|
Flora Of Panama
Panama is a country located in Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, between Colombia and Costa Rica. Panama is located on the narrow and low Isthmus of Panama. This S-shaped isthmus is situated between 7° and 10° north latitude and 77° and 83° west longitude. Panama encompasses approximately . It is long, and between wide. Geology The Cocos and Nazca plates formed in the Miocene. The Panama microplate is made of oceanic crust basalt, similar to the basalt plateau at the bottom of the Caribbean Sea. The isthmus of Panama formed due to convergent tectonics of the eastern Pacific subduction zone, which created a magmatic arc extending from southern North America. The center of the isthmus, from Arenal Volcano in Costa Rica to El Valle volcano in Panama was uplifted during the subduction of the unusually thick Cocos Ridge oceanic crust, which also produced the four kilometer high Talamanca Range. The western edge of the Caribbean Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a single continent, the Americas or America is the 2nd largest continent by area after Asia, and is the 3rd largest continent by population. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. Along with their Lists of islands of the Americas, associated islands, the Americas cover 8% of Earth's total surface area and 28.4% of its land area. The topography is dominated by the American Cordillera, a long chain of mountains that runs the length of the west coast. The flatter eastern side of the Americas is dominated by large river basins, such as the Amazon basin, Amazon, St. Lawrence River–Great Lakes, Mississippi River System, Mississippi, and Río de la Plata Basin, La Plata basins. Since the Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
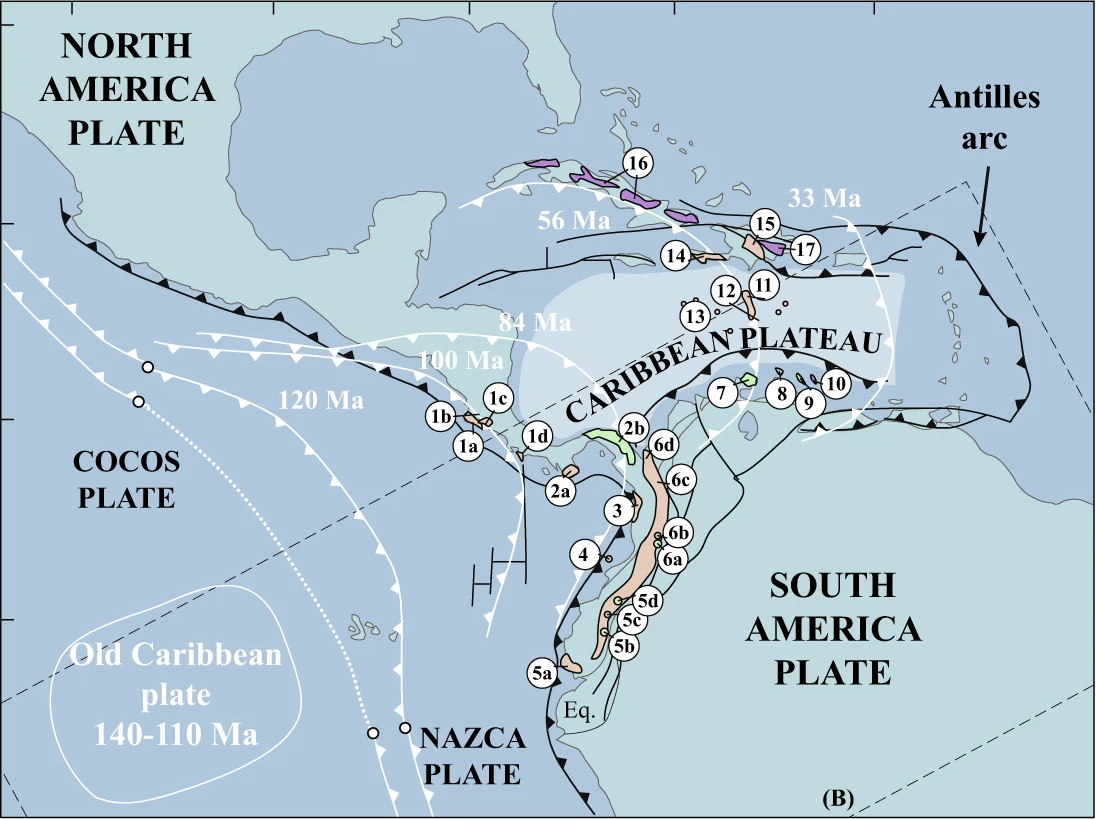
Caribbean Large Igneous Province
The Caribbean large igneous province (CLIP) consists of a major flood basalt, which created this large igneous province (LIP). It is the source of the current large eastern Pacific oceanic plateau, of which the Caribbean-Colombian oceanic plateau is the tectonized remnant. The deeper levels of the plateau have been exposed on its margins at the North American and South American plates. The volcanism took place between 139 and 69 million years ago ( Ma), with the majority of activity appearing to lie between 95 and 88 Ma. The plateau volume has been estimated as on the order of . It has been linked to the Galápagos hotspot. Proto-Caribbean Seaway Divergence between the North American and South American Plates began to create oceanic crust off Colombia's Pacific coast by the end of the Jurassic (150 Ma). This divergence, which continued until at least 66 Ma, first resulted in a " proto-Caribbean spreading ridge" between these plates flanked by a perpendicular transform zone on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogene
The Neogene ( ,) is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period million years ago. It is the second period of the Cenozoic and the eleventh period of the Phanerozoic. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by Paleogene and Neogene and, despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. During this period, mammals and birds continued to evolve into modern forms, while other groups of life remained relatively unchanged. The first human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
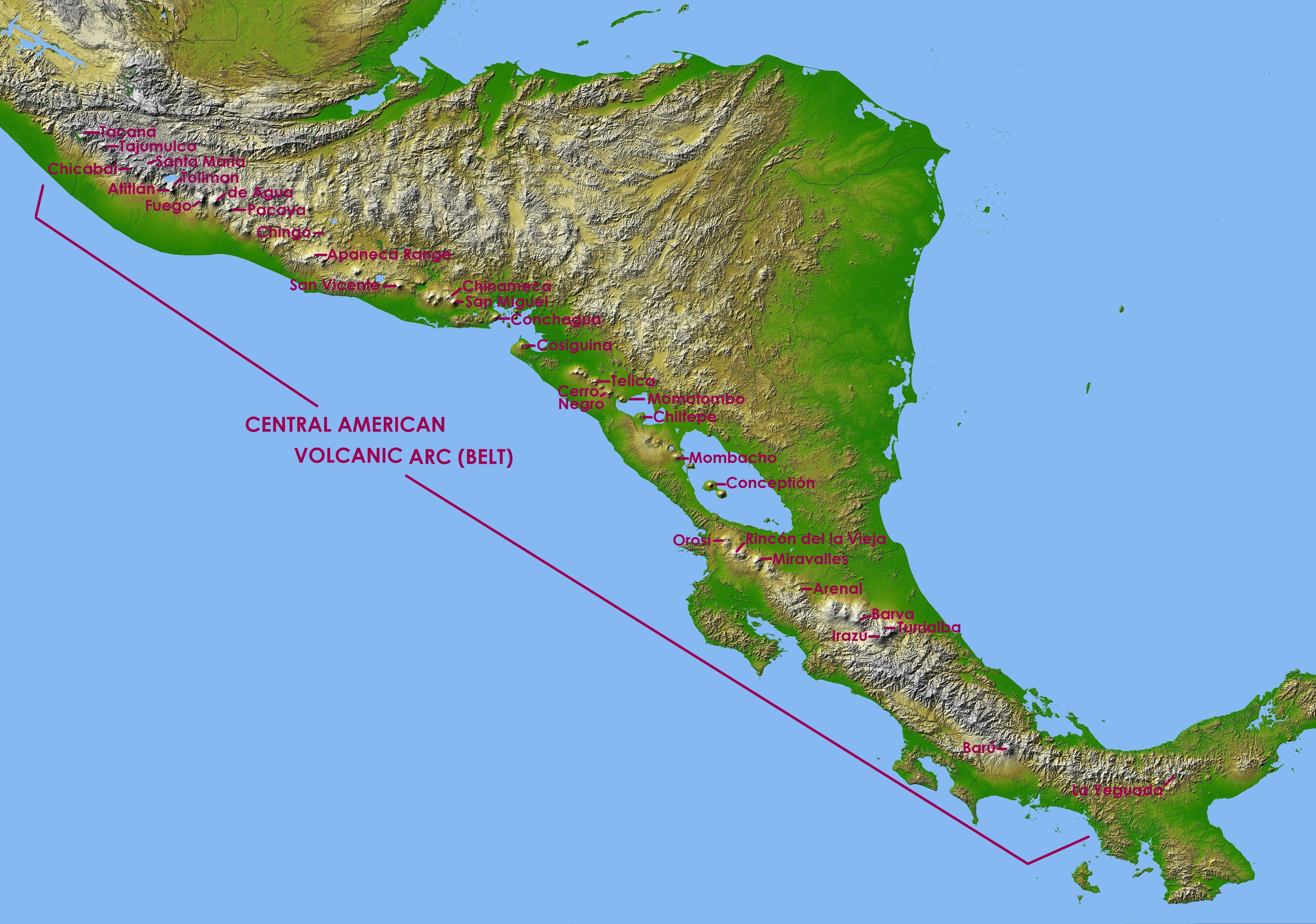
Central American Volcanic Arc
The Central American Volcanic Arc (often abbreviated to CAVA) is a chain of volcanoes which extends parallel to the Pacific coastline of the Central American Isthmus, from Mexico to Panama. This volcanic arc, which has a length of 1,100 kilometers (680 mi)Rose, W., Conway, F., Pullinger, C., Deino, A. and McIntosh, W., 1999. An improved age framework for late Quaternary silicic eruptions in northern Central America. ''Bulletin of Volcanology'', 61(1-2), pp.106-120. is formed by an active subduction zone, with the Cocos plate subducting underneath the Caribbean plate,Álvarez-Gómez, J., Meijer, P., Martínez-Díaz, J. and Capote, R., 2008. Constraints from finite element modeling on the active tectonics of northern Central America and the Middle America Trench. ''Tectonics'', 27(1) the North American plate and the Panama plate. Volcanic activity is recorded in the Central American region since the Permian. Numerous volcanoes are spread throughout various Central American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talamanca Range
The Cordillera de Talamanca is a mountain range that lies in the southeast half of Costa Rica and the far west of Panama. Much of the range and the area around it is included in La Amistad International Park, which also is shared between the two countries. This range in the south of Costa Rica stretches from southwest of San José to beyond the border with Panama and contains the highest peaks of both Costa Rica and Panama, among them Cerro Chirripó at , and the more accessible high peak of Cerro de la Muerte. Much of the Caribbean areas of the range are still unexplored. Exploration and classification The range is covered by the Talamancan montane forests to elevations of approximately . Much of it is covered by rainforests. Above elevations of these are dominated by huge oak trees ('' Quercus costaricensis''). Above , the forests transition to enclaves of sub-páramo, a sort of shrub and dwarf bamboo ''Chusquea'' dominated scrub, above this becomes Costa Rican páramo, a tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocos Ridge
The Cocos Ridge is an aseismic ridge within the Cocos plate that runs northeastwards from just north of the Galápagos islands to the Middle America Trench offshore Panama. It records the effects of the Galápagos hotspot on the Cocos plate since the establishment of the Cocos–Nazca spreading centre during the break-up of the Farallon plate towards the end of the Oligocene Epoch (geology), epoch. It is the counterpart to the Carnegie Ridge, which developed on the Nazca plate. Cocos Island is the only emergent part of the ridge. The volcanic activity that formed the island is much younger than the part of the ridge where it is located. Extent The Cocos Ridge is a ~1000 km long bathymetric high, varying in width up to 200 km. It lies entirely within the Cocos plate. The presence of a shallow area between the Galápagos islands and Cocos Island was first identified by Alexander Agassiz in 1892, naming it the Galapagos Plateau. After the acquisition of more depth soundings it becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic Uplift
Tectonic uplift is the orogeny, geologic uplift of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface that is attributed to plate tectonics. While Isostasy, isostatic response is important, an increase in the mean elevation of a region can only occur in response to tectonic processes of Thrust tectonics, crustal thickening (such as Mountain formation, mountain building events), changes in the density distribution of the crust and underlying Mantle (geology), mantle, and flexural support due to the bending of rigid lithosphere. Tectonic uplift results in denudation (processes that wear away the earth's surface) by raising buried rocks closer to the surface. This process can redistribute large loads from an elevated region to a topographically lower area as well – thus promoting an isostatic response in the region of denudation (which can cause local bedrock uplift). The timing, magnitude, and rate of denudation can be estimated by geologists using pressure-temperature studies. Crustal thickening C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Valle (volcano)
El Valle is a stratovolcano in central Panama and is the easternmost volcano along the Central American Volcanic Arc which has been formed by the subduction of the Nazca Plate below Central America. Some time prior to 200,000 years ago, the volcano underwent a huge eruption event that caused the top of the volcano to collapse into the empty magma chamber below forming a large caldera. Several lava domes have developed inside the caldera since the collapse—forming Cerro Pajita, Cerro Gaital and Cerro Caracoral peaks. Prior to research in the early 1990s, it was thought that no active volcanism existed within Panama. But radioactive dates from El Valle show that the volcano last erupted as recently as 200,000 years ago. Work by de Boer et al. and Defant et al.Defant, M. J., Jackson, T. E., Drummond, M. S., de Boer, J. Z., Bellon, H., Feigenson, M. D., Maury, R. C., and Stewart, R.H., 1992, The geochemistry of young volcanism throughout western Panama and southeastern Costa Rica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arenal Volcano
Arenal Volcano () is an inactive andesitic stratovolcano in north-western Costa Rica around northwest of San José, in the province of Alajuela, canton of San Carlos, and district of La Fortuna. The Arenal volcano measures at least high. It is conically shaped with a crater in diameter. Geologically, Arenal is considered a young volcano and it is estimated to be less than 7,500 years old. It is also known as "Pan de Azúcar", "Canaste", "Volcan Costa Rica", "Volcan Río Frío" or "Guatusos Peak". The volcano was dormant for hundreds of years and exhibited 2 craters at its summit, with minor fumaroles activity, covered by dense vegetation. In 1968 it erupted unexpectedly, destroying the small town of Tabacón. Due to the eruption three more craters were created on the western flanks but only one of them exists today. Arenal's eruption from 1968 to 2010 is the tenth longest duration volcanic eruption on Earth since 1750. Since 2010, Arenal has been dormant. Geographic se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Arc
A volcanic arc (also known as a magmatic arc) is a belt of volcanoes formed above a subducting oceanic tectonic plate, with the belt arranged in an arc shape as seen from above. Volcanic arcs typically parallel an oceanic trench, with the arc located further from the subducting plate than the trench. The oceanic plate is saturated with water, mostly in the form of hydrous minerals such as micas, amphiboles, and serpentines. As the oceanic plate is subducted, it is subjected to increasing pressure and temperature with increasing depth. The heat and pressure break down the hydrous minerals in the plate, releasing water into the overlying mantle. Volatiles such as water drastically lower the melting point of the mantle, causing some of the mantle to melt and form magma at depth under the overriding plate. The magma ascends to form an arc of volcanoes parallel to the subduction zone. Volcanic arcs are distinct from volcanic chains formed over hotspots in the middle of a tecton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction Zone
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the other and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with rates of convergence as high as 11 cm/year. Subduction is possible because the cold and rigid oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the dense subducting lithosphere. The down-going slab sinks into the mantle largely under its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |