|
Farsala
Farsala (), known in Antiquity as Pharsalos (, ), is a town in southern Thessaly, in Greece. Farsala is located in the southern part of Larissa (regional unit), Larissa regional unit, and is one of its largest settlements. Farsala is an economic and agricultural centre of the region. Cotton and livestock are the main agricultural products, and many inhabitants are employed in the production of textile. The area is mostly famous for being the birthplace of the mythical ancient Greek hero Achilles, and the site of a Battle of Pharsalus, major battle between Roman generals Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus in 48 BC. Geography Farsala lies at the southern edge of the Thessalian Plain, 4 km south of the river Enipeas (Thessaly), Enipeas. The Greek National Road 3 (Larissa - Lamia (city), Lamia) and the Greek National Road 30 (Karditsa - Volos) pass through the town. The Palaiofarsalos railway station (litt. "''Ancient Pharsalus''"), on the Piraeus–Platy railway, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larissa (regional Unit)
Larissa () is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Thessaly. Its capital is the city of Larissa. Total population 268,963 (2021). Geography Larissa is the second largest regional unit in Greece, exceeded only by Aetolia-Acarnania. It covers about one-third of Thessaly. It borders the regional units of Kozani to the northwest, Pieria to the northeast, the Aegean Sea to the east, Magnesia to the southeast, Phthiotis to the south, Karditsa to the southwest and Trikala to the west. The tallest mountain in Greece, Mount Olympus (2,917 m) is situated in the northeastern part of the regional unit. Mount Ossa is situated in the east, at the Aegean coast. The lower stretch of the river Pineios flows through the Vale of Tempe, between Olympus and Ossa. The northern part is covered with forests, but most of the regional unit is fertile land, the Thessalian Plain. Climate Larissa has a mainly Mediterranean climate with hot summers and mild winters. Winte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stavros, Larissa
Stavros (, ''Stavrós''; before 1927: Demerli (Δεμερλή, ''Demerli'')) is a village in the south of the Larissa regional unit, Greece. It is part of the municipal unit of Enippeas. In 2021 its population was 465. Stavros is located west of Farsala, east of Karditsa and southwest of Larissa Larissa (; , , ) is the capital and largest city of the Thessaly region in Greece. It is the fifth-most populous city in Greece with a population of 148,562 in the city proper, according to the 2021 census. It is also the capital of the Larissa .... The important railway junction Palaiofarsalos is situated in Stavros. References {{Farsala div Populated places in Larissa (regional unit) Farsala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek National Road 30
National Road 30 (, abbreviated as EO30) is a single carriageway road in central Greece. It connects the cities of Arta and Volos, via Trikala and Karditsa. Route The western end of the Greek National Road 30 is in Arta, where it is connected with GR-5. It runs northeast through the sparsely populated Athamanika mountains, until it reaches the town Pyli, where it enters the Thessalian Plain. At Trikala it connects with the GR-6, and turn southeast towards Karditsa, where it turns east. The section between Neo Monastiri and Farsala is shared with the GR-3. The A1 motorway is crossed at Mikrothives, and the A3 motorway between Karditsa and Sofades. At Nea Anchialos the GR-30 reaches the coast of the Pagasetic Gulf. The GR-30 ends in the centre of Volos. Near Vourgareli there are 2 tunnels (cut&cover 400m. before Scala Scorliga tunnel) and Scala Scorliga tunnel 1200m. opened in 1981. National Road 30 passes through the following places: * Arta *Peta * Vourgareli * Mesoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaiofarsalos Railway Station
Palaiofarsalos railway station () is a railway station near Farsala in Larissa (regional unit), Larissa regional unit, Greece. It is located in the village Stavros, Larissa, Stavros, west of Farsala. It is situated at the junction of the main Piraeus–Platy railway and the Palaiofarsalos-Kalambaka railway, branch line to Trikala and Kalambaka. It is served by intercity trains between Athens and Thessaloniki and by local trains to Kalambaka railway station, Kalambaka.TrainOSE 2013 timetable History The Palaiofarsalos station opened in 1908 as Demerli at the meeting point between the metric line of the Thessaly Railways (S.Th.) and the standard line of the Piraeus-Demerli-Sinoron Railway (S.P.D.S.) or “Larissaykos”. After the ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
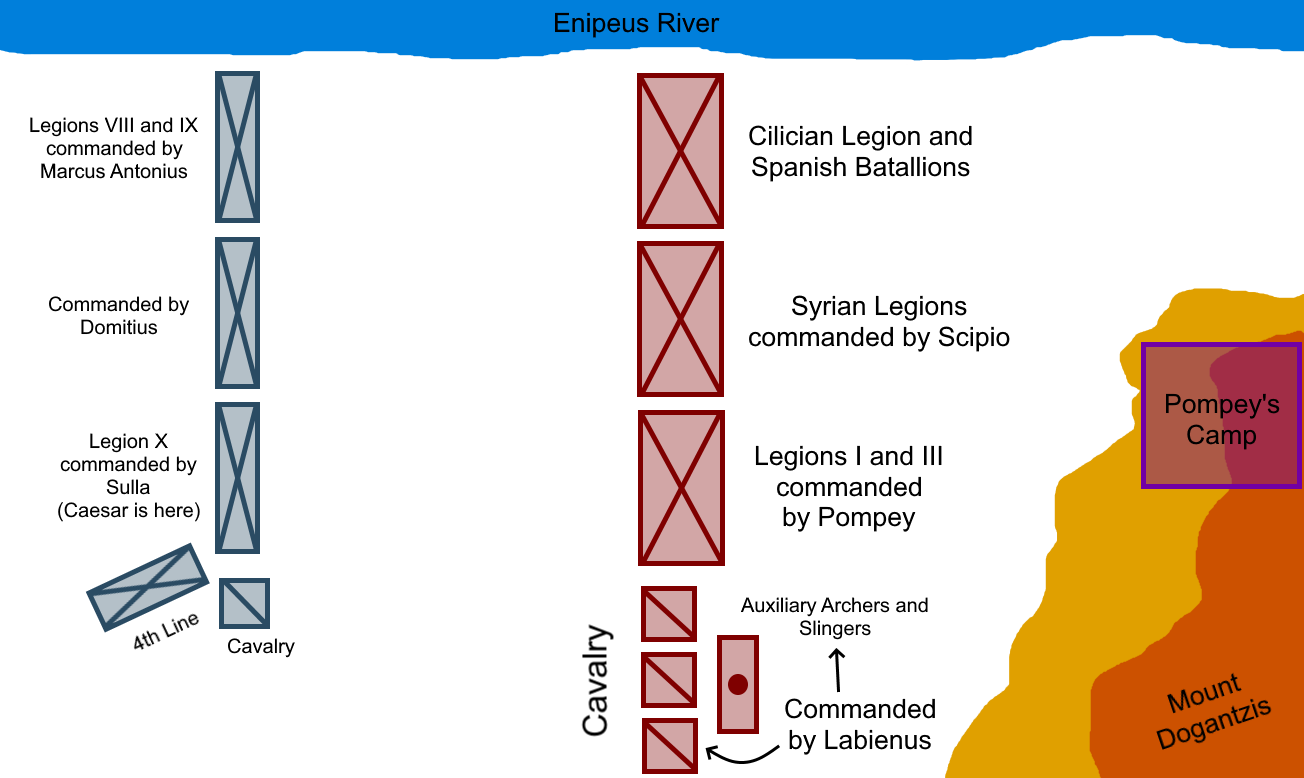
Battle Of Pharsalus
The Battle of Pharsalus was the decisive battle of Caesar's Civil War fought on 9 August 48 BC near Pharsalus in Central Greece. Julius Caesar and his allies formed up opposite the army of the Roman Republic under the command of Pompey. Pompey had the backing of a majority of Roman senators and his army significantly outnumbered the veteran Caesarian legions. Pressured by his officers, Pompey reluctantly engaged in battle and suffered an overwhelming defeat, ultimately fleeing the camp and his men, disguised as an ordinary citizen. Eventually making his way to Egypt, he was assassinated upon his arrival at the order of Ptolemy XIII. Prelude Following the start of the Civil War, Caesar had captured Rome, forced Pompey and his allies to withdraw from Italy, and defeated Pompey's legates in Spain. In the campaign season for 48 BC, Caesar crossed the Adriatic and advanced on Dyrrachium. There, he besieged it, but was defeated. Caesar then withdrew east into Thess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek National Road 3
Greek National Road 3 (, abbreviated as EO3) is a single carriageway road in Greece. It connects Elefsina near Athens with the border of North Macedonia at Niki. It passes through Larissa and Florina. At Niki, it connects with the M5K motorway to Bitola. The section Kozani - Niki is also designated as the A27 motorway, part of which is operational as a 2-lane motorway. Greek National Road 3 is one of the longest national roads in Greece and until the 1960s it served as the main route from Larissa to Thessaloniki. The A1 motorway now offers a faster connection to Thessaloniki. Most of the EO3, except the southernmost section between Eleusis and Bralos, is part of the E65. Future developments Throughout the late 1980s, motorway bypasses were constructed at the towns of Tyrnavos and Elassonas, but in 2002 plans surfaced to convert all of the road into a new motorway, from Larissa to Kozani and further on to Bitola, in North Macedonia. Throughout the 2000s motorway sections we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enipeas (Thessaly)
The Enipeas () or Enipeus () is a river in central Greece, tributary of the Pineios near Farkadona. It is long. p. 12 Its source is in the northern part of , on the plateau of . Its course runs through several of the ''tetrades'' of ancient , from |
Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia (, ), and appears thus in Homer's ''Odyssey''. Thessaly Convention of Constantinople (1881), became part of the modern Greek state in 1881, after four and a half centuries of Ottoman Greece, Ottoman rule. Since 1987 it has formed one of the country's 13 Modern regions of Greece, regions and is further (since the Kallikratis reform of 2011) sub-divided into five regional units of Greece, regional units and 25 municipalities of Greece, municipalities. The capital of the region is Larissa. Thessaly lies in northern central Greece and borders the regions of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia to the north, Epirus (region), Epirus to the west, Central Greece (geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larissa
Larissa (; , , ) is the capital and largest city of the Thessaly region in Greece. It is the fifth-most populous city in Greece with a population of 148,562 in the city proper, according to the 2021 census. It is also the capital of the Larissa regional unit. It is a principal agricultural centre and a national transport hub, linked by road and rail with the port of Volos, the cities of Thessaloniki and Athens. The municipality of Larissa has inhabitants, while the regional unit of Larissa reached a population of (). Legend has it that Achilles was born here. Hippocrates, the "Father of Medicine", died here. Today, Larissa is an important commercial, transportation, educational, agricultural and industrial centre of Greece. The city straddles the Pineios river and N.-NE. of the city are the Mount Olympus and Mount Kissavos. Mythology According to Greek mythology, it is said that the city was founded by Acrisius, who was killed accidentally by his grandson, Perseus. There l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. As a young man, he was a partisan and protégé of the dictator Sulla, after whose death he achieved much military and political success himself. He was an ally and a rival of Julius Caesar, and died in Caesar's civil war, civil war with him. A member of the senatorial nobility, Pompey entered into a military career while still young. He rose to prominence serving Sulla as a commander in Sulla's civil war, the civil war of 83–81 BC. Pompey's success as a general while young enabled him to advance directly to his first Roman consul, consulship without following the traditional ''cursus honorum'' (the required steps to advance in a political career). He was elected as consul on three occasions (70, 55, 52 BC). He celebrated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phthia
Phthia (; or Φθίη ''Phthía, Phthíē'') was a city or district in ancient Thessaly according to Greek mythology. In Literature It is frequently mentioned in Homer's ''Iliad'' as the home of the Myrmidons, the contingent led by Achilles in the Trojan War. It was founded by Aeacus, grandfather of Achilles, and was the home of Achilles' father Peleus, mother Thetis (a sea nymph), and son Neoptolemus (who reigned as king after the Trojan War). Phthia is referenced in Plato's '' Crito'', where Socrates, in jail and awaiting his execution, relates a dream he has had (43d–44b): "I thought that a beautiful and comely woman dressed in white approached me. She called me and said: 'Socrates, may you arrive at fertile Phthia on the third day. The reference is to Homer's ''Iliad'' (ix.363), when Achilles, upset at having his war-prize, Briseis, taken by Agamemnon, rejects Agamemnon's conciliatory presents and threatens to set sail in the morning; he says that with good weathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achilles
In Greek mythology, Achilles ( ) or Achilleus () was a hero of the Trojan War who was known as being the greatest of all the Greek warriors. The central character in Homer's ''Iliad'', he was the son of the Nereids, Nereid Thetis and Peleus, king of Phthia and famous Argonauts, Argonaut. Achilles was raised in Phthia along with his childhood companion Patroclus and received his education by the centaur Chiron. In the ''Iliad'', he is presented as the commander of the mythical tribe of the Myrmidons. Achilles' most notable feat during the Trojan War was the slaying of the Trojan prince Hector outside the gates of Troy. Although the death of Achilles is not presented in the ''Iliad'', other sources concur that he was killed near the end of the Trojan War by Paris (mythology), Paris, who shot him with an arrow. Later legends (beginning with Statius' unfinished epic ''Achilleid'', written in the first century CE) state that Achilles was invulnerable in all of his body except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |