|
Geology Of Namibia
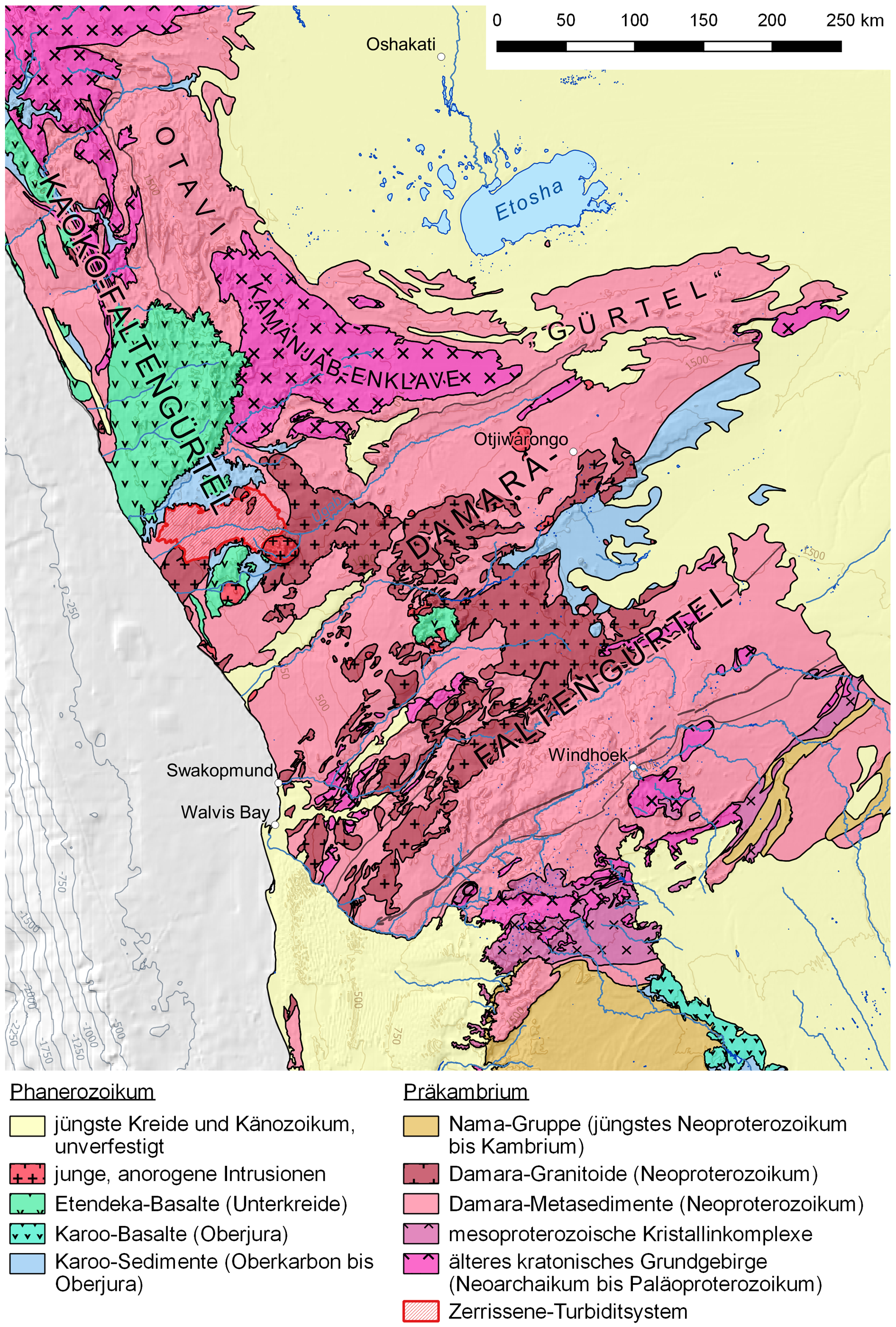
The geology of Namibia encompasses rocks of Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic to Cenozoic age. About 46% of the countryʼs surface are bedrock exposure, while the remainder is covered by the young overburden sediments of the Kalahari Desert, Kalahari and Namib Desert, Namib deserts. The country is famous for its mineral deposits of Tsumeb, as well as many geological sites of interest, from paleontology, paleontological, geomorphology, geomorphological and volcanism, volcanic character. Due to the exposure of the formations in a desert climate and the former German colony, the geology of Namibia is relatively well studied compared to the more tropical less exposed northern neighbors. Stratigraphy and tectonics Large areas of the Namibian geology exposed onshore are associated with the Late Proterozoic Pan-African orogeny, Pan-African orogenic cycle.Kukulus, 2004, p.10 The geology of Namibia is dominated in the north by metasediments of the Neo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country on the west coast of Southern Africa. Its borders include the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south; in the northeast, approximating a quadripoint, Zimbabwe lies less than 200 metres (660 feet) away along the Zambezi, Zambezi River near Kazungula, Zambia. Namibia's capital and largest city is Windhoek. Namibia is the driest country in sub-Saharan Africa, and has been inhabited since prehistoric times by the Khoekhoe, Khoi, San people, San, Damara people, Damara and Nama people. Around the 14th century, immigration, immigrating Bantu peoples arrived as part of the Bantu expansion. From 1600 the Ovambo people#History, Ovambo formed kingdoms, such as Ondonga and Oukwanyama. In 1884, the German Empire established rule over most of the territory, forming a colony known as German South West Africa. Between 1904 and 1908, German troops waged a punitive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epupa Complex
Epupa (Herero for "falling waters") may refer to: * Epupa Falls, waterfalls on the border between Angola and Namibia * Epupa Constituency, electoral constituency in north-western Namibia named after the falls * Epupa, Namibia, the settlement at Epupa Falls Epupa Falls (also known as Monte Negro Falls in Angola) is a series of large waterfalls formed by the Cunene River on the border of Angola and Namibia, in the Kaokoland area of the Kunene Region. The river is about wide in this area and drops in ... {{geodis Otjiherero words and phrases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outjo
Outjo (Otjiherero: ''small hills'') is a town of 15,000 inhabitants in the Kunene Region of Namibia. It is the district capital of Outjo Constituency. It is best known as the main gateway to Etosha National Park. Overview The town was founded by Germans under the command of Theodor Leutwein, Colonel Theodor von Leutwein in 1897 as a small military base in order to explore the northern area of German South West Africa. The local historical museum (Franke Haus Museum) details the campaign of Victor Franke, Major Viktor Franke in Ovamboland. The "Naulila monument" commemorates the small expedition on the Portuguese fort of Naulila in Angola by Major Viktor Franke in October 1914 following the massacre of a German delegation which had been sent to negotiate a treaty of non-aggression. It is one of the fastest developing towns in the Kunene Region. South of Outjo is the Ugab River, one of the major List of rivers of Namibia, rivers of Namibia. The town lies near Gamkarab Cave, know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphic Rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and form 12% of the Earth's land surface. They are classified by their protolith, their chemical and mineral makeup, and their texture. They may be formed simply by being deeply buried beneath the Earth's surface, where they are subject to high temperatures and the great pressure of the rock layers above. They can also form from tectonic processes such as continental collisions, which cause horizontal pressure, friction, and dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epupa Metamorphic Complex
Epupa (Herero for "falling waters") may refer to: * Epupa Falls, waterfalls on the border between Angola and Namibia * Epupa Constituency, electoral constituency in north-western Namibia named after the falls * Epupa, Namibia, the settlement at Epupa Falls Epupa Falls (also known as Monte Negro Falls in Angola) is a series of large waterfalls formed by the Cunene River on the border of Angola and Namibia, in the Kaokoland area of the Kunene Region. The river is about wide in this area and drops in ... {{geodis Otjiherero words and phrases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunene River
The Cunene (Portuguese spelling) or Kunene (common Namibian spelling) is a river in Southern Africa. It flows from the Angola highlands southwards to the border with Namibia. It then flows in a westerly direction along the border until it reaches the Atlantic Ocean. Geography One of the few Perennial stream, perennial rivers in the region, the Cunene is about long, with a drainage basin in area. Its mean annual Discharge (hydrology), discharge is to at its mouth. The Epupa Falls lie on the river. Olushandja Dam dams a tributary of the river, the Etaka, and helps to provide the Ruacana Power Station with water. The main stream rises in 12th parallel south, 12° 30′ S. and about 160 miles in a direct line from the sea at Benguela, Benguella, runs generally from north to south through four degrees of latitude, but finally flows west to the sea through a break in the outer Highland, highlands. Between the mouths of its two Tributary, tributaries, the Cunene traverses a swamp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basement (geology)
In geology, basement and crystalline basement are crystalline rocks lying above the mantle and beneath all other rocks and sediments. They are sometimes exposed at the surface, but often they are buried under miles of rock and sediment. The basement rocks lie below a sedimentary platform or cover, or more generally any rock below sedimentary rocks or sedimentary basins that are metamorphic or igneous in origin. In the same way, the sediments or sedimentary rocks on top of the basement can be called a "cover" or "sedimentary cover". Basement rock consists of continental crustal rock which has been modified several times through tectonic events including deformation, metamorphism, deposition, partial melting and magmatism. Continental crust Basement rock is the thick foundation of ancient, and oldest, metamorphic and igneous rock that forms the crust of continents, often in the form of granite. Basement rock is contrasted to overlying sedimentary rocks which are laid down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nama Group
The Nama Group is a megaregional Vendian to Cambrian group of stratigraphic sequences deposited in the Nama Basin, Nama foreland basin in central and southern Namibia. The Nama Basin is a peripheral foreland basin, and the Nama Group was deposited in two early basins, the Zaris and Witputs, to the north, while the South African Vanrhynsdorp Group was deposited in the southern third. The Nama Group is made of fluvial and shallow-water marine sediments, both siliciclastic and carbonate. La Tinta Group in Argentina is considered equivalent to Nama Group. Description The group extends from the Gariep Belt in the south to outcrops of pre-Damara orogeny, Damara basement (geology), basement in the north.Meert et al., 1997, p.639 Thrombolite-stromatolite reefs in the Nama Group are best developed in the Kuibis Subgroup of the Zaris subbasin, and in the Huns platform of the Witputs subbasin. The Nama Group is a series of interbedded shallow marine carbonates and siliciclastics deposited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |