|
Gondwanatheres
Gondwanatheria is an extinct group of mammaliaforms that lived in parts of Gondwana, including Madagascar, India, South America, Africa, and Antarctica during the Upper Cretaceous through the Miocene (and possibly much earlier, if ''Allostaffia'' is a member of this group). Until recently, they were known only from fragmentary remains. They are generally considered to be closely related to the multituberculates and likely the Euharamiyida, euharamiyidians, well known from the Northern Hemisphere, with which they form the clade Allotheria. Classification For several decades the affinities of the group were not clear, being first interpreted as early xenarthrans, or "toothless" mammals similar to the modern anteater. A variety of studies have placed them as allotheria, allotheres related to Multituberculata, multituberculates, possibly even true multituberculates, closer to Cimolodonta, cimolodonts than "plagiaulacidans" are. However, a more recent study recovered them as nested ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferugliotheriidae
Ferugliotheriidae is one of three known families in the order Gondwanatheria, an enigmatic group of extinct mammals. Gondwanatheres have been classified as a group of uncertain affinities or as members of Multituberculata, a major extinct mammalian order. The best-known representative of Ferugliotheriidae is the genus '' Ferugliotherium'' from the Late Cretaceous epoch in Argentina. A second genus, '' Trapalcotherium'', is known from a single tooth, a first lower molariform ( molar-like tooth), from a different Late Cretaceous Argentinean locality. Another genus known from a single tooth (in this case, a fourth lower premolar), '' Argentodites'', was first described as an unrelated multituberculate, but later identified as possibly related to ''Ferugliotherium''. Finally, a single tooth from the Paleogene of Peru, LACM 149371, perhaps a last upper molariform, and a recent specimen from Mexico, may represent related animals. Ferugliotheriids are known from isolated, low-crowned ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
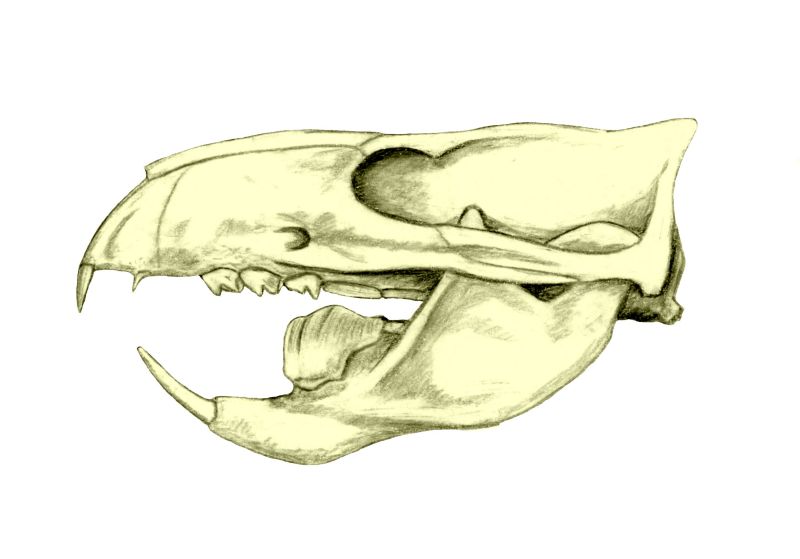
Ferugliotherium
''Ferugliotherium'' is a genus of fossil mammals in the family Ferugliotheriidae from the Campanian and/or Maastrichtian period (Late Cretaceous; around 70 million years ago) of Argentina. It contains a single species, ''Ferugliotherium windhauseni'', which was first described in 1986. Although originally interpreted on the basis of a single brachydont (low- crowned) molar as a member of Multituberculata, an extinct group of small, rodent-like mammals, it was recognized as related to the hypsodont (high-crowned) Sudamericidae following the discovery of additional material in the early 1990s. After a jaw of the sudamericid '' Sudamerica'' was described in 1999, these animals (collectively known as Gondwanatheria) were no longer considered to be multituberculates and a few fossils that were previously considered to be ''Ferugliotherium'' were assigned to unspecified multituberculates instead. Since 2005, a relationship between gondwanatheres and multituberculates has again received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavanify
''Lavanify'' is a mammalian genus from the late Cretaceous (probably Maastrichtian, about 71 to 66 million years ago) of Madagascar. The only species, ''L. miolaka'', is known from two isolated teeth, one of which is damaged. The teeth were collected in 1995–1996 and described in 1997. The animal is classified as a member of Gondwanatheria, an enigmatic extinct group with unclear phylogenetic relationships, and within Gondwanatheria as a member of the family Sudamericidae. ''Lavanify'' is most closely related to the Indian '' Bharattherium''; the South American ''Sudamerica'' and ''Gondwanatherium'' are more distantly related. Gondwanatheres probably ate hard plant material. ''Lavanify'' had high- crowned, curved teeth. One of the two teeth is 11.2 mm high and shows a deep furrow and, is centered laterally in the crown, a V-shaped area that consists of dentine. The other, damaged, tooth is 9.8 mm high and has at least one deep cavity (infundibulum). Characters s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bharattherium
''Bharattherium'' is a mammal that lived in India during the Maastrichtian (latest Cretaceous) and possibly the Paleocene. The genus has a single species, ''Bharattherium bonapartei''. It is part of the gondwanathere family Sudamericidae, which is also found in Madagascar and South America during the latest Cretaceous. The first fossil of ''Bharattherium'' was discovered in 1989 and published in 1997, but the animal was not named until 2007, when two teams independently named the animal ''Bharattherium bonapartei'' and ''Dakshina jederi''. The latter name is now a synonym. ''Bharattherium'' is known from a total of eight isolated fossil teeth, including one incisor and seven molariforms ( molar-like teeth, either premolars or true molars). ''Bharattherium'' molariforms are high, curved teeth, with a height of . In a number of teeth tentatively identified as fourth lower molariforms (mf4), there is a large furrow on one side and a deep cavity (infundibulum) in the middle of the toot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groeberiidae
Groeberiidae is a family of strange non-placental mammals from the Eocene and Oligocene epochs of Patagonia, Argentina and Chile, South America. Originally classified as paucituberculate marsupials, they were suggested to be late representatives of the allothere clade Gondwanatheria. However, the relationship of the type genus, '' Groeberia'', to Gondwanatheria has been firmly rejected by other scholars. History The type species, '' Groeberia minoprioi'', was first described by Bryan Patterson in 1952. This type specimen, MMP 738, is composed of a mandibular symphisis, incisors and four broken molars. A second species within the genus, '' Groeberia pattersoni'', was described by G. G. Simpson in 1970, and is known from at least two specimens.Goin, F.J., Abello M.A. & Chornogubsky L. 2010Middle Tertiary marsupials from Central Patagonia (Early Oligocene of Gran Barranca): Understanding South America’s ''Grande Coupure'' En: Madden R.H., Carlini A.A., Vucetich M.G. & Kay R.F. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentodites
''Argentodites'' is a possible multituberculate mammal from the Cretaceous of Argentina. The single species, ''Argentodites coloniensis'', is known from a single blade-like fourth lower premolar (p4) from the La Colonia Formation, which is mostly or entirely Maastrichtian (latest Cretaceous) in age. The p4 is 4.15 mm long and bears eight cusps on its upper margin and long associated ridges on both sides. The enamel consists of prisms that are completely or partly surrounded by a sheath and that are on average 6.57 μm apart. Zofia Kielan-Jaworowska, who described and named the fossil in 2007, regarded it as a multituberculate, perhaps a cimolodontan—and thus, a member of a mostly Laurasian (northern) group and an immigrant to Argentina from North America—on the basis of the shape of the tooth and features of its enamel. In 2009, however, two teams argued that ''Argentodites'' may in fact be close to or identical with ''Ferugliotherium'', a member of the small Gondwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trapalcotherium
''Trapalcotherium'' is a fossil mammal from the Cretaceous of Argentina in the family Ferugliotheriidae. The single species, ''T. matuastensis'', is known from one tooth, a first lower molar. It is from the Allen Formation, which is probably Maastrichtian in age, and was first described in 2009. The tooth bears two rows of cusps, one at the inner (lingual) side and the other at the outer (labial) side, which are connected by transverse ridges separated by deep valleys. This pattern is reminiscent of ''Ferugliotherium'', a gondwanathere mammal from similarly aged deposits in Argentina, and ''Trapalcotherium'' is therefore recognized as a member of the same family Ferugliotheriidae. Ferugliotheriidae is one of two families of gondwanatheres, an enigmatic group without close relationships to any living mammals. Discovery and context The only known fossil of ''Trapalcotherium'' was found at Cerro Tortuga in Río Negro Province, southern Argentina. This locality is in the Allen For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galulatherium
''Galulatherium'' is an extinct genus of possibly gondwanathere mammal, from the Late Cretaceous (Turonian-Campanian)-aged Galula Formation of Tanzania.P. M. O'Connor, D. W. Krause, N. J. Stevens, J. R. Groenke, R. D. E. MacPhee, D. C. Kalthoff, and E. M. Roberts. (2019). A new mammal from the Turonian–Campanian (Upper Cretaceous) Galula Formation, southwestern Tanzania. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 64(1):65-84 It is known solely from the type specimen TNM 02067 ( Tanzanian National Museums specimen 02067) a fragmentary fossil dentary (lower jaw). The short, deep bone is about long, but the back part is broken off. It contains a large, forward-inclined incisor with a root that extends deep into the jaw, separated by a diastema (gap) from five cheekteeth. Very little remains of the teeth, but enough to determine that they are hypsodont (high-crowned). The third cheektooth is the largest and the roots of the teeth are curved. First described in 2003, TNM 02067 has been tentative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |