|
Flechette Firearms
A flechette or flèchette ( ) is a pointed, fin-stabilized steel projectile. The name comes from French (from \'' flèche''), meaning "little arrow" or " dart", and sometimes retains the grave accent in English: flèchette. They have been used as ballistic weapons since World War I. Delivery systems and methods of launching flechettes vary, from a single shot, to thousands in a single explosive round. The use of flechettes as antipersonnel weapons has been controversial; however in war is not prohibited by the Hague Convention. Air-dropped The weapons were designed to be dropped from an aircraft. They contained no explosive charge but as they fell they developed significant kinetic energy making them lethal and able to easily penetrate soft cover such as jungle canopy, several inches of sand or light armor. During World War I, flechettes were dropped from aircraft to attack infantry and were able to pierce helmets. Also during World War II, a version of the flechette with fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flechettes
A flechette or flèchette ( ) is a pointed, fin-stabilized steel projectile. The name comes from French (from \''wikt:flèche, flèche''), meaning "little arrow" or "Dart (missile), dart", and sometimes retains the grave accent in English: flèchette. They have been used as ballistic weapons since World War I. Delivery systems and methods of launching flechettes vary, from a single shot, to thousands in a single explosive round. The use of flechettes as antipersonnel weapons has been controversial; however in war is not prohibited by the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907, Hague Convention. Air-dropped The weapons were designed to be dropped from an aircraft. They contained no explosive charge but as they fell they developed significant kinetic energy making them lethal and able to easily penetrate soft cover such as jungle canopy, several inches of sand or light armor. During World War I, flechettes were dropped from aircraft to attack infantry and were able to pierce helmets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VX (nerve Agent)
VX is an extremely toxic chemical synthesis, synthetic chemical compound in the organophosphorus compound, organophosphorus class, specifically, a phosphonate, thiophosphonate. In the class of nerve agents, it was developed for military use in chemical warfare after translational science, translation of earlier discoveries of organophosphate toxicity in pesticide research. In its pure form, VX is an oily, relatively Volatility (chemistry), non-volatile liquid that is amber-like in colour. Because of its low volatility, VX persists in environments where it is dispersed. VX, short for "venomous agent X", is one of the best known of the V nerve agents and originated from pesticide development work at Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI). It was developed further at Porton Down in England during the early 1950s, based on research first done by Gerhard Schrader, a chemist working for IG Farben in Germany during the 1930s. It is now one of a broader V-series of agents which are class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Cartridge Company
Federal Premium Ammunition is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Czechoslovak Group, located in Anoka, Minnesota. With a workforce of nearly 1,500, Federal manufactures shotshell, centerfire, and rimfire ammunition and components. History The original Federal Cartridge and Machine Company was founded during the period of increased ammo demand during the First World War, when brothers Harry and Louis Sherman, experienced in the industry, found investors to establish a small plant on the eastern outskirts of Anoka, Minnesota to make shotgun shells. Due to conflicts with investors, the brothers left the company in early 1917 for the American Cartridge Company; seven years later this firm was acquired by Federal. The end of the First World War led to factory's closure in 1920. On April 27, 1922, Charles L. Horn took control of the plant and refounded Federal Cartridge Corporation. Horn launched a distribution plan that involved merchandising Federal products in grocery stores, barb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Cartridge Company
The Western Cartridge Company was an American manufacturer of small arms and ammunition formerly based in East Alton, Illinois. Founded in 1898, it was the forerunner of the Olin Corporation, formed in 1944, of which Western was absorbed into. Prior to that, Western acquired the Winchester Repeating Arms Company after Winchester went into receivership in 1931. The two would merge in 1935 to form Winchester-Western. History Franklin W. Olin received an engineering degree from Cornell University in 1886. After working at powder mills in the eastern United States, he was one of several investors establishing the Equitable Powder Company in 1892 at East Alton, Illinois. Production of blasting powder for southern Illinois coal mining began in 1893. Olin formed the Western Cartridge Company in 1898 to manufacture sporting rifle powder and shotgun shells for settlers of the Great Plains. The shotgun shells used primers manufactured by larger eastern ammunition firms. When the fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Shotgun
A combat shotgun is a shotgun issued by militaries for warfare. The earliest shotguns specifically designed for combat were the trench guns or trench shotguns issued in World War I. While limited in range, the multiple projectiles typically used in a shotgun shell increase the probability of hitting a target at close quarters. History While the sporting shotgun traces its ancestry back to the fowling piece, which was a refinement of the smoothbore musket, the combat shotgun bears more kinship to the shorter blunderbuss. Invented in the 16th century by the Dutch, the blunderbuss was used through the 18th century in warfare by the British, Austrian, Spanish (like the Escopeteros Voluntarios de Cadiz, formed in 1804, or the Compañía de Escopeteros de las Salinas, among others) and Prussian regiments, as well as in the American colonies. As use of the blunderbuss declined, the United States military began loading smaller lead shot (buckshot) in combination with their large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauge (bore Diameter)
The gauge (in American English or more commonly referred to as bore in British English) of a firearm is a unit of measurement used to express the inner diameter (bore diameter) and other necessary parameters to define in general a smoothbore Gun barrel, barrel (compare to caliber, which defines a barrel with rifling and its Cartridge (firearms), cartridge). The gauge of a shotgun is a list that includes all necessary data to define a functional barrel. For example, the dimension of the chamber, the shotgun bore dimension and the valid proof load and commercial ammunition, as defined globally by the Commission internationale permanente pour l'épreuve des armes à feu portatives, C.I.P.; defined in Great Britain by the ''Rules, regulations and scales applicable to the proof of small arms'' (2006) of Worshipful Company of Gunmakers, The London Proof House and Birmingham Proof House, The Birmingham Proof House, as referred in the Gun Barrel Proof Act 1978, Paragraph 6; and defined in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCMITR
SCMITR was part of an experimental military shotgun ammunition created in the 1970s by AAI Corporation. It was a variation on flechette ammunition, but instead of containing a bundle of tiny needle-like steel darts, the cartridge contained a stack of razor-edged stamped sheet-metal arrow shapes designed to fly aerodynamically. It was considered to be very promising (in terms of lethality and effective range) but prohibitively expensive to manufacture, so it has never been mass-produced. Development SCMITR was part of the CAWS (Close Assault Weapon System) program, which investigated ~20 mm smoothbore weapons (basically combat shotguns) designed to be effective to ranges of 150 metres against combatants wearing body armor. Flechettes, with their high sectional density Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Combat Rifle
The Advanced Combat Rifle (ACR) was a United States Army program, started in 1986, to find a replacement for the M16 assault rifle. Under the stress of battle the average soldier with an M16 may shoot a target at 45 meters, but hit probability is reduced to one out of ten shots on target by 220 meters. Because of this, the ACR program was initiated in the late 1980s to create a weapon that could double the hit probability. None of the weapons tested met the criteria, and the program ended in 1990 after an expenditure of approximately US$300 million. The ACR program was preceded by older programs such as the Special Purpose Individual Weapon. Phase I and II Phase I of the program started in February 1986 when development contracts were placed with six companies: AAI Corporation, Ares Incorporated, Colt's Manufacturing Company, Heckler & Koch (H&K), McDonnell Douglas Helicopter Systems (MDHS), and Steyr Mannlicher. Two weapons were cut from the list before Phase II started. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
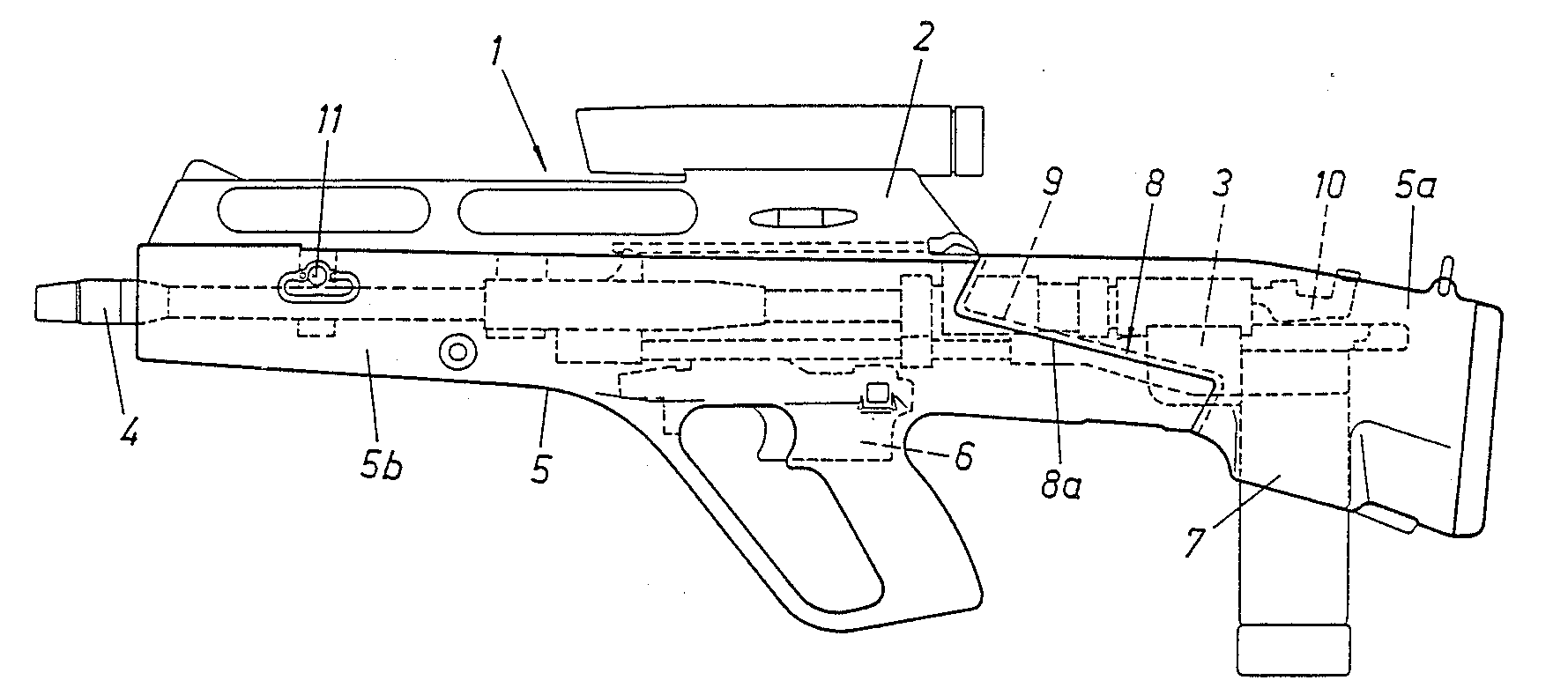
Steyr ACR
The Steyr ACR was a prototype flechette-firing assault rifle built for the US Army's Advanced Combat Rifle program of 1989/90. Although the Steyr Steyr (; ) is a statutory city (Austria), statutory city, located in the Austrian federal state of Upper Austria. It is the administrative capital, though not part of Steyr-Land District. Steyr is Austria's 12th most populated town and the 3rd lar ... design proved effective, as did most of the weapons submitted, the entire ACR program ended with none of the entrants achieving performance 100% better than the M16A2, the baseline for a successful ACR weapon. Design The Steyr ACR has some superficial resemblance to the Steyr AUG, although it is rounder and the barrel is covered for almost its entire length, as opposed to the AUG where much of the barrel was exposed. Like the AUG, the ACR is a bullpup design with the 24-round magazine located quite close to the buttstock of the gun. The stock was "split" from the magazine forward to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Purpose Individual Weapon
The Special Purpose Individual Weapon (SPIW) was a long-running United States Army program to develop, in part, a flechette-firing "rifle", though other concepts were also involved. The concepts continued to be tested under the Future Rifle Program and again in the 1980s under the Advanced Combat Rifle program, but neither program resulted in a system useful enough to warrant replacing the M16. Project SALVO The idea of a flechette-firing individual weapon started in earnest during the Army's Project SALVO. SALVO had earlier concluded that a small weapon with a high rate of fire would be considerably deadlier than the large "full power" weapons being developed in the 1950s, and followed several lines of investigation to find the best way to provide high firing rates. SALVO had a small number of "duplex load" weapons developed, where two bullets were stacked, while Springfield Armory and Olin/Winchester both entered multiple barrel firearms. Even before the SALVO tests, Irwin Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APS Amphibious Rifle
The APS underwater assault rifle () is an underwater firearm designed by the Soviet Union in the early 1970s. It was adopted in 1975. Made by the Tula Arms Plant () in Russia, it is exported by Rosoboronexport. Under water, ordinary bullets are inaccurate and have a very short range. The APS fires a , 5.66 mm calibre steel bolt specially designed for this weapon. Its magazine holds 26 rounds. The APS's barrel is not rifled; the fired projectile is kept in line by hydrodynamic effects; as a result, the APS is somewhat inaccurate when fired out of water. The APS has a longer range and more penetrating power than spearguns. This is useful in such situations such as shooting an opposing diver through a reinforced dry suit, a protective helmet (whether air-holding or not), thick tough parts of breathing sets and their harnesses, and the plastic casings and transparent covers of some small underwater vehicles. The APS is more powerful than a pistol, but is bulkier, heavie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AO-27 Rifle
The AO-27 was a Soviet assault rifle, chambered for the 7.62 mm fin-stabilized flechette sabot round. The flechette itself had a body diameter of 3 mm. The overall length of the round was 63 mm, and the flechette 55 mm. The weight of the round was 10.5 gram The gram (originally gramme; SI unit symbol g) is a Physical unit, unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth of a kilogram. Originally defined in 1795 as "the absolute Mass versus weight, weight of a volume ...s, with 2.4 grams the weight of the flechette. See also * List of assault rifles References Flechette firearms Kalashnikov derivatives Assault rifles of the Soviet Union Trial and research firearms of the Soviet Union {{Rifle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |