|
Geology Of California
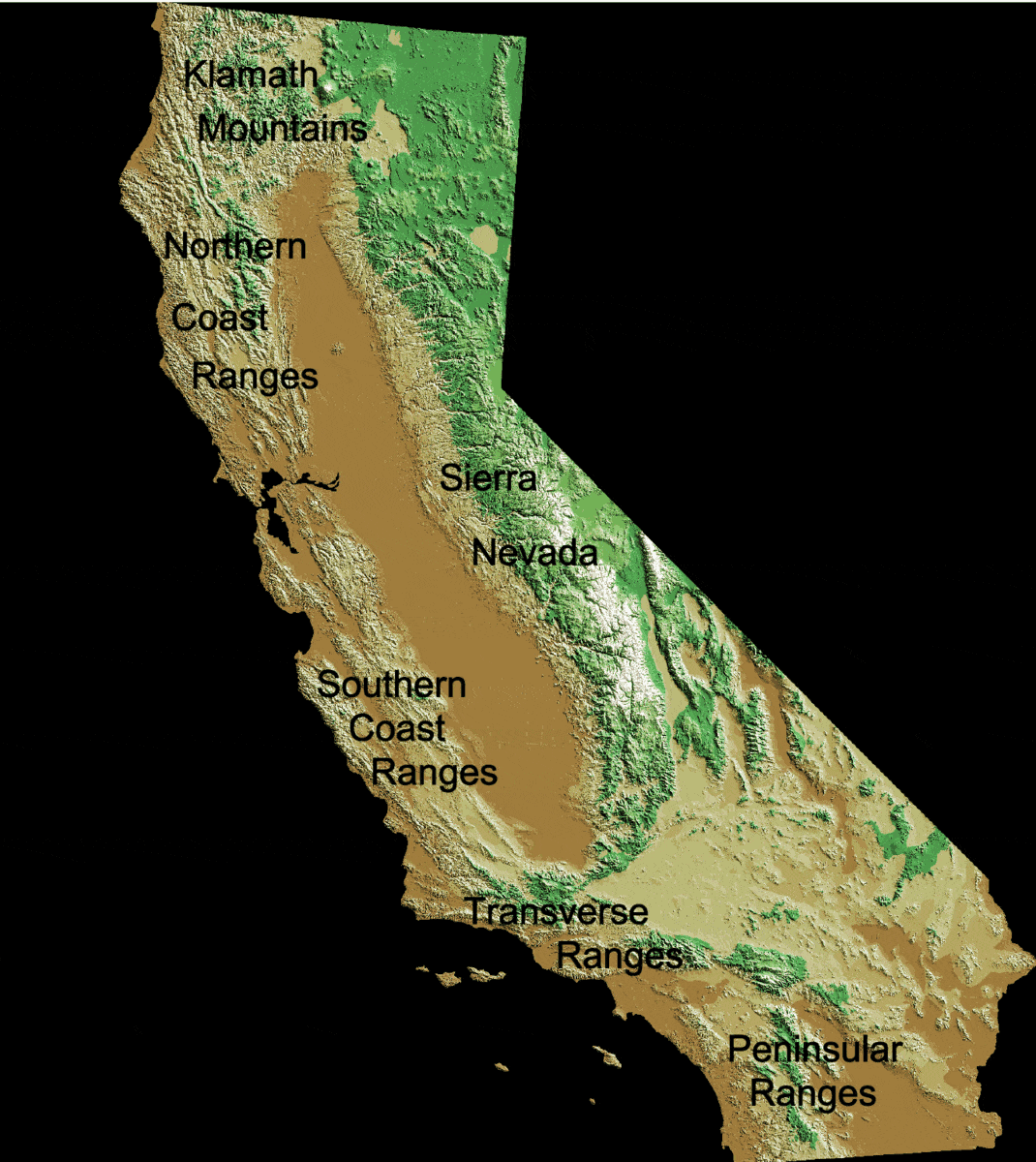
The geology of California is highly complex, with numerous mountain ranges, substantial faulting and tectonic activity, rich natural resources and a history of both ancient and comparatively recent intense geological activity. The area formed as a series of small island arcs, deep-ocean sediments and mafic oceanic crust accreted to the western edge of North America, producing a series of deep basins and high mountain ranges. One of the most important events was the advent of the San Andreas Fault around 29 million years ago in the Oligocene, when the region subducted a spreading center in the East Pacific Rise. This produced major crustal stretching, volcanism and displacement of up to . Geological history The oldest rocks in California date back 1.8 billion years to the Proterozoic and are found in the San Gabriel Mountains, San Bernardino Mountains, and Mojave Desert. The rocks of eastern California formed a shallow continental shelf, with massive deposition of limestone dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Coast Ranges
The Coast Ranges of California span from Del Norte County, California, Del Norte or Humboldt County, California, south to Santa Barbara County, California, Santa Barbara County. The other three coastal California mountain ranges are the Transverse Ranges, Peninsular Ranges and the Klamath Mountains. Physiographically, they are a section of the larger Pacific Border province, which in turn is part of the larger Geography of the United States Pacific Mountain System, Pacific Mountain System physiographic division. UNESCO has included the "California Coast Ranges Biosphere Reserve" in its Man and the Biosphere Programme of World Network of Biosphere Reserves since 1983. * Physiography The northern end of the California Coast Ranges overlap the southern end of the Klamath Mountains for approximately on the west. They extend southward for more than to where the coastline turns eastward along the Santa Barbara Channel, around the area of Point Conception. Here the southern end m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. The Cenozoic started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians ( placentals) in the Northern Hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia and to some extent South America) in the Southern Hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so that large m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the second and middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era as well as the eighth period of the Phanerozoic, Phanerozoic Eon and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP). The beginning of the Toarcian Age started around 183 million years ago and is marked by the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event, a global episode of Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated global temperatures associated with extinctions, likely caused by the eruption of the Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevadan Orogeny
The Nevadan orogeny occurred along the western margin of North America during the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous approximately 155 Ma to 145 Ma. Throughout the duration of this orogeny there were at least two different kinds of orogenic processes occurring. During the early stages of orogenesis an "Andean type" continental magmatic arc developed due to subduction of the Farallon oceanic plate beneath the North American Plate. The latter stages of orogenesis, in contrast, saw multiple oceanic arc terranes accreted onto the western margin of North America in a "Cordilleran type" accretionary orogen. Deformation related to the accretion of these volcanic arc terranes is mostly limited to the western regions of the resulting mountain ranges ( Klamath Mountain range and Sierra Nevada) and is absent from the eastern regions. In addition, the deformation experienced in these mountain ranges is mostly due to the Nevadan orogeny and not other external events such as the more recent Sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dike (geology), dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF diagram, QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles such as the dinosaurs, and of Gymnosperm, gymnosperms such as cycads, ginkgoaceae and Araucariaceae, araucarian conifers; a hot Greenhouse and icehouse earth, greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era and the seventh period of the Phanerozoic Eon. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the other and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with rates of convergence as high as 11 cm/year. Subduction is possible because the cold and rigid oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the dense subducting lithosphere. The down-going slab sinks into the mantle largely under its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Range
The Transverse Ranges are a group of mountain ranges of Southern California, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region in North America. The Transverse Ranges begin at the southern end of the California Coast Ranges and lie within Santa Barbara, Ventura, Los Angeles, San Bernardino, Riverside and Kern counties. The Peninsular Ranges lie to the south. The name is due to the ranges' east–west orientation, making them transverse to the general northwest–southeast orientation of most of California's coastal mountains.Dibblee Jr, T.W., 1982. Regional geology of the Transverse Ranges Province of southern California. ''Geology and mineral wealth of the California Transverse Ranges'', ''10'', pp.7-26. The ranges extend from west of Point Conception eastward approximately 500 kilometers into the Mojave and Colorado Desert. The geology and topography of the ranges express three distinct segments that have contrasting elevations, rock types, and vegetation. The western segment ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |