|
Fauna Of The Colorado Desert
The Colorado Desert is a part of the larger Sonoran Desert located in California, United States, and Baja California, Mexico. It encompasses approximately , including the heavily irrigated Coachella, Imperial and Mexicali valleys. It is home to many unique flora and fauna. Geography and geology The Colorado Desert is a subregion of the larger Sonoran Desert, covering about . The desert occupies Imperial County, parts of San Diego and Riverside counties, and a small part of San Bernardino County in California, United States, as well as the northern part of Mexicali Municipality in Baja California, Mexico. Most of the Colorado Desert lies at a relatively low elevation, below , with the lowest point of the desert floor at below sea level, at the Salton Sea. Although the highest peaks of the Peninsular Ranges reach elevations of nearly , most of the region's mountains do not exceed . In this region, the geology is dominated by the transition of the tectonic plate boundary from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsular Ranges
The Peninsular Ranges (also called the Lower California province) are a group of mountain ranges that stretch from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Pacific Coast Ranges, which run along the Pacific coast from Alaska to Mexico. Elevations range from . Geography The Peninsular Ranges include the Santa Ana Mountains, the Temescal Mountains, other mountains and ranges of the Perris Block, the San Jacinto Mountains, the Laguna Mountains of southern California continuing from north to south with the Sierra de Juárez, the Sierra de San Pedro Mártir, the Sierra de San Borja, the Sierra de San Francisco, the Sierra de la Giganta, and the Sierra de la Laguna in Baja California. Palomar Mountain, home to Palomar Observatory, is in the Peninsular Ranges in San Diego County, as are the San Ysidro Mountains and Viejas Mountain. The Peninsular Ranges run predominantly north-south, unlike the Transverse R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ , or ICZ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal equator though its specific position varies seasonally. When it lies near the geographic equator, it is called the near-equatorial trough. Where the ITCZ is drawn into and merges with a monsoon, monsoonal circulation, it is sometimes referred to as a ''monsoon trough'' (a usage that is more common in Australia and parts of Asia). Meteorology The ITCZ was originally identified from the 1920s to the 1940s as the ''Intertropical Front'' (''ITF''), but after the recognition in the 1940s and the 1950s of the significance of convergence zone, wind field convergence in tropics, tropical weather production, the term ''Intertropical Convergence Zone'' (''ITCZ'') was then applied. The ITCZ appears as a band of clouds, usually thunderstorms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jetstream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow air currents in the Earth's atmosphere. The main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds, flowing west to east around the globe. The northern hemisphere and the southern hemisphere each have a polar jet around their respective polar vortex at around above sea level and typically travelling at around although often considerably faster. Closer to the equator and somewhat higher and somewhat weaker is a subtropical jet. The northern polar jet flows over the middle to northern latitudes of North America, Europe, and Asia and their intervening oceans, while the southern hemisphere polar jet mostly circles Antarctica. Jet streams may start, stop, split into two or more parts, combine into one stream, or flow in various directions including opposite to the direction of the remainder of the jet. The El Niño–Southern Oscillation affects the location of the jet streams, which in turn affects the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the Wet season, rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the Monsoon#Africa (West African and Southeast African), West African, Asian–Australian monsoon, Australian, the North American monsoon, North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first Glossary of the British Raj, used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
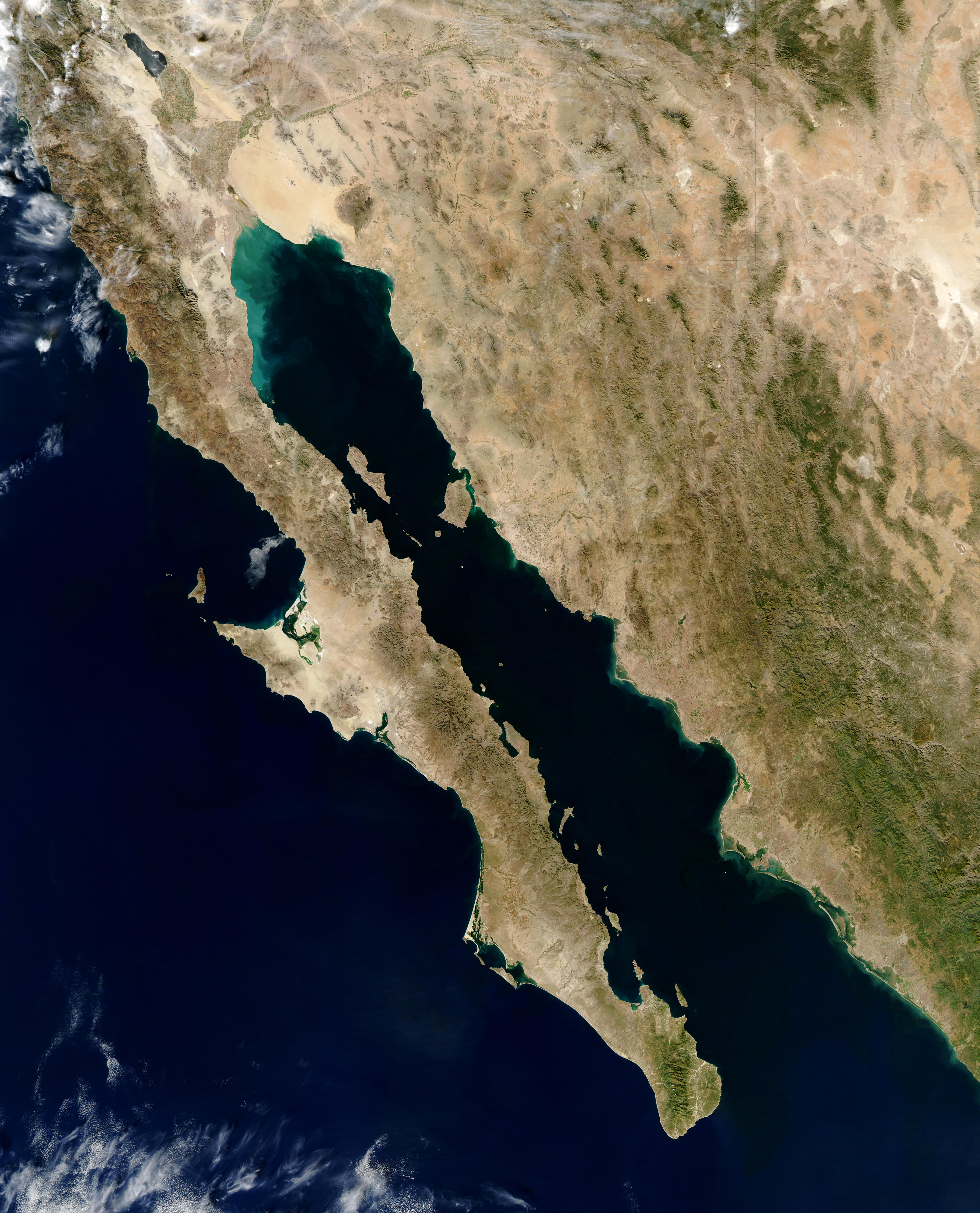
Gulf Of California
The Gulf of California (), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Vermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja California peninsula from the Mexico, Mexican mainland. It is bordered by the states of Baja California, Baja California Sur, Sonora, and Sinaloa with a coastline of approximately . Rivers that flow into the Gulf of California include the Colorado River, Colorado, Fuerte River, Fuerte, Mayo River (Mexico), Mayo, Sinaloa River, Sinaloa, Sonora River, Sonora, and the Yaqui River, Yaqui. The surface of the gulf is about . Maximum depths exceed because of the complex geology, linked to plate tectonics. The gulf is thought to be one of the most diverse seas on Earth and is home to more than 5,000 species of micro-invertebrates. Parts of the Gulf of California are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Geography History The marine expeditions of Fortún Ximénez, Hernán Cort� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allen A
Allen, Allen's or Allens may refer to: Buildings * Allen Arena, an indoor arena at Lipscomb University in Nashville, Tennessee * Allen Center, a skyscraper complex in downtown Houston, Texas * Allen Fieldhouse, an indoor sports arena on the University of Kansas campus in Lawrence * Allen House (other) * Allen Power Plant (other) Businesses *Allen (brand), an American tool company * Allen's, an Australian brand of confectionery *Allens (law firm), an Australian law firm formerly known as Allens Arthur Robinson *Allen's (restaurant), a former hamburger joint and nightclub in Athens, Georgia, United States *Allen & Company LLC, a small, privately held investment bank * Allens of Mayfair, a butcher shop in London from 1830 to 2015 * Allens Boots, a retail store in Austin, Texas * Allens, Inc., a brand of canned vegetables based in Arkansas, US, now owned by Del Monte Foods * Allen's department store, a.k.a. Allen's, George Allen, Inc., Philadelphia, USA People * All ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert (; ; ) is a desert in the rain shadow of the southern Sierra Nevada mountains and Transverse Ranges in the Southwestern United States. Named for the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous Mohave people, it is located primarily in southeastern California and southwestern Nevada, with small portions extending into Arizona and Utah. The Mojave Desert, together with the Sonoran Desert, Sonoran, Chihuahuan Desert, Chihuahuan, and Great Basin Desert, Great Basin deserts, form a larger List of North American deserts, North American desert. Of these, the Mojave is the smallest and driest. It displays typical basin and range topography, generally having a pattern of a series of parallel mountain ranges and valleys. It is also the site of Death Valley, which is the lowest elevation in North America. The Mojave Desert is often colloquially called the "high desert", as most of it lies between . It supports a diversity of flora and fauna. The desert supports a numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. In its most general sense, the word ''earthquake'' is used to describe any seismic event that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes can occur naturally or be induced by human activities, such as mining, fracking, and nuclear weapons testing. The initial point of rupture is called the hypocenter or focus, while the ground level directly above it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Pacific Rise
The East Pacific Rise (EPR) is a mid-ocean rise (usually termed an oceanic rise and not a mid-ocean ridge due to its higher rate of spreading that results in less elevation increase and more regular terrain), at a divergent tectonic plate boundary, located along the floor of the Pacific Ocean. It separates the Pacific plate to the west from (north to south) the North American plate, the Rivera plate, the Cocos plate, the Nazca plate, and the Antarctic plate. It runs south from the Gulf of California in the Salton Sea basin in Southern California to a point near , where it joins the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge (PAR) trending west-south-west towards Antarctica, near New Zealand (though in some uses the PAR is regarded as the southern section of the EPR). Much of the rise lies about off the South American coast and reaches a height about above the surrounding seafloor. Overview The oceanic crust is moving away from the East Pacific Rise to either side. Near Easter Island th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, right-lateral strike-slip transform fault that extends roughly through the U.S. state of California. It forms part of the tectonics, tectonic boundary between the Pacific plate and the North American plate. Traditionally, for scientific purposes, the fault has been classified into three main segments (northern, central, and southern), each with different characteristics and a different degree of earthquake risk. The average slip rate along the entire fault ranges from per year. In the north, the fault terminates offshore near Eureka, California, at the Mendocino triple junction, where three tectonic plates meet. The Cascadia subduction zone intersects the San Andreas fault at the Mendocino triple junction. It has been hypothesized that a major earthquake along the Cascadia subduction zone could trigger a rupture along the San Andreas Fault. In the south, the fault terminates near Bombay Beach, Califor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a Fracture (geology), planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of Rock (geology), rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust (geology), crust result from the action of Plate tectonics, plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction, subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the Plane (geometry), plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geological maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |