|
Greek-language Films
Greek ( el, label= Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Greek Language
The Proto-Greek language (also known as Proto-Hellenic) is the Indo-European language which was the last common ancestor of all varieties of Greek, including Mycenaean Greek, the subsequent ancient Greek dialects Ancient Greek in classical antiquity, before the development of the common Koine Greek of the Hellenistic period, was divided into several varieties. Most of these varieties are known only from inscriptions, but a few of them, principally Aeolic ... (i.e., Attic Greek, Attic, Ionic Greek, Ionic, Aeolic Greek, Aeolic, Doric Greek, Doric, Arcadocypriot Greek, Arcadocypriot, and Ancient Macedonian language, ancient Macedonian—either a dialect or a closely related Hellenic languages, Hellenic language) and, ultimately, Koine Greek, Koine, Medieval Greek, Byzantine and Modern Greek (along with its Varieties of Modern Greek, variants). Proto-Greek speakers entered Greece sometime between 2200 and 1900 BCE, with the diversification into a southern and a northern gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
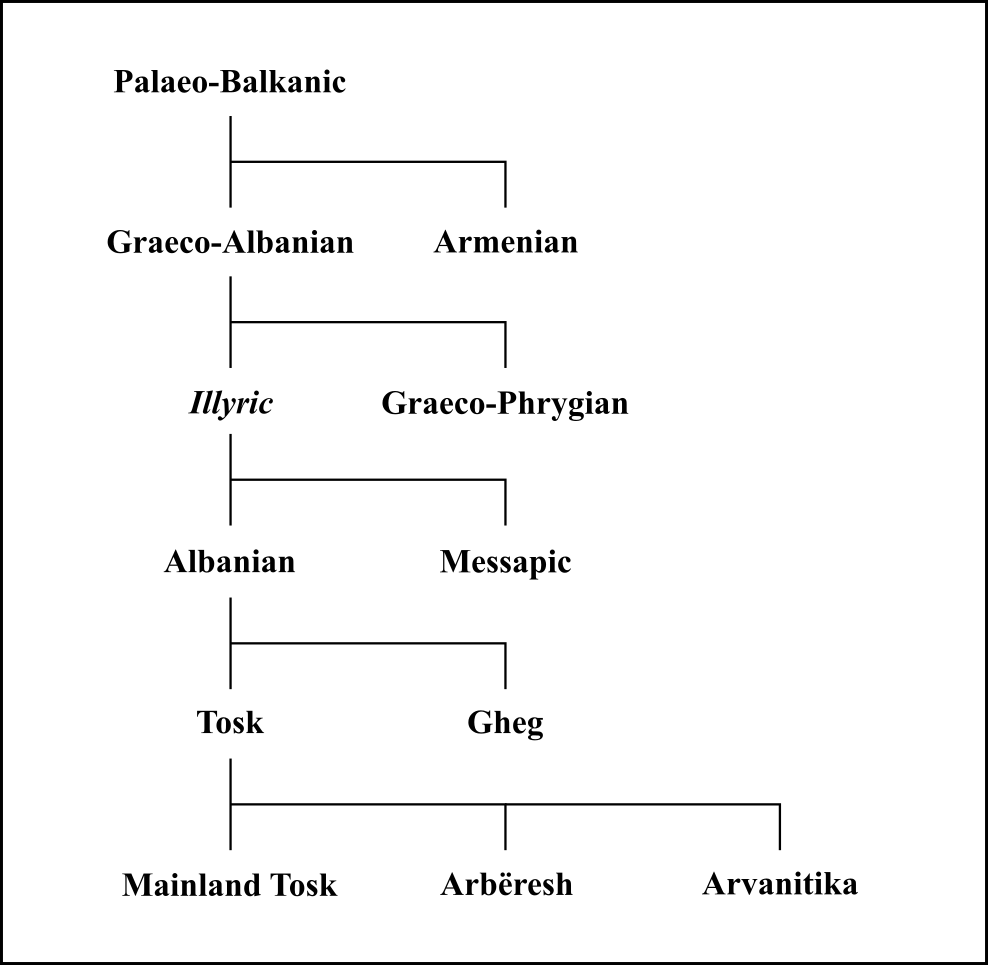
Paleo-Balkan Languages
The Paleo-Balkan languages or Palaeo-Balkan languages is a grouping of various extinct Indo-European languages that were spoken in the Balkans and surrounding areas in ancient times. Paleo-Balkan studies are obscured by the scarce attestation of these languages outside of Ancient Greek and, to a lesser extent, Messapic and Phrygian. Although linguists consider each of them to be a member of the Indo-European family of languages, the internal relationships are still debated. Due to the processes of Hellenization, Romanization and Slavicization in the region, the only modern descendants of Paleo-Balkan languages are Modern Greek—which is descended from Ancient Greek—and Albanian—which evolved from either Illyrian, Thracian, Dacian or another related tongue. Classification *Proto-Indo-European **Paleo-Balkan linguistic area ***Unclassified **** Illyrian languages ( onomastic areas) *****Illyrian proper (or Southeast Dalmatian) *****Central Dalmatian (or Dalmatia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The ( Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various times through the centuries. The encyclopaedia is maintained by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 contributors. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in the Scottish capital of Edinburgh, as three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size: the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810) it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |