|
Eukaryotes
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal kingdom Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as flagellated cells. The leading evolutionary theory is they were created by symbiogenesis between an anaerobic Promethearchaeati archaean and an aerobic proteobacterium, which form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeplastida
The Archaeplastida (or kingdom Plantae '' sensu lato'' "in a broad sense"; pronounced ) are a major group of eukaryotes, comprising the photoautotrophic red algae (Rhodophyta), green algae, land plants, and the minor group glaucophytes. It also includes the non-photosynthetic lineage Rhodelphidia, a predatorial (eukaryotrophic) flagellate that is sister to the Rhodophyta, and probably the microscopic picozoans. The Archaeplastida have chloroplasts that are surrounded by two membranes, suggesting that they were acquired directly through a single endosymbiosis event by phagocytosis of a cyanobacterium. All other groups which have chloroplasts, besides the amoeboid genus '' Paulinella'', have chloroplasts surrounded by three or four membranes, suggesting they were acquired secondarily from red or green algae. Unlike red and green algae, glaucophytes have never been involved in secondary endosymbiosis events. The cells of the Archaeplastida typically lack centrioles and have mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
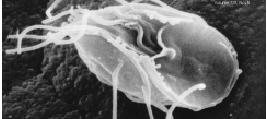
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of Amoeba, amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, Pseudopod#Morphology, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom (biology), kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup (biology), supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetics, Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, named Amorphea. Amoeboz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoba
Excavata is an obsolete, extensive and diverse Paraphyly, paraphyletic group of unicellular Eukaryote, Eukaryota. The group was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and the name latinized and assigned a rank by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic protists, and includes some important parasites of humans such as ''Giardia'' and ''Trichomonas''. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now- obsolete Protist, Protista kingdom. They were distinguished from other lineages based on electron-microscopic information about how the cells are arranged (they have a distinctive ultrastructural identity). They are considered to be a Basal_(phylogenetics), basal flagellate lineage. On the basis of phylogenomic analyses, the group was shown to contain three widely separated eukaryote groups, the discobids, metamonads, and malawimonads. A current view of the composition of the excavates is given below, indicating that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphoretickes
Diaphoretickes is a major group of eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms spanning over 400,000 species. The majority of the earth's biomass that carries out photosynthesis belongs to Diaphoretickes. In older classification systems, members of the Diaphoretickes were variously placed in the Kingdom (biology), kingdoms Protozoa or Protist, Protista. Etymology The name Diaphoretickes derives (''diaforetikés'') meaning diverse, dissimilar, referring to the wide morphology (biology), morphological and cellular diversity among members of this clade. History Eukaryotes, organisms whose cells contain a cell nucleus, nucleus, have been traditionally grouped into four kingdom (biology), kingdoms: animals, plants, fungi and protists. In the late 20th century, molecular phylogenetic analyses revealed that protists are a paraphyletic assortment of many independent evolutionary lineages or clades, from which animals, fungi and plants evolved. However, the relationships between these clades re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorphea
Amorphea is a taxonomic supergroup that includes the basal Amoebozoa and Obazoa. That latter contains the Opisthokonta, which includes the fungi, animals and the choanoflagellates. The taxonomic affinities of the members of this clade were originally described and proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. The International Society of Protistologists, the recognised body for taxonomy of protozoa, recommended in 2012 that the term Unikont be changed to Amorphea because the name "Unikont" is based on a hypothesized synapomorphy that the ISOP authors and other scientists later rejected. It includes amoebozoa, opisthokonts, and apusomonads. Taxonomic revisions within this group Thomas Cavalier-Smith proposed two new phyla: Sulcozoa, which consists of the subphyla Apusozoa ( Apusomonadida and Breviatea), and Varisulca, which includes the subphyla Diphyllatea, Discocelida, Mantamonadidae, Planomonadida and Rigifilida. Further work by Cavalier-Smith showed that Sul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |