|
Ghats Of India
Ghat (), a term used in the Indian subcontinent, to refer to the series of steps leading down to a body of water or wharf, such as a bathing or cremation place along the banks of a river or pond, the Ghats in Varanasi, Dhobi Ghat or the Aapravasi Ghat.Sunithi L. Narayan, Revathy Nagaswami, 1992Discover sublime India: handbook for tourists Page 5.Ghat definition Cambridge dictionary. Etymology The origin of the English 'ghat' is , ' and is normally translated as ghaṭ, quay, landing or bathing place, as well as, steps by a river-side. The word 'ghat' has also been derived from Dravidian etymons such as ''kaṭṭa '' and ''gaṭṭu'' (dam and embankment) derived fr ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
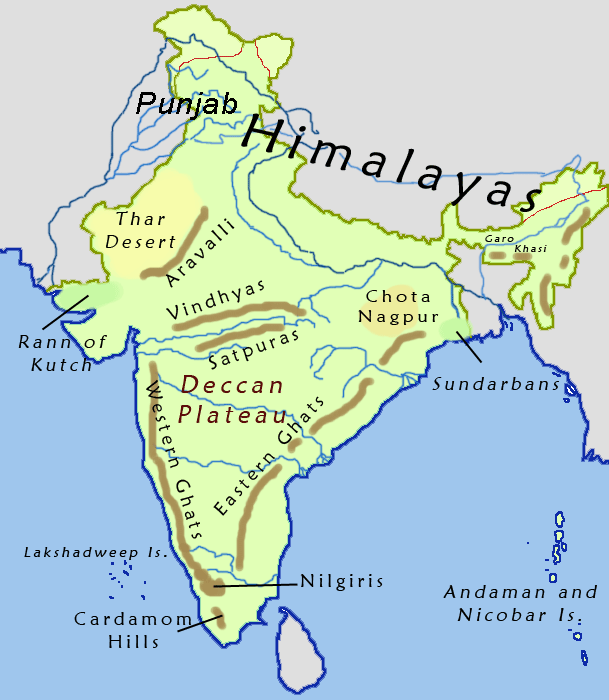
Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats is a mountain range that stretches along the East Coast of India, eastern coast of the Indian peninsula. Covering an area of , it traverses the states and union territories of India, states of Odisha, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu. The range forms a discontinuous chain of mountains along the eastern edge of the Deccan Plateau, stretching from north of the Mahanadi River in Odisha to Vaigai River in Tamil Nadu at the southern end of the peninsula. The Eastern Ghats meet the Western Ghats at the Nilgiris. The average elevation is around and Arma Konda is the highest peak in the mountains at . Geological evidence indicates that the mountains were formed during the archeozoic era and became part of the Indian subcontinent post the break-up of the supercontinent of Rodinia and the formation of Gondwana. The mountains were formed through further metamorphism during the mid-Proterozoic era. The northern section of the range has an elevation r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malwa
Malwa () is a historical region, historical list of regions in India, region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic plateau, volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also synonymous with the former state of Madhya Bharat which was later merged with Madhya Pradesh. At present the historical Malwa region includes districts of western Madhya Pradesh and parts of south-eastern Rajasthan. Sometimes the definition of Malwa is extended to include the Nimar region south of the Vindhya Range, Vindhyas. The Malwa region had been a separate political unit from the time of the ancient Malava Kingdom. It has been ruled by several kingdoms and dynasties, including the Avanti (India), Avanti Kingdom, The Maurya Empire, Mauryans, the Malavas, the Gupta Empire, Guptas, the Paramara dynasty, Paramaras, The Rajput, Rajputs, the Delhi Sultanate, the Malwa Sultanate, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balurghat
Balurghat is a city and municipality located in the Dakshin Dinajpur district of West Bengal, India, serving as the district headquarters. Strategically positioned on National Highway 512, it is well-connected by road and rail, facilitating trade and travel within the state and to neighbouring regions. The Atrai River flows through Balurghat, contributing to the area's agricultural prosperity by providing vital water resources for both the city and its surrounding areas. Known for its rich cultural heritage, the town blends rural and urban characteristics and is a major hub for commerce, education, and government administration in the region. Balurghat has a strong agricultural base, primarily focused on rice cultivation, and hosts numerous small-scale industries. The town has also seen gradual urbanisation, with significant developments in infrastructure, healthcare, and public services, which have enhanced the quality of life for its residents. With a tropical climate featuring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balaghat District
Balaghat district () is a district of Madhya Pradesh state in Central India. Its belongs to Jabalpur Division. Balaghat city is Administrative Headquarter of Balaghat District. Balaghat is known for its tile factories, rice mills and forests. In MP Balaghat district has significant mineral deposits and a number of forests. Balaghat comes under the Bhandara dist. Raghuji is the first Maratha who came to this place from Kirnapur Side. History At the beginning of the 18th century, the district was divided among two Gond kingdoms; the portion of the district west of the Wainganga was part of the Gond kingdom of Deogarh, while the eastern portion was part of the Garha-Mandla kingdom. The Deogarh kingdom was annexed by the Bhonsle Marathas of Nagpur in 1743, and shortly thereafter conquered all but the northern section of the district. This section, together with the rest of the Garha-Mandla kingdom, was annexed in 1781 to the Maratha province of Saugor, then under control of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns and adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry grammatical information (inflectional endings) or lexical information ( derivational/lexical suffixes)''.'' Inflection changes the grammatical properties of a word within its syntactic category. Derivational suffixes fall into two categories: class-changing derivation and class-maintaining derivation. Particularly in the study of Semitic languages, suffixes are called affirmatives, as they can alter the form of the words. In Indo-European studies, a distinction is made between suffixes and endings (see Proto-Indo-European root). A word-final segment that is somewhere between a free morpheme and a bound morpheme is known as a suffixoidKremer, Marion. 1997. ''Person reference and gender in translation: a contrastive investigation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manikarnika Ghat
Manikarnika Ghat (Hindi: मणिकर्णिका घाट) is one of the holiest cremation grounds among the sacred riverfronts ( ghats), located on the banks of River Ganges, in the city of Varanasi in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. In Hinduism, death is considered a gateway to another life marked by the result of one's karma. It is believed that a human's soul attains moksha, and hence breaks the cycle of rebirth when cremated here. The ghat is named after Sati's earrings which fell there. The Hindu genealogy registers at Varanasi are kept there. Location The Manikarnika Ghat is located in Varanasi, India and is flanked by the Dashashwamedh Ghat and the Scindia Ghat Actual origin The Manikarnika Ghat is one of the oldest ghats in Varanasi. It is mentioned in a Gupta inscription of 5th century. It is revered in Hinduism. When Mata Sati (Adi Shakti) sacrificed her life and set her body ablaze after Raja Daksh Prajapati (one of the sons of Brahma) tried to hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (2October 186930January 1948) was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist, and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule. He inspired movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific ''Mahātmā'' (from Sanskrit, meaning great-souled, or venerable), first applied to him in South Africa in 1914, is now used throughout the world. Born and raised in a Hindu family in coastal Gujarat, Gandhi trained in the law at the Inner Temple in London and was called to the bar at the age of 22. After two uncertain years in India, where he was unable to start a successful law practice, Gandhi moved to South Africa in 1893 to represent an Indian merchant in a lawsuit. He went on to live in South Africa for 21 years. Here, Gandhi raised a family and first employed nonviolent resistance in a campaign for civil rights. In 1915, aged 45, he returned to In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography), right bank, Delhi shares borders with the state of Uttar Pradesh in the east and with the state of Haryana in the remaining directions. Delhi became a union territory on 1 November 1956 and the NCT in 1995. The NCT covers an area of . According to the 2011 census, Delhi's city proper population was over 11 million, while the NCT's population was about 16.8 million. The topography of the medieval fort Purana Qila on the banks of the river Yamuna matches the literary description of the citadel Indraprastha in the Sanskrit epic ''Mahabharata''; however, excavations in the area have revealed no signs of an ancient built environment. From the early 13th century until the mid-19th century, Delhi was the capital of two major empires, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raj Ghat
Raj Ghat is a memorial complex in Delhi, India. The first memorial was dedicated to Mahatma Gandhi where a black marble platform was raised to mark the spot of his cremation on 31 January 1948 and consists of an eternal flame at one end. Located on Delhi's Ring Road, a stone footpath leads to the walled enclosure that houses the memorial. Later the memorial complex was expanded to include memorials for other prominent Indian leaders including Charan Singh, Jawaharlal Nehru, Lal Bahadur Shastri, Indira Gandhi, Rajiv Gandhi, Chandra Shekhar and Atal Bihari Vajpayee. Etymology Raj Ghat loosely translates to ''Royal Steps'' with the word "royal" alluding to the importance of the place and "steps" referencing the climb from the banks of the Yamuna river. Location Raj Ghat was the name of a location of historic ghat in Shahjahanabad in Old Delhi on the west bank of the Yamuna River east of Daryaganj. List of memorials The first memorial was dedicated to Mahatma Gandhi on the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigambodh Ghat
Nigambodh Ghat is located on the banks of the Yamuna river coast in Delhi, situated on the Ring Road, Delhi at the back of the historic Red Fort. It consists of a series of bathing and ceremonial stepped piers leading to the waters of the river. It is most known for being the oldest burning ghat in Delhi for performing Antyesti ( Antim Sanskar), Hindu funeral rites and also one of its busiest with 50–60 pyres burning every day. It also has an electric crematorium built in the 1950s and a CNG-run crematorium was added by the Municipal corporation with manages the cremation facilities in 2006. Etymology It is believed that it was on this ghat during the Mahabharat era, that Lord Brahma, Hindu God of Creation, had bathed and recovered his lost memory and sacred books and hence the name Nigambodh Ghat, literally realisation of knowledge. Overview It is believed that the ghats were established by the eldest Pandava brother, Prince Yudhishthira, the king of Indraprastha. At pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shmashana
A shmashana outside an Indian village A shmashana () is a Hindu crematory ground, where dead bodies are brought to be burnt on a pyre. It is usually located near a river or body of water on the outskirts of a village or town; as they are usually located near river ghats, they are also regionally called ''smashan ghat''s. Etymology The word has its origin from Sanskrit language: ''shma'' refers to ''shava'' ("corpse"), while ''shana'' refers to ''shanya'' ("bed"). The other Indian religions like Sikhism, Jainism and Buddhism also use ''shmashana'' for the last rites of the dead. Hinduism As per Hindu rites of Nepal and India, the dead body is brought to shmashana for the ritual of '' antyesti'' (last rites). At the cremation ground, the chief mourner has to obtain the sacred fire from one who resides by the shmashana and light funeral pyres (''chita'') for a fee. Various Hindu scriptures also give details of how to select the site of shmashana: it should be on the norther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poonah - British Library X123(13)
Pune ( ; , ISO: ), previously spelled in English as Poona ( the official name until 1978), is a city in the state of Maharashtra in the Deccan plateau in Western India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Pune district, and of Pune division. In terms of the total amount of land under its jurisdiction, Pune is the largest city in Maharashtra, with a geographical area of 516.18 sq km, though by population it comes in a distant second to Mumbai. According to the 2011 Census of India, Pune has 7.2 million residents in the metropolitan region, making it the seventh-most populous metropolitan area in India. The city of Pune is part of Pune Metropolitan Region. Pune is one of the largest IT hubs in India. It is also one of the most important automobile and manufacturing hubs of India. Pune is often referred to as the "Oxford of the East" because of its educational institutions. It has been ranked "the most liveable city in India" several times. Pune at different point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |