|
Guatemala–Mexico Border
The international border between Guatemala and Mexico measures . It runs between north and west Guatemala (the Guatemalan departments of San Marcos Department, San Marcos, Huehuetenango Department, Huehuetenango, Quiché Department, El Quiché and Petén Department, El Petén) and the Mexican states of Campeche, Tabasco and Chiapas. The border includes stretches of the Usumacinta River, the Salinas River (Guatemala), Salinas River, and the Suchiate River. Geopolitically, this border represents much of the western and northern boundary of the region of Central America within North America. It is across this border that most of the commerce between Mexico and Guatemala and the rest of Central America takes place. History In 1881, problems arose for Guatemala when President Justo Rufino Barrios claimed lands in Soconusco and Chiapas. The initial position of the Government of Mexico was not to accept discussion about their rights in that region. However, from 1882 began talks to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapa De La Frontera México-Guatemala
Mapa or MAPA may refer to: People * Alec Mapa (born 1965), American actor, comedian and writer * Dennis Mapa (born 1969), Filipino economist and statistician * Jao Mapa (born 1976), Filipino actor * Placido Mapa Jr. (born 1932), Filipino businessman, economist, and government official * Suraj Mapa (born 1980), Sri Lankan actor * Victorino Mapa (1855–1927), Filipino chief justice and government official Other uses * Mapa (song), "Mapa" (song), a 2021 song by SB19 * Mexican American Political Association * Mapa (publisher), an Israeli subsidiary of Ituran * Mapa Group, a Turkish conglomerate * Mapa, a company producing latex gloves that merged with Hutchinson SA in 1973 * Most Affected People and Areas, a climate justice concept * Mapa (girl group), a Japanese girl group See also * * Mappa (other) * Mapah (other) {{disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Border Guatemala-Mexico 1
Borders are generally defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders can be established through warfare, colonization, or mutual agreements between the political entities that reside in those areas. Some borders—such as most states' internal administrative borders, or inter-state borders within the Schengen Area—are open and completely unguarded. Most external political borders are partially or fully controlled, and may be crossed legally only at designated border checkpoints; adjacent border zones may also be controlled. For the purposes of border control, airports and seaports are also classed as borders. Most countries have some form of border control to regulate or limit the movement of people, animals, and goods into and out of the country. Under international law, each country is generally perm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chixoy River
The Chixoy River or Río Chixoy is a river in Guatemala. The river is called Río Negro from its sources in the highlands of Huehuetenango and El Quiché until it reaches the Chixoy hydroelectric dam (located at ), where the Río Salamá and Rio Carchela converge with the Río Negro. After the Chixoy dam, the river is called Río Chixoy and flows northwards, marking the departmental limits between Alta Verapaz and El Quiché, until it reaches the border with Mexico. It continues along the border for another as the Salinas river until it finally converges with the Río la Pasión (at ) to form the Usumacinta river which flows into the Gulf of Mexico The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw .... The Chixoy river's water discharge of is Guatemala's highest. This was one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
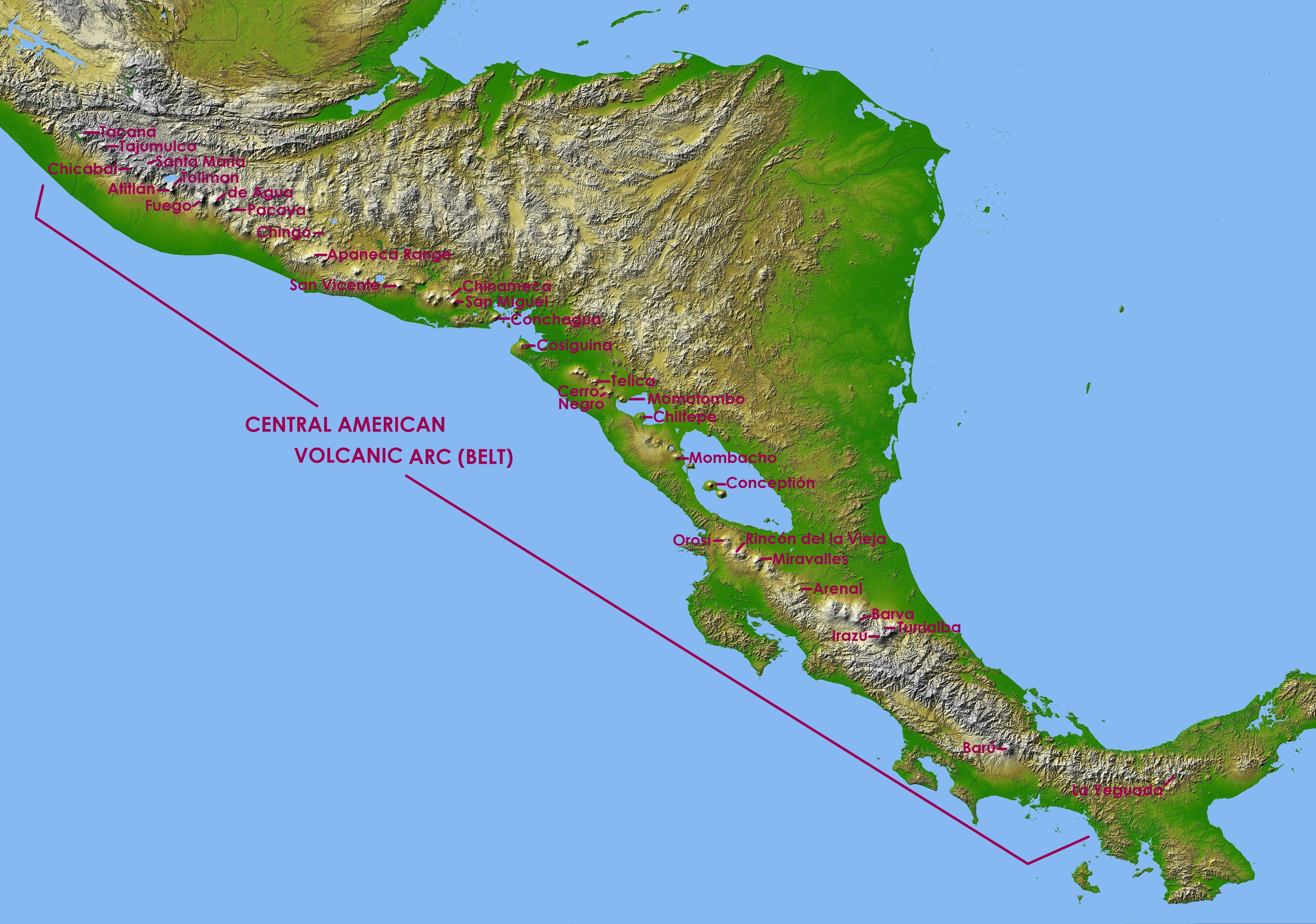
Volcán Tacaná
The volcano Tacaná is the second highest peak in Central America at , located in the Sierra Madre de Chiapas of western Guatemala and southern Mexico. It is also known in Mexico as ''Volcán Tacina''. Geography The volcano is located within the Tacaná municipality of the San Marcos Department in Guatemala; and within the Cacahoatán and Unión Juárez, Chiapas, Unión Juárez Municipalities of Chiapas state in Mexico. Its last known eruption was registered in 1986 — a small phreatic eruption in May — but it is still considered as dangerous to more than 250,000 people residing in the area. Tacaná is the first of hundreds of volcanoes in a km row, arranged NW to SE, parallel to the Pacific Ocean coast of Central America, known as the Central America Volcanic Arc, formed by an active subduction zone along the western boundary of the Caribbean Plate. The agricultural valley at its NNE foothills is covered with thick deposits of lahars. From its headwaters in Guatema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motozintla
Motozintla (Motozintla de Mendoza) is a city and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas in southern Mexico Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar .... Motozintla occupies part of Mexico's border with Guatemala and is adjacent to the municipalities of Siltepec (to the north), Escuintla and Huixtla (to the west), Tuzantán and Tapachula (to the south), and Mazapa de Madero and El Porvenir (to the northeast). It covers an area of 782.5 km². As of 2010, the municipality had a total population of 69,119, up from 59,875 as of 2005. The municipality had 416 localities, the largest of which (with 2010 populations in parentheses) were: Motozintla de Mendoza (23,755), classified as urban, and Belisario Domínguez (2,011), classified as rural. Climate Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Suchiate
The Suchiate River (, ) is a river that marks the southwesternmost part of the border between Mexico (state of Chiapas) and Guatemala (department of San Marcos). From its sources on the southern slopes of the Tacaná volcano in the Sierra Madre range of Guatemala, the 161 km (100 mi) long river flows in a south-southwesterly direction to the border with Mexico at Unión Juárez (), past the border towns Talismán and El Carmen, and then Ciudad Tecún Umán and Ciudad Hidalgo (Chiapas) further downstream, where the Puente Rodolfo Robles and a railway bridge cross the river, and on to the Pacific Ocean. Its name comes from the Nahuatl Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller popul ... name ''Xochiatl'' meaning "flower-water". The pre-Columbian archaeological site of Izapa l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demarcation Line
{{Refimprove, date=January 2008 A political demarcation line is a geopolitical border, often agreed upon as part of an armistice or ceasefire. Africa * Moroccan Wall, delimiting the Moroccan-controlled part of Western Sahara from the Sahrawi-controlled part Americas * During European imperialism overseas, the lines of amity were drawn to differentiate Europe from the rest of the world. The Line of Demarcation was one specific line drawn along a meridian in the Atlantic Ocean as part of the Treaty of Tordesillas in 1494 to divide new lands claimed by Portugal from those of Spain. This line was drawn in 1493 after Christopher Columbus returned from his maiden voyage to the Americas. * The Mason–Dixon line (or "Mason and Dixon's Line") is a demarcation line between four U.S. states, forming part of the borders of Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, and West Virginia (then part of Virginia). It was surveyed between 1763 and 1767 by Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Mexican States
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundaries with the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Caribbean Sea to the southeast, and the Gulf of Mexico to the east. Mexico covers 1,972,550 km2 (761,610 sq mi), and is the thirteenth-largest country in the world by land area. With a population exceeding 130 million, Mexico is the tenth-most populous country in the world and is home to the largest number of native Spanish speakers. Mexico City is the capital and largest city, which ranks among the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. Human presence in Mexico dates back to at least 8,000 BC. Mesoamerica, considered a cradle of civilization, was home to numerous advanced societies, including the Olmecs, Maya, Zapotecs, Teotihuacan civilization, and Purépecha. Spanish colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and financial centers in the world, and is classified as an Globalization and World Cities Research Network, Alpha world city according to the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) 2024 ranking. Mexico City is located in the Valley of Mexico within the high Mexican central plateau, at an altitude of . The city has 16 Boroughs of Mexico City, boroughs or , which are in turn divided into List of neighborhoods in Mexico City, neighborhoods or . The 2020 population for the city proper was 9,209,944, with a land area of . According to the most recent definition agreed upon by the federal and state governments, the population of Greater Mexico City is 21,804,515, which makes it the list of largest cities#List, sixth-largest metropolitan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive with a respective county. The city is the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the United States by both population and urban area. New York is a global center of finance and commerce, culture, technology, entertainment and media, academics, and scientific output, the arts and fashion, and, as home to the headquarters of the United Nations, international diplomacy. With an estimated population in 2024 of 8,478,072 distributed over , the city is the most densely populated major city in the United States. New York City has more than double the population of Los Angeles, the nation's second-most populous city. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Arbitration
International arbitration can refer to arbitration between companies or individuals in different states, usually by including a provision for future disputes in a contract (typically referred to as international commercial arbitration) or between different states qua states (typically referred to as interstate arbitration). Civil and commercial arbitration agreements and arbitral awards are enforced under the United Nations Convention on the Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Arbitral Awards of 1958 (the "New York Convention"). The International Centre for the Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID) also handles arbitration, but it is limited to investor-state dispute settlement. The New York Convention was drafted under the auspices of the United Nations and has been ratified by more than 150 countries, including most major countries involved in significant international trade and economic transactions.Jason Fry, Recognition And Enforcement Of Foreign Arbitral Awards: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matías Romero
Matías Romero Avendaño (24 February 1837 – 30 December 1898) was a Mexican politician and diplomat who served three times as Secretary of Finance and twice as ambassador of Mexico to the United States during the 19th century. Early life Romero began preparatory courses in Law while still living in Oaxaca. In 1855 he moved to Mexico City, and he received his law degree on 12 October 1857. He joined the liberals under command of General Ignacio Zaragoza, and traveled to Guanajuato to join the Army. However, he was instead commissioned into the Ministry of Relations. He accompanied Juárez to Guadalajara, but was briefly imprisoned by Commander Landa. After being freed, he followed Juárez to Veracruz via Panamá. He served as Melchor Ocampo's private secretary in Veracruz, and as official in various secretariats. Diplomatic career In 1859, Romero published a work on Mexican foreign treaties. In December of that year he was named Secretary of the Mexican Legation in Washing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |