|
Geodesy
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the Figure of the Earth, geometry, Gravity of Earth, gravity, and Earth's rotation, spatial orientation of the Earth in Relative change, temporally varying Three-dimensional space, 3D. It is called planetary geodesy when studying other astronomical body, astronomical bodies, such as planets or Natural satellite, circumplanetary systems. Geodynamics, Geodynamical phenomena, including crust (geology), crustal motion, tides, and polar motion, can be studied by designing global and national Geodetic control network, control networks, applying space geodesy and terrestrial geodetic techniques, and relying on Geodetic datum, datums and coordinate systems. Geodetic job titles include geodesist and geodetic surveyor. History Geodesy began in pre-scientific Classical antiquity, antiquity, so the very word geodesy comes from the Ancient Greek word or ''geodaisia'' (literally, "division of Earth"). Early ideas about t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
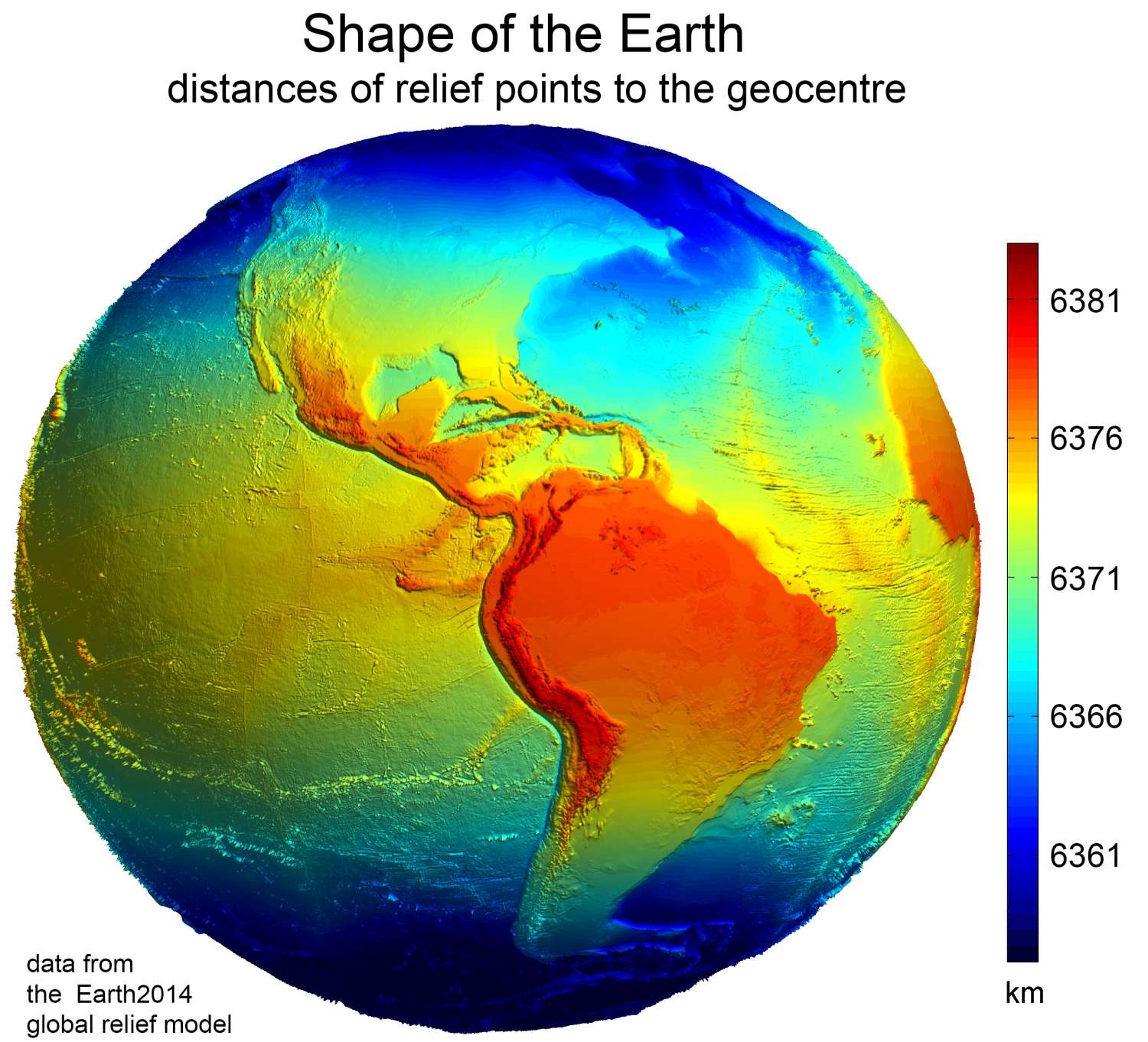
Figure Of The Earth
In geodesy, the figure of the Earth is the size and shape used to model planet Earth. The kind of figure depends on application, including the precision needed for the model. A spherical Earth is a well-known historical approximation that is satisfactory for geography, astronomy and many other purposes. Several models with greater accuracy (including ellipsoid) have been developed so that coordinate systems can serve the precise needs of navigation, surveying, cadastre, land use, and various other concerns. Motivation Earth's topographic surface is apparent with its variety of land forms and water areas. This topographic surface is generally the concern of topographers, hydrographers, and geophysicists. While it is the surface on which Earth measurements are made, mathematically modeling it while taking the irregularities into account would be extremely complicated. The Pythagorean concept of a spherical Earth offers a simple surface that is easy to deal with mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomatics
Geomatics is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as the "discipline concerned with the collection, distribution, storage, analysis, processing, presentation of geographic data or geographic information". Under another definition, it consists of products, services and tools involved in the collection, integration and management of geographic (geospatial) data. Surveying engineering was the widely used name for geomatic(s) engineering in the past. Geomatics was placed by the UNESCO Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems under the branch of technical geography. History and etymology The term was proposed in French ("géomatique") at the end of the 1960s by scientist Bernard Dubuisson to reflect at the time recent changes in the jobs of surveyor and photogrammetrist. The term was first employed in a French Ministry of Public Works memorandum dated 1 June 1971 instituting a "standing committee of geomatics" in the government. The term was popularised in English by Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Of Earth
The gravity of Earth, denoted by , is the net force, net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation (from mass distribution within Earth) and the centrifugal force (from the Earth's rotation). It is a Euclidean vector, vector quantity, whose direction coincides with a plumb bob and strength or magnitude is given by the Euclidean norm, norm g=\, \mathit\, . In International System of Units, SI units, this acceleration is expressed in metre per second squared, metres per second squared (in symbols, metre, m/second, s2 or m·s−2) or equivalently in Newton (unit), newtons per kilogram (N/kg or N·kg−1). Near Earth's surface, the acceleration due to gravity, accurate to 2 significant figures, is . This means that, ignoring the effects of drag (physics), air resistance, the speed of an object free fall, falling freely will increase by about every second. The precise strength of Earth's gravity varies with location. The agreed-upon value for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Rotation
Earth's rotation or Earth's spin is the rotation of planet Earth around its own Rotation around a fixed axis, axis, as well as changes in the orientation (geometry), orientation of the rotation axis in space. Earth rotates eastward, in prograde motion. As viewed from the northern polar star Polaris, Earth turns counterclockwise. The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. This point is distinct from Earth's north magnetic pole. The South Pole is the other point where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface, in Antarctica. Earth rotates once in about 24 hours with respect to the Sun, but once every 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4 seconds with respect to other distant stars (#Stellar and sidereal day, see below). Earth's rotation is slowing slightly with time; thus, a day was shorter in the past. This is due to the tidal acceleration, tidal effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Geodesy
{{Space-stub ...
Space geodesy is geodesy by means of sources external to Earth, mainly artificial satellites (in satellite geodesy) but also quasars (in very-long-baseline interferometry, VLBI), visible stars (in stellar triangulation), and the retroreflectors on the Moon (in lunar laser ranging, LLR). See also * Astronomical geodesy Geodesy Geodesy Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the Figure of the Earth, geometry, Gravity of Earth, gravity, and Earth's rotation, spatial orientation of the Earth in Relative change, temporally varying Three-dimensional spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Motion
Polar motion of the Earth is the motion of the Earth's rotation, Earth's rotational axis relative to its Earth's crust, crust. This is measured with respect to a reference frame in which the solid Earth is fixed (a so-called ''Earth-centered, Earth-fixed'' or ECEF reference frame). This variation is a few meters on the surface of the Earth. Analysis Polar motion is defined relative to a conventionally defined reference axis, the CIO (Conventional International Origin), being the pole's average location over the year 1900. It consists of three major components: a free oscillation called Chandler wobble with a period of about 435 days, an annual oscillation, and an irregular drift in the direction of the 80th Meridian (geography), meridian west, which has lately been less extremely west. Causes The slow drift, about 20 m since 1900, is partly due to motions in the Earth's core and mantle, and partly to the redistribution of water mass as the Greenland ice sheet melts, and to iso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodetic Datum
A geodetic datum or geodetic system (also: geodetic reference datum, geodetic reference system, or geodetic reference frame, or terrestrial reference frame) is a global datum reference or reference frame for unambiguously representing the position of locations on Earth by means of either geodetic coordinates (and related vertical coordinates) or geocentric coordinates. DatumsThe plural is not "data" in this case are crucial to any technology or technique based on spatial location, including geodesy, navigation, surveying, geographic information systems, remote sensing, and cartography. A horizontal datum is used to measure a horizontal position, across the Earth's surface, in latitude and longitude or another related coordinate system. A ''vertical datum'' is used to measure the elevation or depth relative to a standard origin, such as mean sea level (MSL). A three-dimensional datum enables the expression of both horizontal and vertical position components in a unified form. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodynamics
Geodynamics is a subfield of geophysics dealing with dynamics of the Earth. It applies physics, chemistry and mathematics to the understanding of how mantle convection leads to plate tectonics and geologic phenomena such as seafloor spreading, mountain building, volcanoes, earthquakes, faulting. It also attempts to probe the internal activity by measuring magnetic fields, gravity, and seismic waves, as well as the mineralogy of rocks and their isotopic composition. Methods of geodynamics are also applied to exploration of other planets. Overview Geodynamics is generally concerned with processes that move materials throughout the Earth. In the Earth's interior, movement happens when rocks melt or deform and flow in response to a stress field.Turcotte, D. L. and G. Schubert (2014). "Geodynamics." This deformation may be brittle, elastic, or plastic, depending on the magnitude of the stress and the material's physical properties, especially the stress relaxation time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geospatial Information
Geographic data and information is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as data and information having an implicit or explicit association with a location relative to Earth (a geographic location or geographic position). It is also called geospatial data and information, georeferenced data and information, as well as geodata and geoinformation. Location information (known by the many names mentioned here) is stored in a geographic information system (GIS). There are also many different types of geodata, including vector files, raster files, geographic databases, web files, and multi-temporal data. Spatial data or spatial information is broader class of data whose geometry is relevant but it is not necessarily georeferenced, such as in computer-aided design (CAD), see geometric modeling. Fields of study Geographic data and information are the subject of a number of overlapping fields of study, mainly: * Geocomputation * Geographic information science ** Geogra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodetic Control Network
A geodetic control network is a network, often of triangles, that are measured precisely by techniques of ''control surveying'', such as terrestrial surveying or satellite geodesy. It is also known as a geodetic network, reference network, control point network, or simply control network. A geodetic control network consists of stable, identifiable points with published datum values derived from observations that tie the points together. Classically, a control is divided into horizontal (X-Y) and vertical (Z) controls (components of the control), however with the advent of satellite navigation systems, GPS in particular, this division is becoming obsolete. In the U.S., there is a national control network called the National Spatial Reference System (NSRS). Many organizations contribute information to the geodetic control network. The higher-order (high precision, usually millimeter-to-decimeter on a scale of continents) control points are normally defined in both space and time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |