|
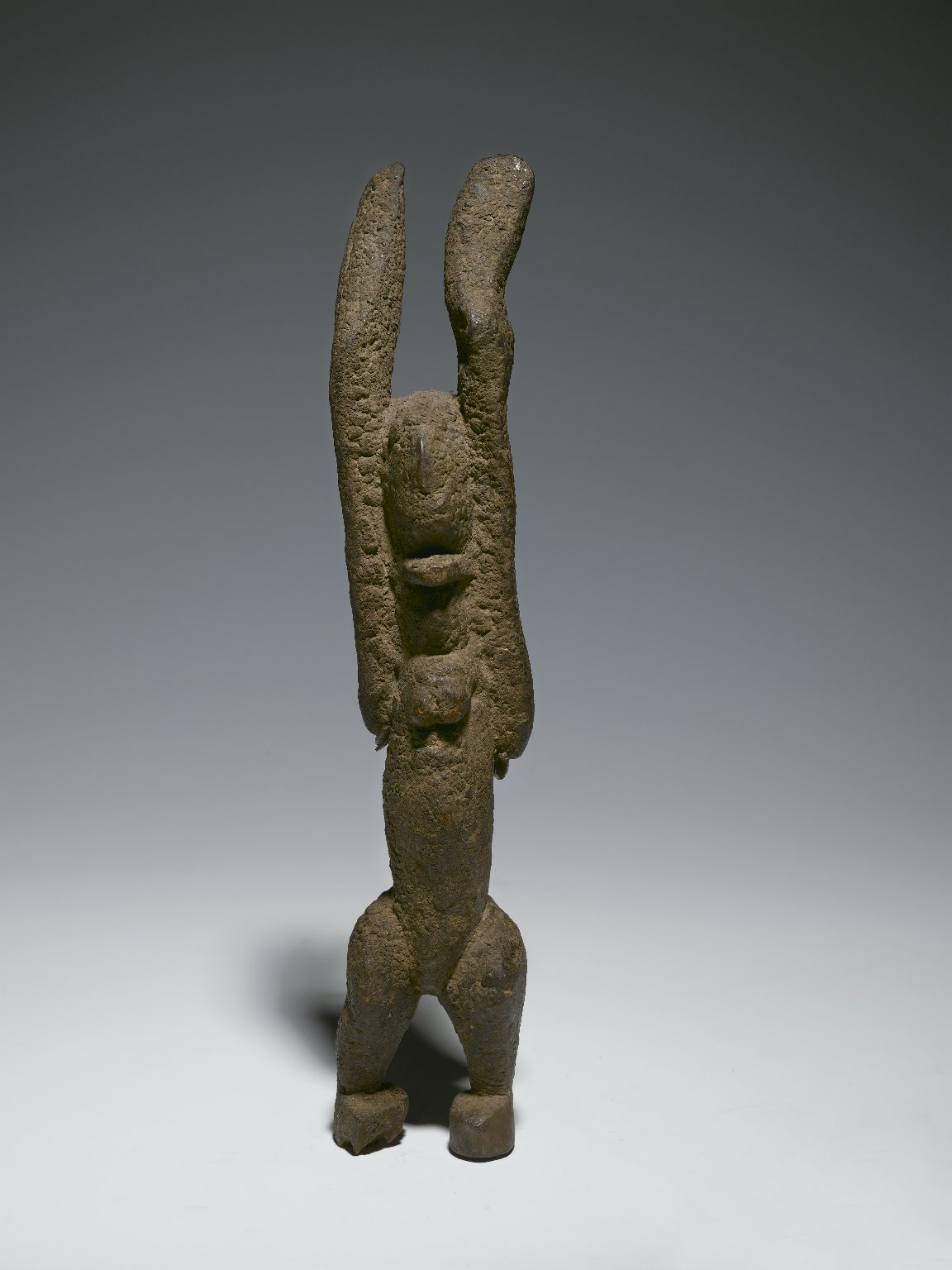
Dogon Religion
The Dogon religion is the traditional religious or spiritual beliefs of the Dogon people of Mali. Dogons who adhere to the Dogon religion believe in one Supreme Creator called Amma (or Ama). Insoll, Timothy, ''Archaeology, Ritual, Religion'', Routledge (2004), p. 123–125, (retrieved March 3, 2020/ref> They also believe in ancestral spirits known as the Nommo also referred to as "Water Spirits". Veneration of the dead is an important element in their spiritual belief. They hold ritual mask dances immediately after the death of a person and sometimes long after they have passed on to the next life. Twins, "the need for duality and the doubling of individual lives" (masculine and feminine principles) is a fundamental element in their belief system. Like other traditional African religions, balance, and reverence for nature are also key elements. The Dogon religion is an ancient religion or spiritual system. The Dogon religion, cosmogony, cosmology and astronomy have been su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brooklyn Museum 1989
Brooklyn is a borough of New York City located at the westernmost end of Long Island in the State of New York. Formerly an independent city, the borough is coextensive with Kings County, one of twelve original counties established under English rule in 1683 in what was then the Province of New York. As of the 2020 United States census, the population stood at 2,736,074, making it the most populous of the five boroughs of New York City, and the most populous county in the state.Table 2: Population, Land Area, and Population Density by County, New York State - 2020 |
Cosmogony
Cosmogony is any model concerning the origin of the cosmos or the universe. Overview Scientific theories In astronomy, cosmogony is the study of the origin of particular astrophysical objects or systems, and is most commonly used in reference to the origin of the universe, the Solar System, or the Earth–Moon system. The prevalent physical cosmology, cosmological scientific theory, model of the early development of the universe is the Big Bang theory. Sean M. Carroll, who specializes in Physical cosmology, theoretical cosmology and Field (physics), field theory, explains two competing explanations for the origins of the Gravitational singularity, singularity, which is the center of a space in which a characteristic is limitless (one example is the singularity of a black hole, where gravity is the characteristic that becomes infinite). It is generally accepted that the universe began at a point of singularity. When the universe started to expand, the Big Bang occurred, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With nearly billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Demographics of Africa, Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will exceed 3.8 billion people by 2100. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including Geography of Africa, geography, Climate of Africa, climate, corruption, Scramble for Africa, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
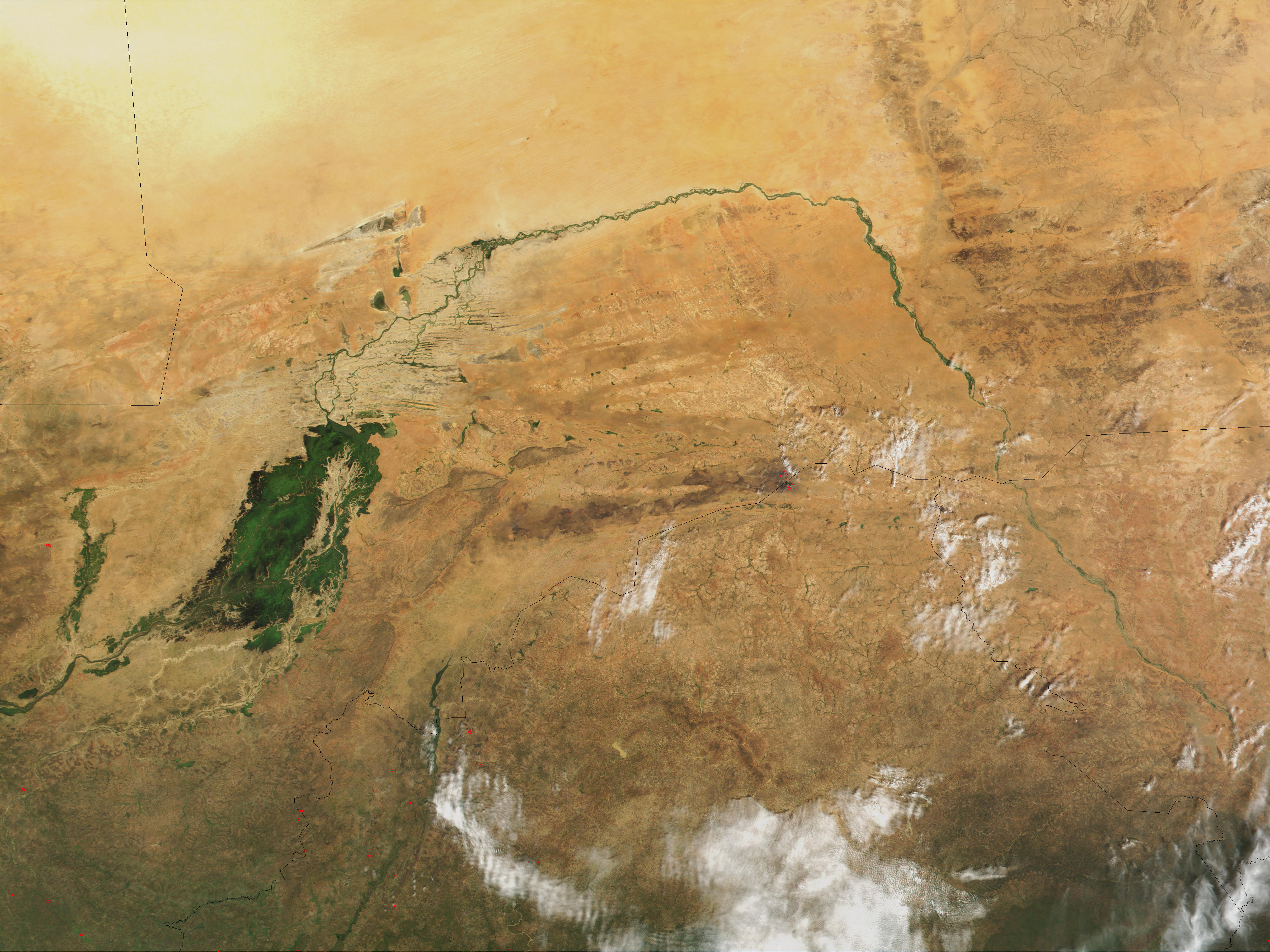
Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Niger, on the border with Benin and then through Nigeria, discharging through a massive River delta, delta, known as the Niger Delta, into the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean. The Niger is the third-longest river in Africa, exceeded by the Nile and the Congo River. Its main tributary is the Benue River. Etymology The Niger has different names in the different languages of the region: * Fula language, Fula: ''Maayo Jaaliba'' * Manding languages, Manding: ''Jeliba'' or ''Joliba'' "great river" * Tuareg languages, Tuareg: ''Eġərəw n-Igərǝwăn'' "river of rivers" * Songhay languages, Songhay: ''Isa'' "the river" * Zarma language, Zarma: ''Isa Beeri'' "great river" * Hausa language, Hausa: ''Kwara'' *Nupe language, Nupe: ''Èdù'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and dependent territories in Africa, African countries and territories that are situated fully in that specified region, the term may also include polities that only have part of their territory located in that region, per the definition of the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations (UN). This is considered a non-standardised geographical region with the number of countries included varying from 46 to 48 depending on the organisation describing the region (e.g. United Nations, UN, World Health Organization, WHO, World Bank, etc.). The Regions of the African Union, African Union (AU) uses a different regional breakdown, recognising all 55 member states on the continent—grouping them into five distinct and standard regions. The te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kim Stallwood
Kim W. Stallwood (born 1955) is a British animal rights advocate, author, independent scholar, and consultant. He is European director of the Animals and Society Institute, an animal rights think tank. He was executive editor of ''The Animals' Agenda'', an animal rights magazine (1993–2002), and is the editor of ''Speaking Out for Animals'' (2001) and ''A Primer on Animal Rights'' (2002). Stallwood blogs under the name Grumpy Vegan. Life and work Stallwood was born and raised in Camberley, Surrey, England. Stallwood is a former national director of People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (1987–1992), campaigns officer for the British Union for the Abolition of Vivisection (1981–1985), and national organizer for Compassion in World Farming (1976–1978), for which he remains a consultant. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indiana University Press
Indiana University Press, also known as IU Press, is an academic publisher founded in 1950 at Indiana University that specializes in the humanities and social sciences. Its headquarters are located in Bloomington, Indiana. IU Press publishes approximately 100 new books annually, in addition to 38 academic journals, and maintains a current catalog comprising some 2,000 titles. Indiana University Press primarily publishes in the following areas: African, African American, Asian, cultural, Jewish, Holocaust, Middle Eastern studies, Russian and Eastern European, and women's and gender studies; anthropology, film studies, folklore, history, bioethics, music, paleontology, philanthropy, philosophy, and religion. IU Press undertakes extensive regional publishing under its Quarry Books imprint. History IU Press began in 1950 as part of Indiana University's post-war growth under President Herman B Wells. Bernard Perry, son of Harvard philosophy professor Ralph Barton Per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International African Institute
The International African Institute (IAI) was founded (as the International Institute of African Languages and Cultures - IIALC) in 1926 in London for the study of African languages. Frederick Lugard was the first chairman (1926 to his death in 1945); Diedrich Hermann Westermann (1926 to 1939) and Maurice Delafosse (1926) were the initial co-directors. Since 1928, the IAI has published a quarterly journal, ''Africa''. For some years during the 1950s and 1960s, the assistant editor was the novelist Barbara Pym. The IAI's mission is "to promote the education of the public in the study of Africa and its languages and cultures". Its operations includes seminars, journals, monographs, edited volumes and stimulating scholarship within Africa. Publications The IAI has been involved in scholarly publishing since 1927. Scholars whose work has been published by the institute include Emmanuel K. Akyeampong, Samir Amin, Karin Barber, Alex de Waal, Patrick Chabal, Mary Douglas, E. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the world". In 1731, German philosopher Christian Wolff used the term cosmology in Latin (''cosmologia'') to denote a branch of metaphysics that deals with the general nature of the physical world. Religious or mythological cosmology is a body of beliefs based on mythological, religious, and esoteric literature and traditions of creation myths and eschatology. In the science of astronomy, cosmology is concerned with the study of the chronology of the universe. Physical cosmology is the study of the observable universe's origin, its large-scale structures and dynamics, and the ultimate fate of the universe, including the laws of science that govern these areas. It is investigated by scientists, including astronomers and physicists, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogotommeli
Ogotemmeli (also: Ogotemmêli or Ogotommeli, died 1962) was the Dogon elder and hogon who narrated the cosmogony, cosmology and symbols of the Dogon people to French anthropologist Marcel Griaule during the 1930s, 1940s, and 1950s, that went on to be documented and adapted by contemporary scholars. A lot of what is known about the Dogon religion, cosmogony and symbolism came from Griaule's work, which in turn came from Ogotemmeli—who taught it to him.Indian Council for Africa, Indian Centre for Africa; ''Africa Quarterly, Volumes 45–46'', Indian Centre for Africa (2006), p. 51. Early life and work Ogotommeli was blind since his youth as a result of his gun accidentally exploding in his face during a hunting expedition. That incident occurred as he was about to fire at a porcupine. Despite the painful accident and his disability, Ogotemmeli attributed it to fate. As a diviner, elder and hogon, Ogotemmeli recounted that this fate was previously made known to him, but he chos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hogon
A hogon is a spiritual leader in a Dogon village who plays an important role in Dogon religion. The life of a hogon A hogon is a religious figure as well as a temporal authority; the hogon may be hereditary or may be chosen from among the village elders—custom varies from place to place. The hogon is always a man. After being chosen, a hogon must pass through several months without washing or shaving. After initiation, he wears a red cap, and a pearl bracelet. Hogon live alone and should be celibate, but a village girl may act as a maid. Nobody should touch the hogon. Ritual The hogon has a key role in village rituals and in ensuring fertility and germination. The hogon is central to a wide range of fertility and marriage rituals, which are closely related to Dogon origin myths. The hogon may conduct rituals in the Sanctuaire de Binou, a special building the door of which is blocked with rocks. Creation myth According to legend, the first hogon, Lebe, was descended from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcel Griaule
Marcel Griaule (16 May 1898 – 23 February 1956) was a French author and anthropologist known for his studies of the Dogon people of West Africa, and for pioneering ethnographic field studies in France. He worked together with Germaine Dieterlen and Jean Rouch on African subjects. His publications number over 170 books and articles for scholarly journals. Biography Born in Aisy-sur-Armançon, Griaule received a good education and was preparing to become an engineer and enrolled at the prestigious Lycée Louis-le-Grand when in 1917 at the end of World War I he volunteered to become a pilot in the French Air Force. In 1920 he returned to university, where he attended the lectures of Marcel Mauss and Marcel Cohen. Intrigued by anthropology, he gave up plans for a technical career. In 1927 he received a degree from the École Nationale de Langues Orientales, where he concentrated on Amharic and Ge'ez. Between 1928 and 1933 Griaule participated in two large-scale et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |