|
Geology Of Estonia
The geology of Estonia is the study of rocks, minerals, water, landforms and geologic history in Estonia. The crust is part of the East European Craton and formed beginning in the Paleoproterozoic nearly two billion years ago. Shallow marine environments predominated in Estonia, producing extensive natural resources from organic matter such as oil shale and phosphorite. The Mesozoic and much of the Cenozoic are not well-preserved in the rock record, although the glaciations during the Pleistocene buried deep valleys in sediment, rechanneled streams and left a landscape of extensive lakes and peat bogs. Stratigraphy, tectonics and geologic history Estonia is part of the East European craton, East European Craton, with an average continental crust thickness between 40 and 64 kilometers. The crust consolidated during the Svecofennian orogeny, Svecofennian Orogeny in the late Paleoproterozoic, nearly two billion years ago. The contact between the crystalline basement and overlying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of the Paleozoic Era, and the third of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods ( myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of Fold (geology), fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest Bed (geology), beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex curve, convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that Strike and dip, dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various Stratum, rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. The progressing age of the rock strata towards the core and uplifted center, are the trademark indications for evidence of anticlines on a geological map. These formations occur because anticlinal ridges typically develop above thrust faults during crustal deformations. The uplifted core of the fold cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltica
Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains. The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, is more than three billion years old and formed part of the Rodinia supercontinent at 1 . Tectonic history Baltica formed at 2.0–1.7 Ga by the collision of three Archaean-Proterozoic continental blocks: Fennoscandia (including the exposed Baltic Shield), Sarmatia ( Ukrainian Shield and Voronezh Massif), and Volgo-Uralia (covered by younger deposits). Sarmatia and Volgo-Uralia formed a proto-craton (sometimes called "Proto-Baltica") at c. 2.0 Ga which collided with Fennoscandia c. 1.8–1.7 Ga. The sutures between these three blocks were reactivated during the Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic. Between 750 and 600 million years ago, Baltica and Laurentia rotated clockwise together and drifted away from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kukersite
Kukersite is a light-brown marine type oil shale of Ordovician age. It is found in the Baltic Oil Shale Basin in Estonia and North-West Russia. It is of the lowest Upper Ordovician formation, formed some 460 million years ago. It was named after the German name of the Kukruse Manor in the north-east of Estonia by the Russian paleobotanist Mikhail Zalessky in 1917. Some minor kukersite resources occur in sedimentary basins of Michigan, Illinois, Wisconsin, North Dakota, and Oklahoma in North America and in the Amadeus and Canning basins of Australia. Baltic Oil Shale Basin The Baltic Oil Shale Basin covers about . Main kukersite deposits are Estonian and Tapa deposits in Estonia, and Leningrad deposit in Russia (also known as Gdov or Oudova deposit). Other occurrences in Russia are Veimarn and Chudovo–Babinskoe deposits. The Estonian deposit, which covers about , is exploited industrially; the Tapa deposit is not accounted as reserves due its lower val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
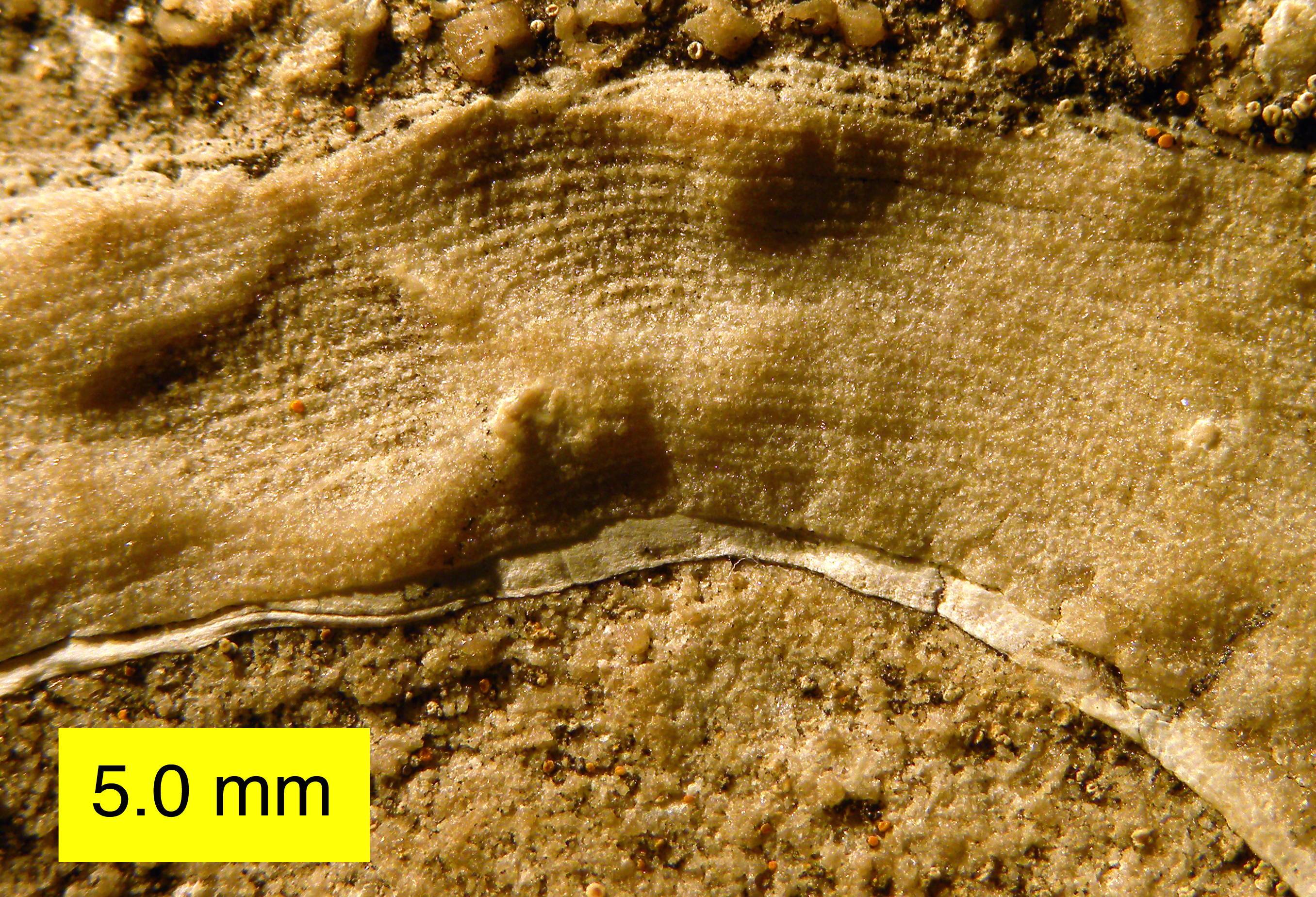
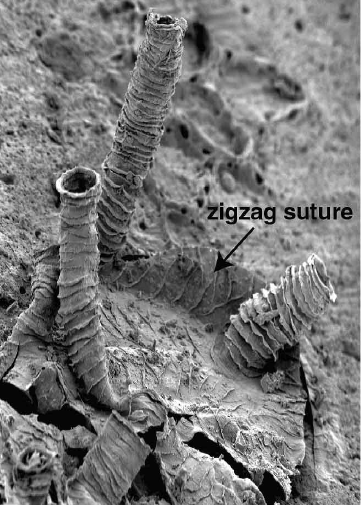
Stromatoporoid
Stromatoporoidea is an extinct clade of sea sponges common in the fossil record from the Middle Ordovician to the Late Devonian.Stock, C.W. 2001, Stromatoporoidea, 1926–2000: ''Journal of Paleontology'', v. 75, p. 1079–1089. They can be characterized by their densely layered calcite skeletons lacking spicules. Stromatoporoids were among the most abundant and important reef-builders of their time, living close together in flat biostromes or elevated bioherms on soft tropical carbonate platforms. Externally, some species have raised bumps (mamelons) and star-shaped crevices (astrorhizae), which together help vent exhalant water away from the living surface. Internally, stromatoporoids have a mesh-like skeletal system combining extensive horizontal layers (laminae), vertical rods (pillars), and boxy spaces (galleries), along with other features. The most common growth forms range from laminar (flattened) to domical (dome-shaped). Spheroidal, finger-like, or tree-like species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graptolite
Graptolites are a group of colonial animals, members of the subclass Graptolithina within the class Pterobranchia. These filter-feeding organisms are known chiefly from fossils found from the Middle Cambrian ( Miaolingian, Wuliuan) through the Lower Carboniferous ( Mississippian). A possible early graptolite, ''Chaunograptus'', is known from the Middle Cambrian. Recent analyses have favored the idea that the living pterobranch '' Rhabdopleura'' represents an extant graptolite which diverged from the rest of the group in the Cambrian. Fossil graptolites and ''Rhabdopleura'' share a colony structure of interconnected zooids housed in organic tubes (theca) which have a basic structure of stacked half-rings (fuselli). Most extinct graptolites belong to two major orders: the bush-like sessile Dendroidea and the planktonic, free-floating Graptoloidea. These orders most likely evolved from encrusting pterobranchs similar to ''Rhabdopleura''. Due to their widespread abundance, pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostracod
Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a Class (biology), class of the crustacean, Crustacea (class Ostracoda), sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 33,000 species (only 13,000 of which are extant taxon, extant) have been identified,Brandão, S.N.; Antonietto, L.S; Nery, D.G.; Santos, S.G.; Karanovic, I. (2023). World Ostracoda Database. Accessed at https://www.marinespecies.org/ostracoda on 2023-09-12. grouped into 7 valid orders. They are small crustaceans, typically around in size, but varying from , the latter in the case of the marine ''Gigantocypris.'' The largest known freshwater species is ''Megalocypris princeps'', which reach 8 mm in length. In most cases, their bodies are flattened from side to side and protected by a bivalve-like valve or "shell" made of chitin, and often calcium carbonate. The family Entocytheridae and many planktonic forms do not have calcium carbonate. The hinge of the two valves is in the upper (dorsal) region of the body. Ostracods are grouped toget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three-lobed entities") are extinction, extinct marine arthropods that form the class (biology), class Trilobita. One of the earliest groups of arthropods to appear in the fossil record, trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270million years, with over 22,000 species having been described. Because trilobites had wide diversity and an easily fossilized mineralised exoskeleton made of calcite, they left an extensive fossil record. The study of their fossils has facilitated important contributions to biostratigraphy, paleontology, evolution, evolutionary biology, and plate tectonics. Trilobites are placed within the clade Artiopoda, which includes many organisms that are morphologically similar to trilobites, but are largely unmineralised. The relationship of Artiopoda to other arthropods is uncertain. Trilobites evolved into many ecological niches; some moved over the seabed as predators, scavengers, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiopod
Brachiopods (), phylum (biology), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major categories are traditionally recognized, articulate and inarticulate brachiopods. The word "articulate" is used to describe the tooth-and-groove structures of the valve-hinge which is present in the articulate group, and absent from the inarticulate group. This is the leading diagnostic skeletal feature, by which the two main groups can be readily distinguished as fossils. Articulate brachiopods have toothed hinges and simple, vertically oriented opening and closing muscles. Conversely, inarticulate brachiopods have weak, untoothed hinges and a more complex system of vertical and oblique (diagonal) muscles used to keep the two valves aligned. In many brachio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caledonian Orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building cycle recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Caledonides, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly 490–390 million years ago ( Ma). It was caused by the closure of the Iapetus Ocean when the Laurentia and Baltica continents and the Avalonia microcontinent collided. The orogeny is named for Caledonia, the Latin name for Scotland. The term was first used in 1885 by Austrian geologist Eduard Suess for an episode of mountain building in northern Europe that predated the Devonian period. Geologists like Émile Haug and Hans Stille saw the Caledonian event as one of several episodic phases of mountain building that had occurred during Earth's history.McKerrow ''et al.'' (2002) Current understanding has it that the Caledonian orogeny encompasses a number of tectonic phases th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |