|
Gates Of The Arctic National Park And Preserve
Gates of the Arctic National Park and Preserve is a national park of the United States that protects portions of the Brooks Range in northern Alaska. The park is the northernmost national park in the United States, situated entirely north of the Arctic Circle. The area of the park and preserve is the second largest in the U.S. at ; the National Park portion is the second largest in the U.S., after the National Park portion of Wrangell–St. Elias National Park and Preserve. Gates of the Arctic was initially designated as a national monument on December 1, 1978, before being redesignated as a national park and preserve upon passage of the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act in 1980. About 85% of the park has additional protection as the Gates of the Arctic Wilderness which covers . The wilderness area adjoins the Noatak Wilderness. Together, they form the largest contiguous wilderness in the United States. Park purpose According to the National Park website: Activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bettles, Alaska
Bettles ( in Koyukon; ''Atchiiniq'' in Iñupiaq) is a city in Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area, Alaska, United States. It is near Gates of the Arctic National Park and Preserve. The population was 23 at the 2020 census, up from 12 in 2010. It is the second smallest incorporated city in the state. History The original village was founded a mile southwest of the junction of the John & Koyukuk Rivers in the late 1890s during the Alaska Gold Rush and was named for Gordon C. Bettles, a newspaper man, Montana Silver prospector, and trader who established the trading post and community in 1898. A post office was established in 1901 and continued intermittently until 1956. Residents began relocating east to Evansville, where the airstrip that serves the community today was built in World War II and is now used for commercial air service. The Hickel Highway was used to transport equipment and supplies to the North Slope for oil exploration, and to build the Dalton Highway, which is now us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairbanks, Alaska
Fairbanks is a Municipal home rule, home rule city and the county seat, borough seat of the Fairbanks North Star Borough, Alaska, United States. Fairbanks is the largest city in the Interior Alaska, interior region of Alaska and the second largest in the state. The 2020 United States census, 2020 census put the population of the city proper at 32,515 and the population of the Fairbanks North Star Borough at 95,655, making it the second most populous metropolitan area in Alaska, after Anchorage, Alaska, Anchorage. The Metropolitan Statistical Area encompasses all of the Fairbanks North Star Borough and is the northernmost metropolitan statistical area in the United States, located by road ( by air) south of the Arctic Circle. In August 1901, E. T. Barnette founded a trading post on the south bank of the Chena River. A gold discovery near the trading post sparked the Fairbanks Gold Rush, and many miners moved to the area. There was a boom in construction, and in November 190 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hughes, Alaska
Hughes ( in Koyukon) is a city in Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area, Alaska, United States. The population was 85 at the 2020 census, up from 77 in 2010. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , all of it land. Demographics Hughes first appeared on the 1920 U.S. Census as an unincorporated village. It did not appear on the 1930 census, but returned in 1940. It formally incorporated in 1973. The majority of the town's population are ethnic Koyukon, Alaskan Athabaskans. Some of the town's population, as of the 1970s, spoke the Central Dialect of the Koyukon language. As of the census of 2020, there were 85 people, 36 households, and 11 families residing in the city. The population density was . There were 47 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the city was 5.88% White, 89.41% Native American, and 4.7% from two or more races. 1.18% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. There were 36 households ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evansville, Alaska
Evansville is a census-designated place (CDP) in Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area, Alaska, United States. The population was 15 at the 2010 census, down from 28 in 2000. The community is adjacent to Bettles. The community is named after Wilford Evans, Sr, who took part in the founding of Bettles Lodge. Geography Evansville is located on the southeast bank of the Koyukuk River at (66.902950, -151.499190). The community is on the former Hickel Highway, that now connects to the Dalton Highway as a winter ice road only and crosses the Jim River. Evansville is north of the Arctic Circle, just south of the Brooks Range, home of the Gates of the Arctic National Park and Preserve. According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of , of which, of it is land and of it (0.85%) is water. Climate As with much of Interior Alaska, Evansville experiences a subarctic climate (Köppen ''Dfc'') with very long, frigid winters and short, warm summers, and is located in USD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaktuvuk Pass, Alaska
Anaktuvuk Pass (, , or , ) is a city in North Slope Borough, Alaska, United States. The population was 282 at the 2000 census and 324 as of the 2010 census. History Anaktuvuk Pass was named after the Anaktuvuk River. ''Anaktuvuk'' is the English way of spelling "anaqtuġvik", ''place of caribou droppings'' in Inupiaq, the language of the Inupiat. A nomadic group of Inupiat called ''Nunamiut'' lived inland in northern Alaska, hunting caribou instead of the marine mammals and fish hunted by the rest of the Inupiat, who live on the coast. The Nunamiut traded with the coastal people for other items they needed. A decline in caribou populations around 1900 and in the 1920s caused many Nunamiut to move to the coast. In 1938, several Nunamiut families moved back to the Brooks Range, around Tulugak and the Killik River. In 1949 the Killik River group moved to Tulugak Lake, 15 miles north of where the village lies today. Anaktuvuk Pass is the only Nunamiut settlement. This se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambler, Alaska
Ambler (, ) is a city in Northwest Arctic Borough, Alaska, United States. At the 2010 census the population was 258, down from 309 in 2000. The city is located in the large Iñupiaq language speaking region of Alaska, and the local dialect is known as the Ambler dialect (related to the Shugnak dialect). , over 91% of the community speaks and understands the language (Kraus, 1999), with many young children actively learning the language in school. It has important relationships with the "hub" city of Kotzebue, Alaska and has important relationships with Maniilaq Health Association. Geography Ambler is located at , on the north bank of the Kobuk River, near the confluence of the Ambler and the Kobuk Rivers. It lies 45 miles north of the Arctic Circle. It is 138 miles northeast of Kotzebue, 30 miles northwest of Kobuk and 30 miles downriver from Shungnak. Ambler is located in the Kotzebue Recording District. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allakaket, Alaska
Allakaket ( ) (''Aalaa Kkaakk’et'' in Koyukon) is a second class city in the Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area of the Unorganized Borough of the U.S. state of Alaska. The population wa177at the 2020 census. History and culture Several Native groups have lived in the area, including Koyukon Athabascans and Kobuk, Selawik, and Nunamiut Eskimos from the north and northwest. The Koyukon lived in several camps throughout the year, moving as the seasons changed, following the wild game and fish. The various bands established joint settlements after 1851. The old site of Alatna was a traditional trading center for Athabascans and Eskimos. The first mission on the Koyukuk River, St. John's-in-the-Wilderness Episcopal Mission, was established in 1906. A post office was opened in 1925. In 1938, the name of the community was changed to Allakaket (the old name for the mission), and the name Alatna was assumed by the small Eskimo community across the river. The first public school was establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alatna, Alaska
Alatna (''Alaasuq'' in Iñupiaq ) is a census-designated place (CDP) in the Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area of the Unorganized Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. The population was fifteen at the time of the 2020 census. Geography Alatna is at (66.548906, -152.844806) (Sec. 33, T021N, R024W, Fairbanks Meridian) in the Fairbanks Recording District. Alatna is on the north bank of the Koyukuk River, southwest of its junction with the Alatna River, approximately northwest of Fairbanks and upriver from Hughes. Alatna lies just west of the municipal boundaries of the city of Allakaket. The area experiences a cold, continental climate with extreme temperature differences. The average high temperature during July is 70 °F (21 °C). The average low during January is well below 0 °F (-18 °C), and extended periods of -40 °F/C are common. The highest temperature ever recorded was 94 °F (34 °C); the lowest, -75 °F (-59 °C). Average an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
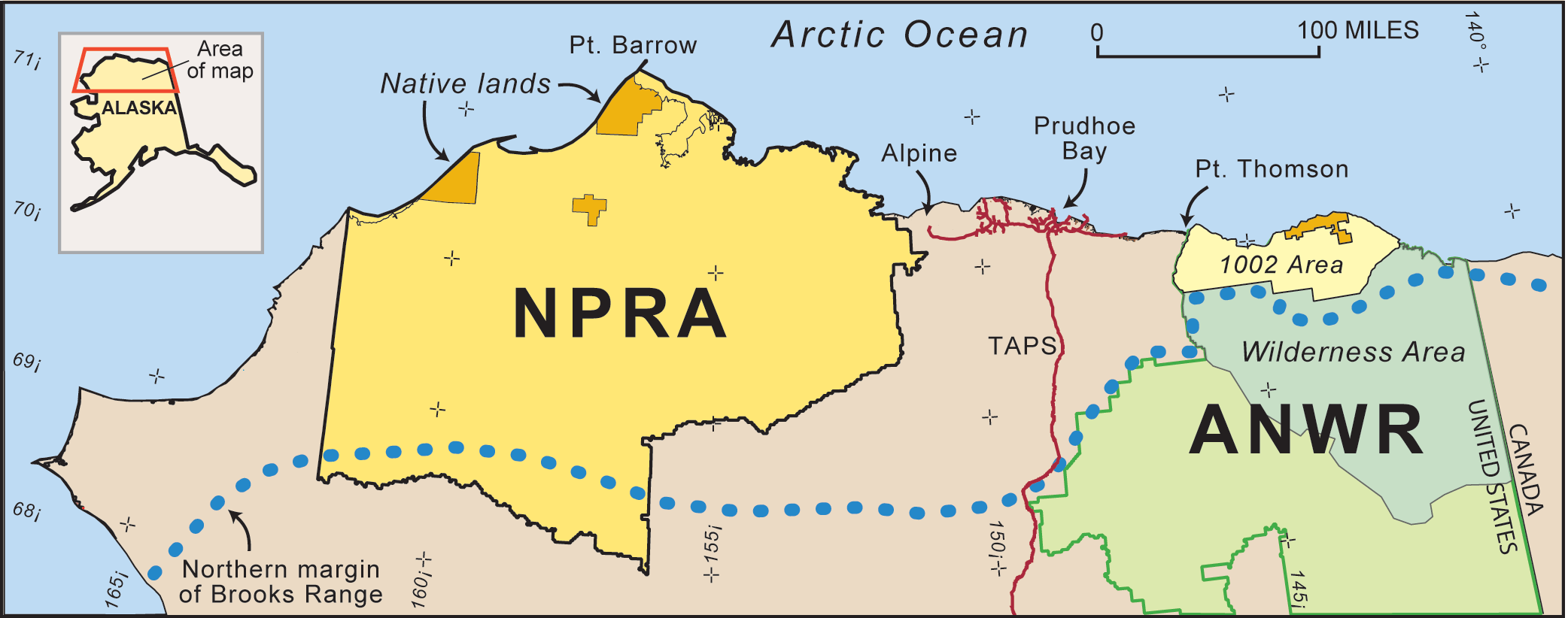
National Petroleum Reserve–Alaska
The National Petroleum Reserve in Alaska (NPRA) is an area of land on the Alaska North Slope owned by the United States federal government and managed by the Department of the Interior, Bureau of Land Management (BLM). It lies to the west of the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, which, as a U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service managed National Wildlife Refuge, is also federal land. At a size of , the NPRA is the largest tract of undisturbed public land in the United States. Iñupiat live in several villages around its perimeter, the largest of which is Utqiaġvik, the seat of the North Slope Borough. Due to the proximity of Inuit communities, drilling on the NPRA has sparked controversy revolving around the economic, ecological, and cultural importance of the land. The NPRA is an ecologically very important area for arctic wildlife; For birds, it has been called "Heathrow at the top of the world". Ecological importance The NPRA is an ecologically very important area, and human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noatak National Preserve
Noatak National Preserve is a United States National Preserve in northwestern Alaska that was established to protect the Noatak River Basin. The Noatak River system, located just north of the Arctic Circle, is thought to be the last remaining complete river system in the United States that has not been altered by human activities. The roadless basin was proclaimed a United States National Monument in 1978 and a National Preserve in 1980 through the passage of the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act (ANILCA). Noatak National Preserve borders Kobuk Valley National Park on the south and Gates of the Arctic National Park on the east. Unlike the national parks that it borders, sport hunting is allowed in Noatak National Preserve. All of the preserve, except for about east of the village of Noatak, has been designated the Noatak Wilderness. The wilderness is the fourth-largest in the United States, following the Wrangell-Saint Elias Wilderness, the Mollie Beattie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanuti National Wildlife Refuge
Kanuti National Wildlife Refuge is a national wildlife refuge in central Alaska, United States. One of 16 refuges in Alaska, it was established in 1980 when Congress passed The Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act (ANILCA). At , Kanuti Refuge is about the size of the state of Delaware. Located at the Arctic Circle, the refuge is a prime example of Alaska's boreal ecosystem. It is dominated by black and white spruce, with some white birch and poplars. Description and species The region's short, hot summers are marked by numerous thunderstorms and lightning strikes, leading to a continuous cycle of burn and recovery. Natural wildfires create diverse habitats with the different plant species supporting a variety of wildlife. The refuge's boreal forest is home to 37 species of mammals, including two species of fox, Canadian lynx, brown and black bear species, wolf packs, moose, mink, coyote, muskrat, beaver, marten, river otter, muskoxen, and wolverine. Caribou from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic National Wildlife Refuge
The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge (ANWR, pronounced as “''ANN-warr''”) or Arctic Refuge is a national wildlife refuge in northeastern Alaska, United States, on traditional Inupiaq, Iñupiaq and Gwichʼin, Gwich'in lands. The refuge is of the Alaska North Slope region, with a northern coastline and vast inland forest, taiga, and tundra regions. ANWR is the largest national wildlife refuge in the country, slightly larger than the Yukon Delta National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is administered from offices in Fairbanks, Alaska, Fairbanks. ANWR is home to a diverse range of endemism, endemic mammal species; notably, it is one of the few North American locations with all three endemic American bears—the polar bear, grizzly bear, and American black bear, each of which resides predominantly in its own ecological niche. Besides the bears, other mammal species include the moose, Reindeer, caribou, Grey wolf, wolves, red fox, red and Arctic fox, Canada lynx, wolverine, pine marte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |