|
Ebolaviruses
The genus ''Ebolavirus'' (- or ; - or ) is a virological taxon included in the family ''Filoviridae'' (filament-shaped viruses), order ''Mononegavirales''. The members of this genus are called ebolaviruses, and encode their genome in the form of single-stranded negative-sense RNA. The six known virus species are named for the region where each was originally identified: ''Bundibugyo ebolavirus'', ''Reston ebolavirus'', ''Sudan ebolavirus'', ''Taï Forest ebolavirus'' (originally ''Côte d'Ivoire ebolavirus''), ''Zaire ebolavirus'', and ''Bombali ebolavirus''. The last is the most recent species to be named and was isolated from Angolan free-tailed bats in Sierra Leone. Each species of the genus ''Ebolavirus'' has one member virus, and four of these cause Ebola virus disease (EVD) in humans, a type of hemorrhagic fever having a very high case fatality rate. The Reston virus has caused EVD in other primates. ''Zaire ebolavirus'' has the highest mortality rate of the ebolavirus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebola Virus Disease
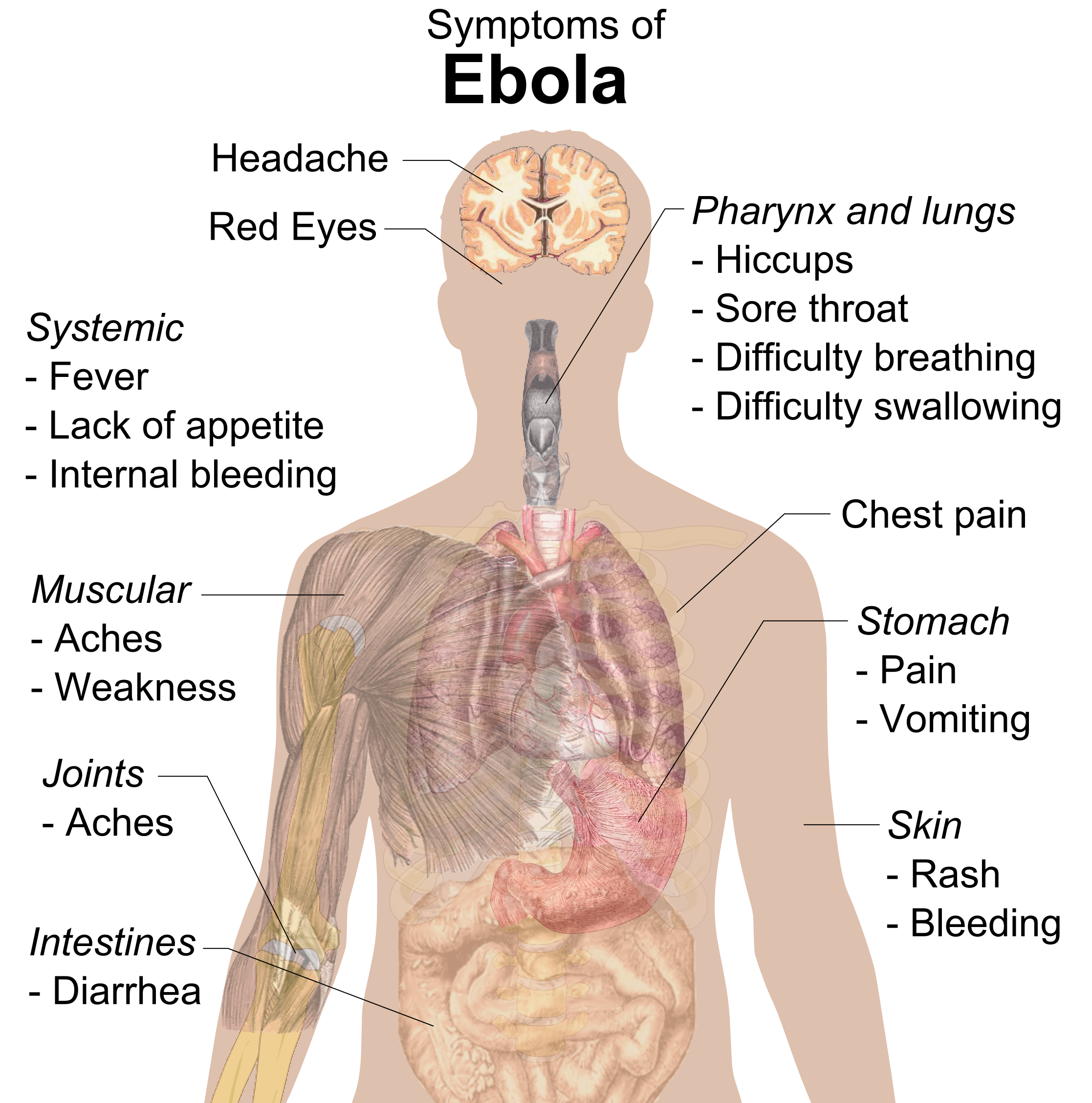
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becoming infected with the virus. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point, some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. The disease kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals, or from contact with items that have recently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebola Virus
''Zaire ebolavirus'', more commonly known as Ebola virus (; EBOV), is one of six known species within the genus '' Ebolavirus''. Four of the six known ebolaviruses, including EBOV, cause a severe and often fatal hemorrhagic fever in humans and other mammals, known as Ebola virus disease (EVD). Ebola virus has caused the majority of human deaths from EVD, and was the cause of the 2013–2016 epidemic in western Africa, which resulted in at least suspected cases and confirmed deaths. Ebola virus and its genus were both originally named for Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo), the country where it was first described, and was at first suspected to be a new "strain" of the closely related Marburg virus. The virus was renamed "Ebola virus" in 2010 to avoid confusion. Ebola virus is the single member of the species ''Zaire ebolavirus'', which is assigned to the genus '' Ebolavirus'', family '' Filoviridae'', order '' Mononegavirales''. The members of the species are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombali Ebolavirus
''Bombali ebolavirus'' or Bombali virus (BOMV) is a species of the genus '' Ebolavirus,'' first reported on 27 July 2018. It was discovered and sequenced by a PREDICT research team from the U.S. in the Bombali area in the north of Sierra Leone, west Africa. The virus was found in the Angolan free-tailed bat and the Little free-tailed bat. In 2019, the virus was demonstrated in Angolan free-tailed bats in southeast Kenya and southeast Guinea. Bombali ebolavirus has the capacity to infect human cells There are many different types of cells in the human body. Cells derived primarily from endoderm Exocrine secretory epithelial cells * Brunner's gland cell in duodenum (enzymes and alkaline mucus) *Insulated goblet cell of respiratory and ..., although it has not yet been shown to be pathogenic. The team reporting the virus also published its full genome sequence (NC_039345). See also * '' Zaire ebolavirus'' References Further reading * External links * {{Taxonba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundibugyo Ebolavirus
The species ''Bundibugyo ebolavirus'' ( ) is the taxonomic home of one virus, Bundibugyo virus (BDBV), that forms filamentous virions and is closely related to the infamous Ebola virus (EBOV). The virus causes severe disease in humans in the form of viral hemorrhagic fever and is a Select agent, World Health Organization Risk Group 4 Pathogen (requiring Biosafety Level 4-equivalent containment), National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Category A Priority Pathogen, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Category A Bioterrorism Agent, and is listed as a Biological Agent for Export Control by the Australia Group. Use of term The species ''Bundibugyo ebolavirus'' is a virological taxon (i.e. a man-made concept) that was suggested in 2008 to be included in the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The species has a single virus member, Bundibugyo virus (BDBV). The members of the species are called Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reston Ebolavirus
Reston virus (RESTV) is one of six known viruses within the genus ''Ebolavirus''. Reston virus causes Ebola virus disease in non-human primates; unlike the other five ebolaviruses, it is not known to cause disease in humans, but has caused asymptomatic infections. Reston virus was first described in 1990 as a new "strain" of Ebola virus (EBOV). It is the single member of the species ''Reston ebolavirus'', which is included into the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. Reston virus is named after Reston, Virginia, US, where the virus was first discovered. RESTV was discovered in crab-eating macaques from Hazleton Laboratories (now Labcorp Drug Development) in 1989. This attracted significant media attention due to Reston's location in the Washington, DC metro area and the lethality of a closely related Ebola virus. Despite its status as a level-4 organism, Reston virus is non-pathogenic to humans, though hazardous to monkeys; the perception of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan Ebolavirus
The species ''Sudan ebolavirus'' is a virological taxon included in the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The species has a single virus member, Sudan virus (SUDV). The members of the species are called Sudan ebolaviruses. It was discovered in 1977 and causes Ebola clinically indistinguishable from the ebola Zaire strain, but is less transmissible than it. Unlike with ebola Zaire there is no vaccine available. Nomenclature The name ''Sudan ebolavirus'' is derived from '' Sudan'' (the country in which Sudan virus was first discovered) and the taxonomic suffix ''ebolavirus'' (which denotes an ebolavirus species). The species was introduced in 1998 as ''Sudan Ebola virus''. In 2002, the name was changed to ''Sudan ebolavirus''. A virus of the genus ''Ebolavirus'' is a member of the species ''Sudan ebolavirus'' if: * it is endemic in Sudan and/or Uganda * it has a genome with three gene overlaps (''VP35''/''VP40'', ''GP''/''VP30'', ''VP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2014 West Africa Ebola Virus Outbreak
The 2013–2016 epidemic of Ebola virus disease, centered in Western Africa, was the most widespread outbreak of the disease in history. It caused major loss of life and socioeconomic disruption in the region, mainly in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone. The first cases were recorded in Guinea in December 2013; later, the disease spread to neighbouring Liberia and Sierra Leone, with minor outbreaks occurring in Ebola virus disease in Nigeria, Nigeria and Mali. Secondary infections of medical workers occurred in the United States and Spain. In addition, isolated cases were recorded in Senegal, the United Kingdom and Italy. The number of cases peaked in October 2014 and then began to decline gradually, following the commitment of substantial international resources. It caused significant mortality, with a considerable case fatality rate. By the end of the epidemic, 28,616 people had been infected; of these, 11,310 had died, for a case-fatality rate of 40%. , the World Healt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taï Forest Ebolavirus
The species ''Taï Forest ebolavirus'' () is a virological taxon included in the genus ''Ebolavirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The species has a single virus member, Taï Forest virus (TAFV). The members of the species are called Taï Forest ebolaviruses. ''Tai Forest ebolavirus'' has been seen in a single human infection due to contact with chimpanzees from the Tai Forest in Côte d'Ivoire. Nomenclature The name ''Taï Forest ebolavirus'' is derived from '' Parc National de Taï'' (the name of a national park in Côte d'Ivoire, where Taï Forest virus was first discovered) and the taxonomic suffix ''ebolavirus'' (which denotes an ebolavirus species). According to the rules for taxon naming established by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), the name ''Taï Forest ebolavirus'' is always to be capitalized, italicized, never abbreviated, and to be preceded by the word "species". The names of its members (Taï Forest ebolavir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaire
Zaire (, ), officially the Republic of Zaire (french: République du Zaïre, link=no, ), was a Congolese state from 1971 to 1997 in Central Africa that was previously and is now again known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Zaire was, by area, the third-largest country in Africa (after Sudan and Algeria), and the 11th-largest country in the world. With a population of over 23 million inhabitants, Zaire was the most-populous officially Francophone country in Africa, as well as one of the most populous in Africa. The country was a one-party totalitarian military dictatorship, run by Mobutu Sese Seko and his ruling Popular Movement of the Revolution party. Zaire was established following Mobutu's seizure of power in a military coup in 1965, following five years of political upheaval following independence from Belgium known as the Congo Crisis. Zaire had a strongly centralist constitution, and foreign assets were nationalized. The period is sometimes referre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Egypt to the north, Eritrea to the northeast, Ethiopia to the southeast, Libya to the northwest, South Sudan to the south and the Red Sea. It has a population of 45.70 million people as of 2022 and occupies 1,886,068 square kilometres (728,215 square miles), making it Africa's List of African countries by area, third-largest country by area, and the third-largest by area in the Arab League. It was the largest country by area in Africa and the Arab League until the 2011 South Sudanese independence referendum, secession of South Sudan in 2011, since which both titles have been held by Algeria. Its Capital city, capital is Khartoum and its most populated city is Omdurman (part of the metropolitan area of Khar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns, adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry grammatical information ( inflectional suffixes) or lexical information ( derivational/lexical suffixes'').'' An inflectional suffix or a grammatical suffix. Such inflection changes the grammatical properties of a word within its syntactic category. For derivational suffixes, they can be divided into two categories: class-changing derivation and class-maintaining derivation. Particularly in the study of Semitic languages, suffixes are called affirmatives, as they can alter the form of the words. In Indo-European studies, a distinction is made between suffixes and endings (see Proto-Indo-European root). Suffixes can carry grammatical information or lexical information. A word-final segment that is somewhere between a free morpheme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)