|
Fluoroarenes
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide (also known as a haloarene) is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide ion (such as fluorine F''−'', chlorine Cl−1,−3,−5, bromine Br−1, or iodine I−). Aryl halides are distinct from haloalkanes (alkyl halides) due to significant differences in their methods of preparation, chemical reactivity, and physical properties. The most common and important members of this class are aryl chlorides, but the group encompasses a wide range of derivatives with diverse applications in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. Classification according to halide Aryl fluorides Aryl fluorides are used as synthetic intermediates, e.g. for the preparation of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and liquid crystals. The conversion of diazonium salts is a well established route to aryl fluorides. Thus, anilines are precursors to aryl fluorides. In the classic Schiemann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halex Process
In chemistry, the Halex process is used to convert aromatic chlorides to the corresponding aromatic fluorides. The process entails ''Hal''ide ''ex''change, hence the name. The reaction conditions call for hot (150-250 °C) solution of the aryl chloride and anhydrous potassium fluoride. Typical solvents are dimethylsulfoxide, dimethylformamide, and sulfolane. Potassium chloride is generated in the process. The reaction is mainly applied to nitro-substituted aryl chlorides. Sometimes more soluble fluorides, such as caesium fluoride and TBAF are used. The following reactions are practiced commercially in this manner:{{Ullmann, first1=Günter , last1=Siegemund, first2=Werner, last2=Schwertfeger, first3=Andrew, last3=Feiring, first4=Bruce, last4=Smart, first5=Fred, last5=Behr, first6=Herward, last6=Vogel, first7=Blaine , last7=McKusick, title=Fluorine Compounds, Organic, year=2002, doi=10.1002/14356007.a11_349. :2-Nitrochlorobenzene, 2-nitrochlorobenzene → 2-Fluoronitrobenzen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toluene
Toluene (), also known as toluol (), is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula , often abbreviated as , where Ph stands for the phenyl group. It is a colorless, water Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...-insoluble liquid with the odor associated with paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, consisting of a methyl group (CH3) attached to a phenyl group by a single bond. As such, its systematic IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry, IUPAC name is methylbenzene. Toluene is predominantly used as an industrial feedstock and a solvent. As the solvent in some types of paint thinner, permanent markers, contact cement and certain types of glue, toluene is sometimes used as a recreational inhalant and has the potential of causin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Contrast Agent
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography ( contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iodine, or more rarely barium sulfate. The contrast agents absorb external X-rays, resulting in decreased exposure on the X-ray detector. This is different from radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine which emit radiation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) functions through different principles and thus MRI contrast agents have a different mode of action. These compounds work by altering the magnetic properties of nearby hydrogen nuclei. Types and uses Radiocontrast agents used in X-ray examinations can be grouped in positive (iodinated agents, barium sulfate), and negative agents (air, carbon dioxide, methylcellulose). Iodine (circulatory system) Iodinated contrast contains iodine. It is the main type of radiocontrast used for int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazonium Compound
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide. The parent, compound where R is hydrogen, is diazenylium. Structure and general properties Arene derivatives According to X-ray crystallography the linkage is linear in typical diazonium salts. The bond distance in benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate is 1.083(3) Angstrom, Å, which is almost identical to that for dinitrogen molecule (N≡N). The linear free energy constants σm and σp indicate that the diazonium group is strongly electron-withdrawing. Thus, the diazonio-substituted phenols and benzoic acids have greatly reduced p''K''a values compared to their unsubstituted counterparts. The p''K''a of phenolic proton of 4-hydroxybenzenediazonium is 3.4, versus 9.9 for phenol itself. In other words, the diazonium group raises the ionization constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phthalic Anhydride
Phthalic anhydride is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is the anhydride of phthalic acid. Phthalic anhydride is a principal commercial form of phthalic acid. It was the first anhydride of a dicarboxylic acid to be used commercially. This white solid is an important industrial chemical, especially for the large-scale production of plasticizers for plastics. In 2000, the worldwide production volume was estimated to be about 3 million tonnes per year. Synthesis and production Phthalic anhydride was first reported in 1836 by Auguste Laurent. Early procedures involved liquid-phase mercury-catalyzed oxidation of naphthalene. The modern industrial variant process instead uses vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) as the catalyst in a gas-phase reaction with naphthalene using molecular oxygen. The overall process involves oxidative cleavage of one of the rings and loss of two of the carbon atoms as carbon dioxide. An alternative process involves oxidation of the two m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns. It is acutely toxic and is considered a health hazard. Phenol was first extracted from coal tar, but today is produced on a large scale (about 7 million tonnes a year) from petroleum-derived feedstocks. It is an important industrial commodity as a precursor to many materials and useful compounds, and is a liquid when manufactured. It is primarily used to synthesize plastics and related materials. Phenol and its chemical derivatives are essential for production of polycarbonates, epoxies, explosives such as picric acid, Bakelite, nylon, detergents, herbicides such as phenoxy herbicides, and numerous pharmaceuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flame Retardant
Flame retardants are a diverse group of chemicals that are added to manufactured materials, such as plastics and textiles, and surface finishes and coatings. Flame retardants are activated by the presence of an combustion, ignition source and prevent or slow the further development of flames by a variety of different physical and chemical mechanisms. They may be added as a copolymer during the polymerisation process, or later added to the polymer at a moulding or extrusion process or (particularly for textiles) applied as a topical finish. Mineral flame retardants are typically additive, while organohalogen and organophosphorus compounds can be either reactive or additive. Classes Both reactive and additive flame retardants types can be further separated into four distinct classes: * Minerals such as aluminium hydroxide (ATH), magnesium hydroxide (MDH), huntite and hydromagnesite, various hydrates, red phosphorus, and boron compounds, mostly borates. * Organohalogen compounds. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrabromobisphenol-A
Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) is a brominated flame retardant. The compound is a white solid (not colorless), although commercial samples appear yellow. It is one of the most common flame retardants. Production and use TBBPA is produced by the reaction of bromine with bisphenol A. Most commercial TBBPA products consist of a mixture that differ in the degree of bromination with the formula C15H16−xBrxO2 where x = 1 to 4. Its fire-retarding properties correlate with its bromine content. The annual consumption in Europe has been estimated as 6200 tons in 2004. TBBPA is mainly used as a reactive component of polymers, meaning that it is incorporated into the polymer backbone. It is used to prepare fire-resistant polycarbonates by replacing some bisphenol A. A lower grade of TBBPA is used to prepare epoxy resins, used in printed circuit boards. Toxicity A study was published by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in December 2011 on the exposure of TBBPA and its derivativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decabromodiphenyl Ether
Decabromodiphenyl ether (also referred to as decaBDE, DBDE, BDE-209) is a brominated flame retardant which belongs to the group of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). It was commercialised in the 1970s and was initially thought to be safe, but is now recognised as a hazardous and persistent pollutant. It was added to Annex A of the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2017, which means that treaty members must take measures to eliminate its production and use. The plastics industry started switching to decabromodiphenyl ethane as an alternative in the 1990s, but this is now also coming under regulatory pressure due to concerns over human health. Composition, uses, and production Commercial decaBDE is a technical mixture of various PBDE congeners (related compounds). Congener number 209 (decabromodiphenyl ether) and nonabromodiphenyl ether are the main components.Joint Research Centre European inventory of Existing Commercial chemical Substances The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
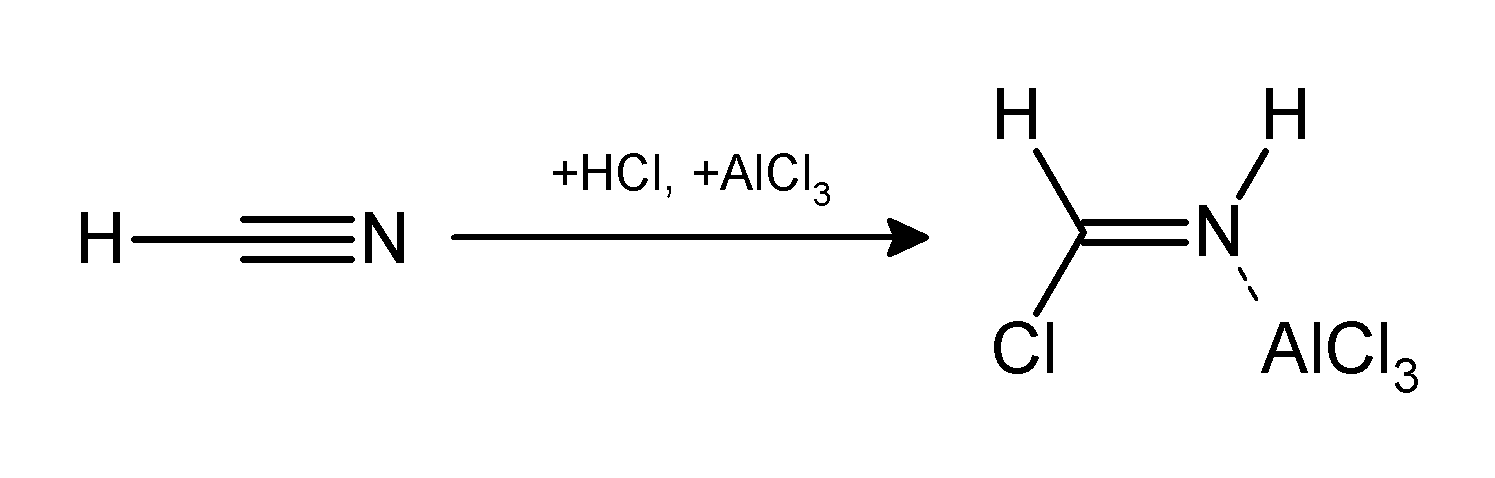
Gatterman Reaction
The Gattermann reaction (also known as the Gattermann formylation and the Gattermann salicylaldehyde synthesis) is a chemical reaction in which aromatic compounds are formylation reaction, formylated by a mixture of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst such as aluminium chloride (AlCl3). It is named for the German chemist Ludwig Gattermann and is similar to the Friedel–Crafts reaction. Modifications have shown that it is possible to use sodium cyanide or cyanogen bromide in place of hydrogen cyanide. The reaction can be simplified by replacing the HCN/AlCl3 combination with zinc cyanide. Although it is also highly toxic, Zn(CN)2 is a solid, making it safer to work with than gaseous HCN. The Zn(CN)2 reacts with the HCl to form the key HCN reactant and Zn(Cl)2 that serves as the Lewis-acid catalyst ''in-situ''. An example of the Zn(CN)2 method is the synthesis of mesitaldehyde from mesitylene. Gattermann–Koch reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |