|
Eblaite Deities
Eblaite (, also known as Eblan ISO 639-3), or Palaeosyrian, is an extinct East Semitic language used during the 3rd millennium BC in Northern Syria. It was named after the ancient city of Ebla, in modern western Syria. Variants of the language were also spoken in Mari and Nagar. According to Cyrus H. Gordon, although scribes might have spoken it sometimes, Eblaite was probably not spoken much, being rather a written lingua franca with East and West Semitic features. The language was discovered through cuneiform tablets found in Ebla. Discovery The 1964 discovery at the Tell Mardikh site in Northern Syria of an ancient city from the second half of the third millennium BC completely altered archaeological knowledge of the time, as it indicated the existence of a contemporary urban culture during the Early Dynastic Period of Mesopotamia, within a geographic zone where, at the time, previous excavations had revealed nothing on the same scale. In agreement with Ignace Gel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
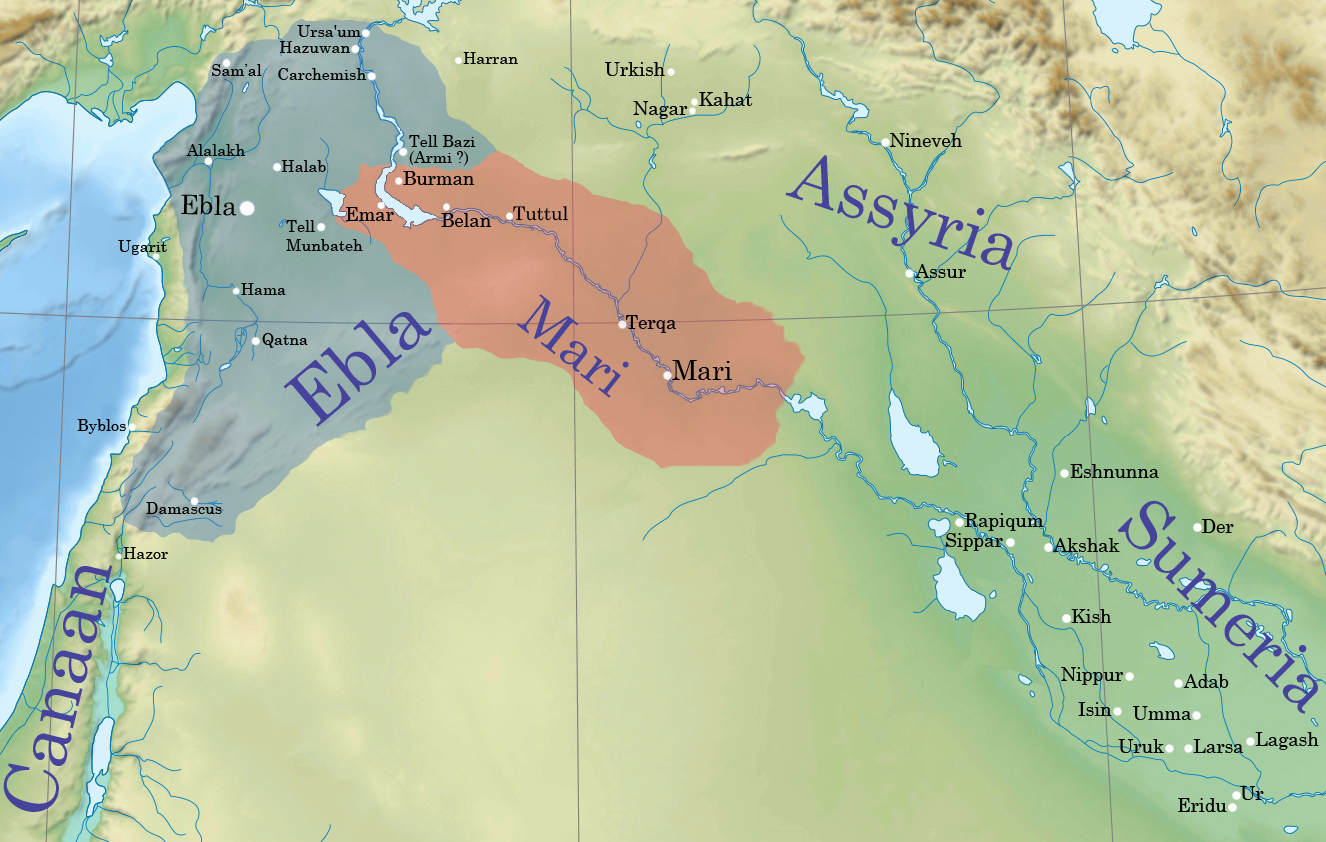
Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Ancient Egypt, Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Ancient Near East, Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitic People
Semitic people or Semites is a term for an ethnic, cultural or racial groupOn the use of the terms “(anti-)Semitic” and “(anti-) Zionist” in modern Middle Eastern discourse, Orientalia Suecana LXI Suppl. (2012) b Lutz Eberhard Edzard "In linguistics context, the term "Semitic" is generally speaking non-controversial... As an ethnic term, "Semitic" should best be avoided these days, in spite of ongoing genetic research (which also is supported by the Israeli scholarly community itself) that tries to scientifically underpin such a concept." [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexicon
A lexicon (plural: lexicons, rarely lexica) is the vocabulary of a language or branch of knowledge (such as nautical or medical). In linguistics, a lexicon is a language's inventory of lexemes. The word ''lexicon'' derives from Greek word (), neuter of () meaning 'of or for words'. Linguistic theories generally regard human languages as consisting of two parts: a lexicon, essentially a catalogue of a language's words (its wordstock); and a grammar, a system of rules which allow for the combination of those words into meaningful sentences. The lexicon is also thought to include bound morphemes, which cannot stand alone as words (such as most affixes). In some analyses, compound words and certain classes of idiomatic expressions, collocations and other phrasemes are also considered to be part of the lexicon. Dictionaries are lists of the lexicon, in alphabetical order, of a given language; usually, however, bound morphemes are not included. Size and organization Items ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Pettinato
Giovanni Pettinato (30 April 1934, in Troina – 19 May 2011, in Rome) was an Assyriologist and paleographer of writings from the ancient Near East, specializing in the Eblaite language, His major contributions to the field include the deciphering of the Eblaite script, discovered by Paolo Matthiae in 1974–75. Pettinato graduated from Heidelberg in 1968, where he had studied for ten years. In 1968 he began teaching Assyriology at the University of Rome. Pettinato died on 19 May 2011 at the age of 76. He was an emeritus of several associations, including the Accademia dei Lincei and authored several publications about the Sumerian and Mesopotamia Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...n civilizations. References 1934 births 2011 deaths Italian Assyriologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paolo Matthiae
Paolo Matthiae (born 1940) is an Italian archaeologist. He is a professor of History of Art of the Ancient Near East in the University of Rome La Sapienza; he has been Director of the Ebla Expedition since 1963—in fact, its discoverer—and has published many articles and books about Ebla and about the History of Art of Mesopotamia and Syria in general. In 1972 and 1973, Matthiae co-directed the excavation of Tell Fray in the Euphrates Valley that was to be flooded by Lake Assad, the reservoir of the Tabqa Dam which was being constructed at that time. He is a member of institutions as the Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei (Rome), the Academie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres and the Deutsches Archaeologisches Institut, and is doctor Honoris Causa of the Autonomous University of Madrid. Books *''Ebla: An Empire Rediscovered'' *''Ebla: La città rivelata'', collection «Universale Electa/Gallimard●Storia e civiltà» (nº 56), Electa/Gallimard, 1995 *''Aux origines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excavation (archaeology)
In archaeology, excavation is the exposure, processing and recording of archaeological remains. An excavation site or "dig" is the area being studied. These locations range from one to several areas at a time during a project and can be conducted over a few weeks to several years. Excavation involves the recovery of several types of data from a site. This data includes artifacts (portable objects made or modified by humans), features (non-portable modifications to the site itself such as post molds, burials, and hearths), ecofacts (evidence of human activity through organic remains such as animal bones, pollen, or charcoal), and archaeological context (relationships among the other types of data).Kelly&Thomas (2011). ''Archaeology: down to earth'' (4th ed.). Belmont, Calif.: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning. Before excavating, the presence or absence of archaeological remains can often be suggested by, non-intrusive remote sensing, such as ground-penetrating radar. Basic inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramaic
Aramaic (; ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, Sinai, southeastern Anatolia, and Eastern Arabia, where it has been continually written and spoken in different varieties for over three thousand years. Aramaic served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires, particularly the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Babylonian Empire, and Achaemenid Empire, and also as a language of divine worship and religious study within Judaism, Christianity, and Gnosticism. Several modern varieties of Aramaic are still spoken. The modern eastern branch is spoken by Assyrians, Mandeans, and Mizrahi Jews.{{cite book , last1=Huehnergard , first1=John , author-link1=John Huehnergard , last2=Rubin , first2=Aaron D. , author-link2=Aaron D. Rubin , date=2011 , editor-last=Weninger , editor-first=Stefan , title=The Semitic Languages: An International Handbook , pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Semitic Languages
The West Semitic languages are a proposed major sub-grouping of Semitic languages. The term was first coined in 1883 by Fritz Hommel.The Semitic Languages: An International Handbook, Chapter V page 425 The grouping supported by Semiticists like Robert Hetzron and John Huehnergard divides the Semitic language family into two branches: Eastern and Western. The West Semitic languages consist of the clearly defined sub-groups: |
Amorite Language
Amorite is an extinct early Semitic language, formerly spoken during the Bronze Age by the Amorite tribes prominent in ancient Near Eastern history. It is known from Ugaritic, which is classed by some as its westernmost dialect, and from non- Akkadian proper names recorded by Akkadian scribes during periods of Amorite rule in Babylonia (the end of the 3rd and the beginning of the 2nd millennium BC), notably from Mari and to a lesser extent Alalakh, Tell Harmal and Khafajah. Occasionally, such names are also found in early Egyptian texts; and one place name, "Sənīr" (שְׂנִיר) for Mount Hermon, is known from the Bible (Book of Deuteronomy, ). Amorite is considered an archaic Northwest Semitic language. Notable characteristics include the following: * The usual Northwest Semitic imperfective-perfective distinction is found: ''Yantin-Dagan'', 'Dagon gives' (''ntn''); ''Raṣa-Dagan'', 'Dagon was pleased' (rṣy). It included a 3rd-person suffix -''a'' (unlike Akkadian o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
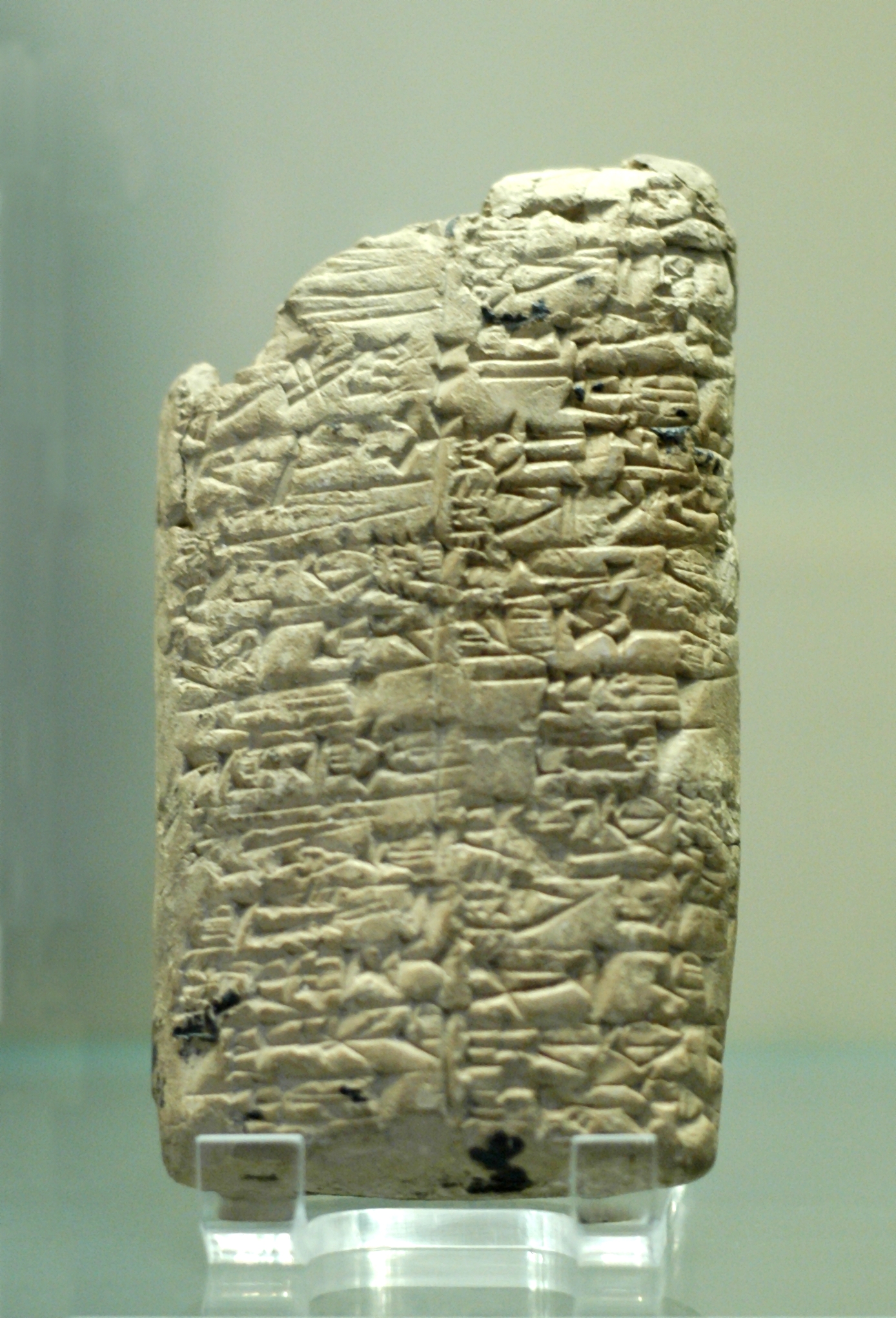
Clay Tablet
In the Ancient Near East, clay tablets (Akkadian language, Akkadian ) were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age. Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay tablet with a stylus often made of Reed (plant), reed (reed pen). Once written upon, many tablets were dried in the sun or air, remaining fragile. Later, these unfired clay tablets could be soaked in water and recycled into new clean tablets. Other tablets, once written, were either deliberately fired in hot kilns, or inadvertently fired when buildings were burnt down by accident or during conflict, making them hard and durable. Collections of these clay documents made up the first archives. They were at the root of the first library, libraries. Tens of thousands of written tablets, including many fragments, have been found in the Middle East. Most of the documents on tablets that survive from the Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |