|
Fluorides
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts typically have distinctive bitter tastes, and are odorless. Its salts and minerals are important chemical reagents and industrial chemicals, mainly used in the production of hydrogen fluoride for fluorocarbons. Fluoride is classified as a weak base since it only partially associates in solution, but concentrated fluoride is corrosive and can attack the skin. Fluoride is the simplest fluorine anion. In terms of charge and size, the fluoride ion resembles the hydroxide ion. Fluoride ions occur on Earth in several minerals, particularly fluorite, but are present only in trace quantities in bodies of water in nature. Nomenclature Fluorides include compounds that contain ionic fluoride and those in which fluoride does not dissociate. The nome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions as pale yellow Diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. Fluorine is extremely Reactivity (chemistry), reactive as it reacts with all other Periodic table, elements except for the light Noble gas, noble gases. It is highly toxicity, toxic. Among the elements, fluorine ranks Abundance of the chemical elements, 24th in cosmic abundance and 13th in crustal abundance. Fluorite, the primary mineral source of fluorine, which gave the element its name, was first described in 1529; as it was added to metal ores to lower their melting points for smelting, the Latin verb meaning gave the mineral its name. Proposed as an element in 1810, fluorine proved difficult and dangerous to separate from its compounds, and several early experimenters died or sustained injuries from their attempts. Only in 1886 did French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
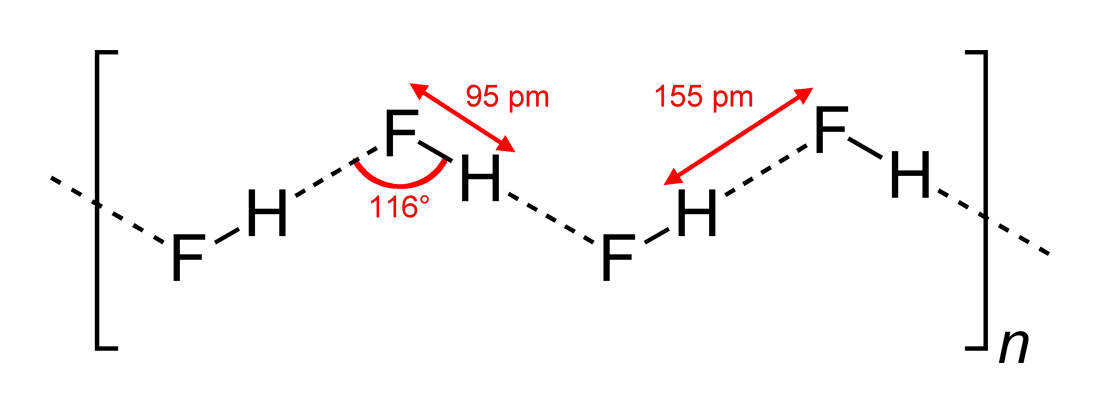
Hydrogen Fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride (fluorane) is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a very poisonous, colorless gas or liquid that dissolves in water to yield hydrofluoric acid. It is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the form of hydrofluoric acid, and is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is also widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Due to strong and extensive hydrogen bonding, it boils near room temperature, a much higher temperature than other hydrogen halides. Hydrogen fluoride is an extremely dangerous gas, forming corrosive and penetrating hydrofluoric acid upon contact with moisture. The gas can also cause blindness by rapid destruction of the corneas. History In 1771 Carl Wilhelm Scheele prepared the aqueous solution, hydrofluoric acid in large quantities, although hydrofluoric acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trivial Name
In chemistry, a trivial name is a non-systematic name for a chemical substance. That is, the name is not recognized according to the rules of any formal system of chemical nomenclature such as IUPAC inorganic or IUPAC organic nomenclature. A trivial name is not a formal name and is usually a common name. Generally, trivial names are not useful in describing the essential properties of the thing being named. Properties such as the molecular structure of a chemical compound are not indicated. And, in some cases, trivial names can be ambiguous or will carry different meanings in different industries or in different geographic regions (for example, a trivial name such as '' white metal'' can mean various things). Trivial names are simpler. As a result, a limited number of trivial chemical names are retained names, an accepted part of the nomenclature. Trivial names often arise in the common language; they may come from historic usages in, for example, alchemy. Many trivial name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pronunciation of the word "chloride" is . Chloride salts such as sodium chloride are often soluble in water.Green, John, and Sadru Damji. "Chapter 3." ''Chemistry''. Camberwell, Vic.: IBID, 2001. Print. It is an essential electrolyte located in all body fluids responsible for maintaining acid/base balance, transmitting nerve impulses and regulating liquid flow in and out of cells. Other examples of ionic chlorides include potassium chloride (), calcium chloride (), and ammonium chloride (). Examples of covalent chlorides include methyl chloride (), carbon tetrachloride (), sulfuryl chloride (), and monochloramine (). Electronic properties A chloride ion (diameter 167 pm) is much larger than a chlorine atom (diameter 99 pm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Litre
The litre ( Commonwealth spelling) or liter ( American spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metres (m3). A cubic decimetre (or litre) occupies a volume of (see figure) and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre. The original French metric system used the litre as a base unit. The word ''litre'' is derived from an older French unit, the '' litron'', whose name came from Byzantine Greek—where it was a unit of weight, not volume—via Late Medieval Latin, and which equalled approximately 0.831 litres. The litre was also used in several subsequent versions of the metric system and is accepted for use with the SI, despite it not being an SI unit The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI (from French ), is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATSDR
The Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) is a federal public health agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The agency focuses on minimizing human health risks associated with exposure to hazardous substances. It works closely with other federal, state, and local agencies; tribal governments; local communities; and healthcare providers. Its mission is to "Serve the public through responsive public health actions to promote healthy and safe environments and prevent harmful exposures." ATSDR was created as an advisory, nonregulatory agency by the Superfund legislation and was formally organized in 1985. Although ATSDR is an independent operating agency within HHS, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) performs many of its administrative functions. The CDC director also serves as the ATSDR administrator, and ATSDR has a joint Office of the Director with the National Center for Environmental Health (NCEH). The ATSDR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saline Water
Saline water (more commonly known as salt water) is water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts (mainly sodium chloride). On the United States Geological Survey (USGS) salinity scale, saline water is saltier than brackish water, but less salty than brine. The salt concentration is usually expressed in parts per thousand (permille, ‰) and parts per million (ppm). The USGS salinity scale defines three levels of saline water. The salt concentration in slightly saline water is 1,000 to 3,000 ppm (0.1–0.3%); in moderately saline water is 3,000 to 10,000 ppm (0.3–1%); and in highly saline water is 10,000 to 35,000 ppm (1–3.5%). Seawater has a salinity of roughly 35,000 ppm, equivalent to 35 grams of salt per one liter (or kilogram) of water. The saturation level is only nominally dependent on the temperature of the water. At one liter of water can dissolve about 357 grams of salt, a concentration of 26.3 percent by weight (% w/w). At (the boiling temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresh Water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salt (chemistry), salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mineral water, mineral-rich waters, such as chalybeate springs. Fresh water may encompass frozen water, frozen and meltwater in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, snowfields and icebergs, natural precipitations such as rainfall, snowfall, hail/ice pellets, sleet and graupel, and surface runoffs that form inland bodies of water such as wetlands, ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, as well as groundwater contained in aquifers, subterranea (geography), subterranean subterranean river, rivers and underground lake, lakes. Water is critical to the survival of all living organisms. Many organisms can thrive on salt water, but the great majority of vascular plants and most insects, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds need fresh water to sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorine Cycle
The fluorine cycle is the series of biogeochemical processes through which fluorine moves through the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. Fluorine originates from the Earth’s crust, and its cycling between various sources and sinks is modulated by a variety of natural and anthropogenic processes. Overview Fluorine is the thirteenth most abundant element on Earth and the 24th most abundant element in the universe. It is the most electronegative element and it is highly reactive. Thus, it is rarely found in its elemental state, although elemental fluorine has been identified in certain geochemical contexts. Instead, it is most frequently found in ionic compounds (e.g. HF, CaF2). The major mechanisms that mobilize fluorine are chemical and mechanical weathering of rocks. Major anthropogenic sources include industrial chemicals and fertilizers, brick manufacturing, and groundwater extraction. Fluorine is primarily carried by rivers to the oceans, where it has a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |