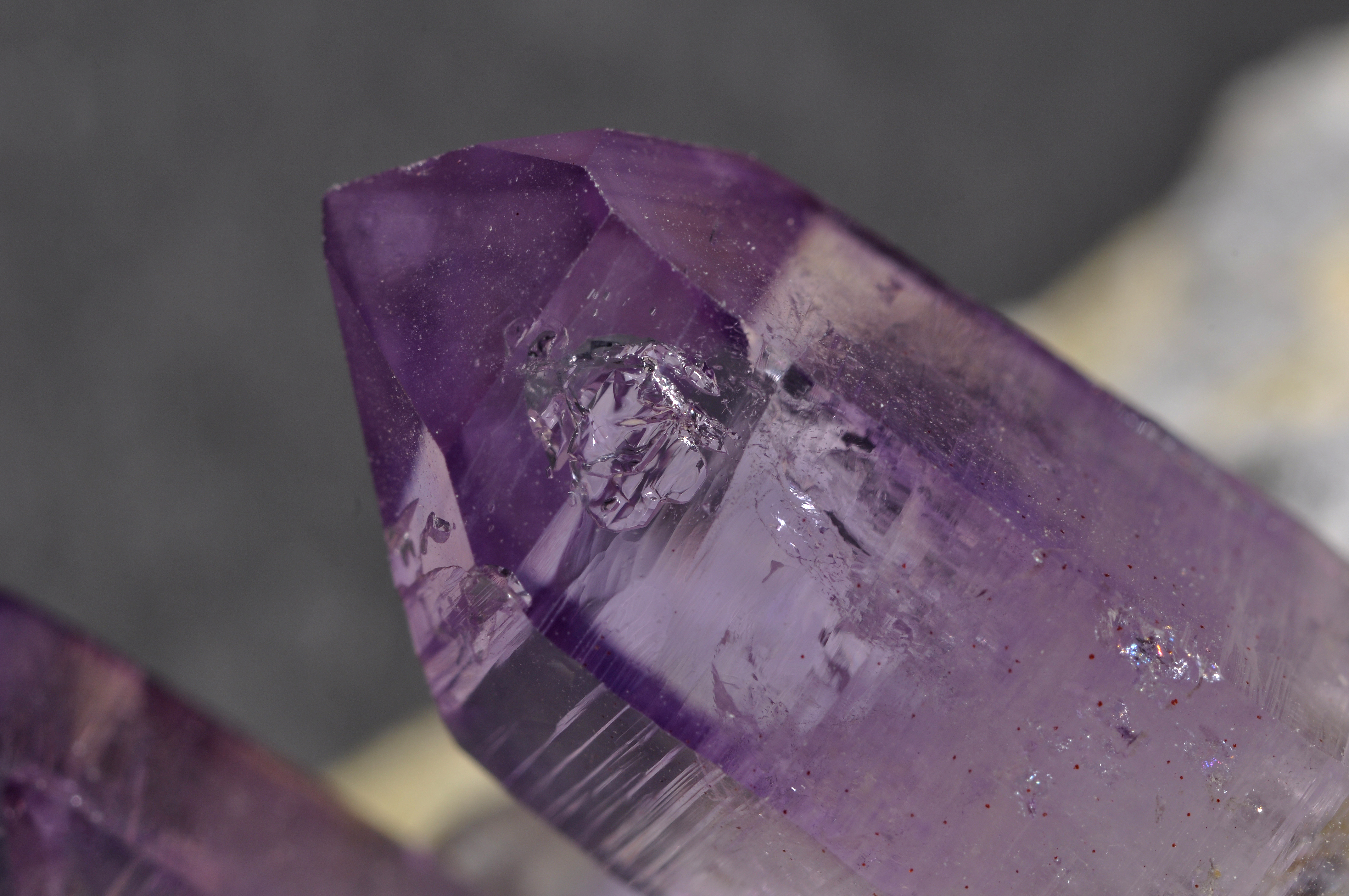
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and " rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recrystallization (chemistry)
Recrystallization is a broad class of List of purification methods in chemistry , chemical purification techniques characterized by the dissolution of an impure sample in a solvent or solvent mixture, followed by some change in conditions that encourages the formation of pure isolate as solid crystals. Recrystallization as a purification technique is driven by spontaneous process , spontaneous processes of molecular self-assembly , self-assembly that leverage the highly ordered (i.e. low-entropy) and periodic characteristics of a crystal's molecular structure to produce purification. Basic principles The driving force of this purification emerges from the difference in molecular interactions between the isolate and the impurities: if a molecule of the desired isolate interacts with any isolate crystal present, it is likely the molecule Deposition (chemistry) , deposits on the crystal's ordered surface and contributes to the crystal's growth; if a molecule of the impurity inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |