|
Enediynes
Enediynes are organic compounds containing two triple bonds and one double bond. Enediynes are most notable for their limited use as antitumor antibiotics (known as enediyne Chemotherapy, anticancer antibiotics). They are efficient at inducing apoptosis in Cell biology, cells, but cannot differentiate Cancer cell, cancerous cells from healthy cells. Consequently, research is being conducted to increase the specificity of enediyne toxicity. Structure and reactivity A nine- or ten-membered ring containing a double bond between two triple bonds is termed the warhead of the enediyne. In this state, the warhead is inactive. Enediynes are triggered into a chemically active state via Bergman cyclization, Bergman or Myers-Saito cyclization. The triggering mechanism can be attributed to an intramolecular nucleophilic attack initiated by one of the variable regions of the molecule. Triggering can also occur via attack by an external nucleophile. Bergman cyclization restructures the ened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-1027
C-1027 or lidamycin is an antitumor antibiotic consisting of a complex of an enediyne chromophore and an apoenzyme, apoprotein. It shows antibiotic activity against most Gram-positive bacteria. It is one of the most potent cytotoxic molecules known, due to its induction of a higher ratio of DNA double-strand breaks than single-strand breaks. C-1027's chromophore contains a nine-membered enediyne that is responsible for most of the molecule's biological activity. Unlike other enediynes, this molecule contains no triggering mechanism. It is already primed to undergo the cycloaromatization reaction without external activation to produce the toxic 1,4-benzenoid diradical species. C-1027 can induce oxygen-independent interstrand DNA crosslinks in addition to the oxygen-dependent single- and double-stranded DNA breaks typically generated by other enediynes. This unique oxygen-independent mechanism suggests that C-1027 may be effective against Tumor hypoxia, hypoxic tumor cells. C-102 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calicheamicin
The calicheamicins are a class of enediyne antitumor antibiotics derived from the bacterium '' Micromonospora echinospora'', with calicheamicin γ1 being the most notable. It was isolated originally in the mid-1980s from the chalky soil, or "caliche pits", located in Kerrville, Texas. The sample was collected by a scientist working for Lederle Labs. It is extremely toxic to all cells and, in 2000, a CD33 antigen-targeted immunoconjugate N-acetyl dimethyl hydrazide calicheamicin was developed and marketed as targeted therapy against the non-solid tumor cancer acute myeloid leukemia (AML). A second calicheamicin-linked monoclonal antibody, inotuzumab ozogamicin (marketed as Besponsa), an anti-CD22-directed antibody-drug conjugate, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on August 17, 2017, for use in the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Calicheamicin γ1 and the related enediyne esperamicin are two of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
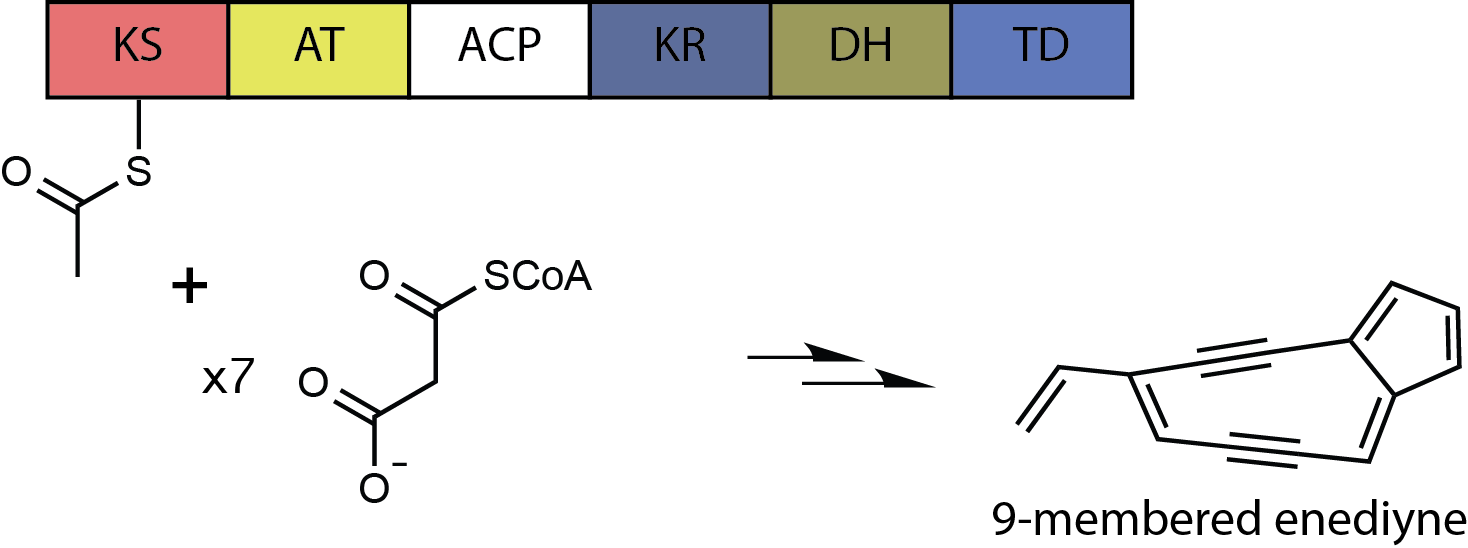
Neocarzinostatin
Neocarzinostatin (NCS) is a macromolecular chromoprotein enediyne antitumor antibiotic secreted by ''Streptomyces macromomyceticus''. It consists of two parts, a labile chromophore (the non-protein molecular entity shown at right) and a 113 amino acid protein to which the chromophore is tightly and non- covalently bound with high affinity (Kd ~ 10−10 M). The non-protein component is a very potent DNA-damaging agent; However it is extremely unstable and the role of the protein is to protect it and release it to the target DNA. Opening of the epoxide under reductive conditions present in cells creates favorable conditions for a Bergman cyclization, leading to formation of a benzenoid diradical, followed by DNA strand cleavage. Another important member of the chromoprotein group of natural products is kedarcidin. As a medicine it is among the most potent, and in Japan only it has been used against liver cancer clinically. __TOC__ Biosynthesis of NCS Chromophore The biosynt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
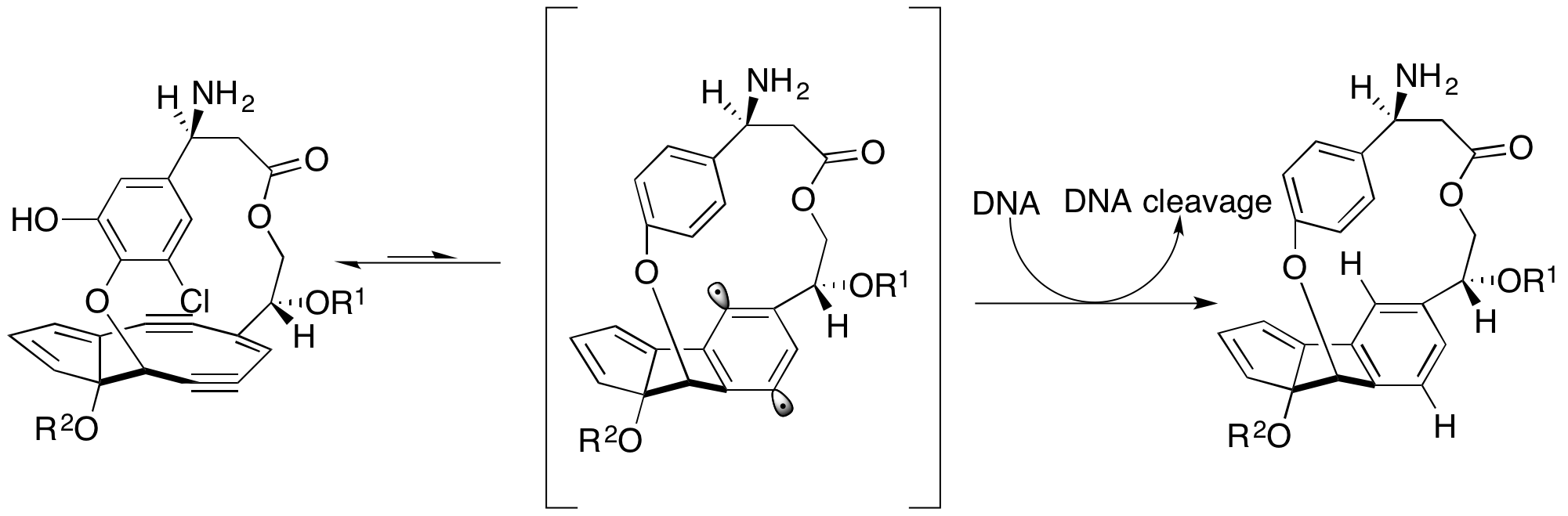
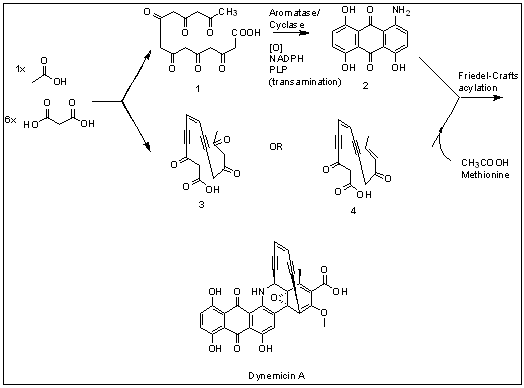
Dynemicin A
Dynemicin A is an anti-cancer enediyne drug. It displays properties which illustrate promise for cancer treatments, but still requires further research. History and background Dynemicin A was first isolated from the soil in the Gujarat State of India. It was discovered to be the natural product of the indigenous bacteria ''Micromonospora chersina''. The natural product displays a bright purple color due to the anthraquinone chromophore structure within it. Initially, this compound was isolated for its aesthetic properties as a dye until further research demonstrated its anti-cancer properties. Shortly after the compound's discovery, the Bristol-Myers Pharmaceutical Company elucidated the structure in Japan using X-ray diffraction studies of triacetyldynemicin A; a closely related compound. Synthesis The first reported chemical synthesis of dynemicin was accomplished by Myers and coworkers. Biosynthesis Dynemicin A is an antitumor natural product isolated from ''Micromonos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |