|
Dinocaridida
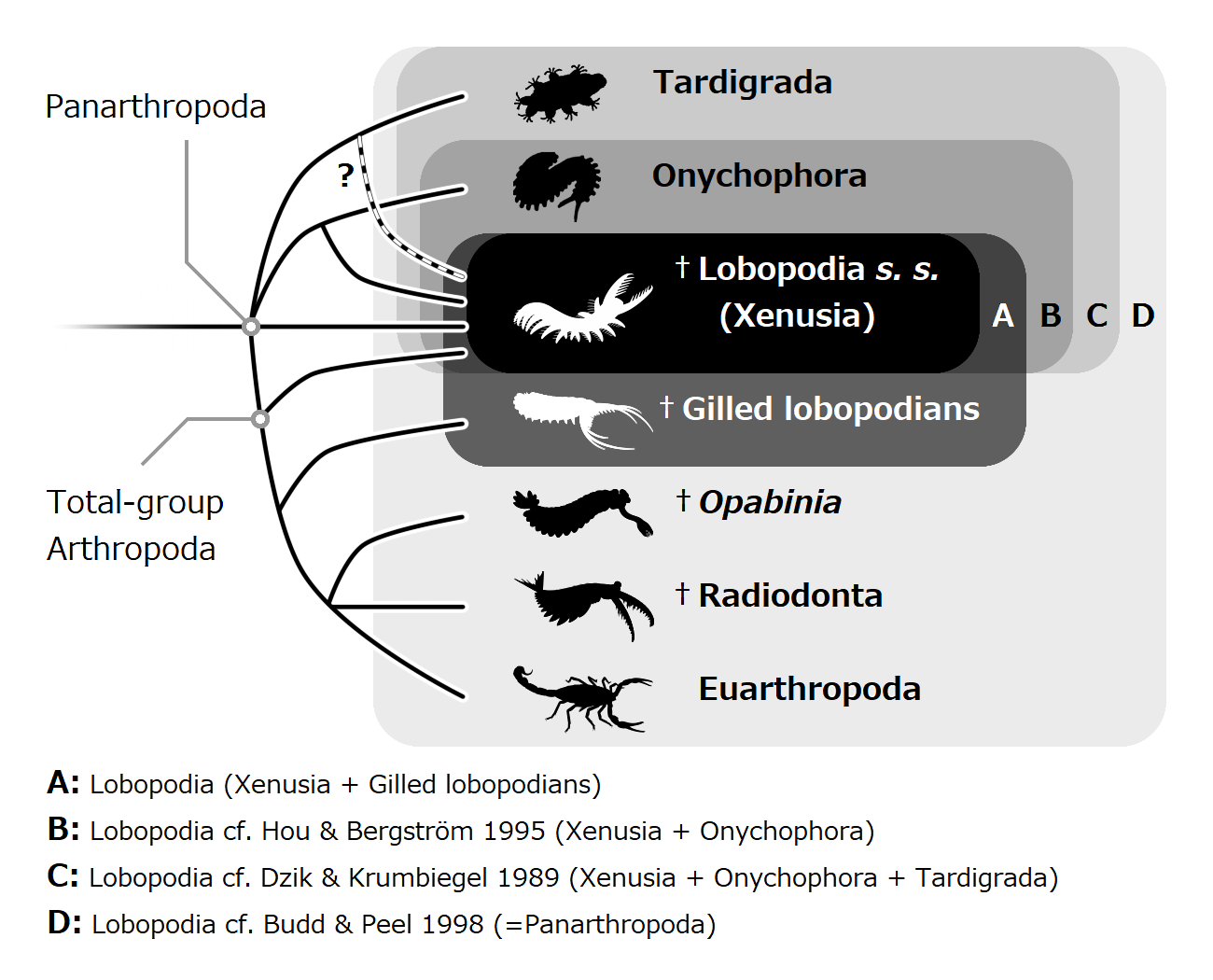
DinocarididaGreek for ''deinos'' "terrible" and Latin for ''caris'' "crab" – sometimes informally spelt Dinocarida, but the second 'id' is linguistically correct – see is a proposed fossil taxon of basal arthropods, which flourished during the Cambrian period and survived up to Early Devonian. Characterized by a pair of frontal appendages and series of body flaps, the name of Dinocaridids (Greek for ''deinos'' "terrible" and Latin for ''caris'' "crab") refers to the suggested role of some of these members as the largest marine predators of their time. Dinocaridids are occasionally referred to as the 'AOPK group' by some literatures, as the group composed of Radiodonta (''Anomalocaris'' and relatives), Opabiniidae (''Opabinia'' and relatives), and the "gilled lobopodians" ''Pambdelurion'' and Kerygmachelidae. It is most likely paraphyletic, with Kerygmachelidae and ''Pambdelurion'' more basal than the clade compose of Opabiniidae, Radiodonta and other arthropods. Anatomy D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerygmachela
''Kerygmachela kierkegaardi'' is a Kerygmachelidae, kerygmachelid Lobopodia#Gilled lobopodians, gilled lobopodian from the Cambrian Stage 3 aged Sirius Passet Lagerstätte in northern Greenland. Its anatomy strongly suggests that it, along with its relative ''Pambdelurion whittingtoni'', was a close relative of radiodont (''Anomalocaris'' and relatives) and euarthropods. The Generic name (biology), generic name "''Kerygmachela''" derives from the Greek language, Greek words ''Kerygma'' (proclamation) and ''Chela'' (claw), in reference to the flamboyant frontal appendages. The Specific name (zoology), specific name, "''kierkegaardi''" honors Denmark, Danish philosopher Søren Kierkegaard. Morphology The head of ''Kerygmachela'' possesses a pair of well-developed frontal appendages which correspond to those of other Dinocaridida, dinocaridids and Lobopodia#Siberion and similar taxa, siberiid lobopodians. Each of them terminates in a series of long spines. A pair of sessile, sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobopodia
Lobopodians are members of the informal group Lobopodia (), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998). They are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, marine worm-like fossil panarthropods such as '' Aysheaia'' and '' Hallucigenia''. However, other genera like '' Kerygmachela'' and '' Pambdelurion'' (which have features similar to other groups) are often referred to as “gilled lobopodians”. The oldest near-complete fossil lobopodians date to the Lower Cambrian; some are also known from Ordovician, Silurian and Carboniferous Lagerstätten. Some bear toughened claws, plates or spines, which are commonly preserved as carbonaceous or mineralized microfossils in Cambrian strata. The grouping is considered to be paraphyletic, as the three living panarthropod groups (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opabiniidae
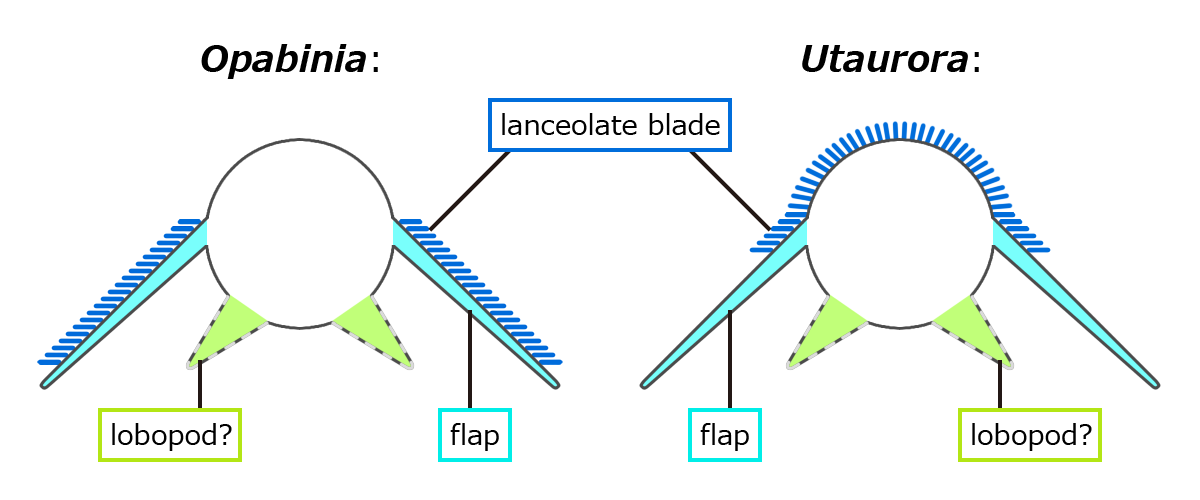
Opabiniidae is an extinct family of marine stem-arthropods. Its type and best-known genus is ''Opabinia''. It also contains ''Utaurora, and Mieridduryn''. Opabiniids closely resemble radiodonts, but their frontal appendages were basally fused into a proboscis. Opabiniids also distinguishable from radiodonts by setal blades covering at least part of the body flaps and serrated caudal rami. History of study Opabiniidae was named by Charles Doolittle Walcott in 1912, alongside its type species ''Opabinia''. Walcott interpreted Opabiniidae as a family of anostracan crustaceans, most closely related to Thamnocephalidae. ''Opabinia'' was restudied in the 1970s, and reinterpreted as a stranger animal. Stephen Jay Gould referred to ''Opabinia'' as a "weird wonder", and an illustration of ''Opabinia'' prompted laughter when it was first revealed at a paleontological conference. In 2022, more opabiniids were discovered. That being ''Utaurora'', and '' Mieridduryn''. '' Myoscolex'' f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobopodia
Lobopodians are members of the informal group Lobopodia (), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998). They are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, marine worm-like fossil panarthropods such as '' Aysheaia'' and '' Hallucigenia''. However, other genera like '' Kerygmachela'' and '' Pambdelurion'' (which have features similar to other groups) are often referred to as “gilled lobopodians”. The oldest near-complete fossil lobopodians date to the Lower Cambrian; some are also known from Ordovician, Silurian and Carboniferous Lagerstätten. Some bear toughened claws, plates or spines, which are commonly preserved as carbonaceous or mineralized microfossils in Cambrian strata. The grouping is considered to be paraphyletic, as the three living panarthropod groups (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opabinia
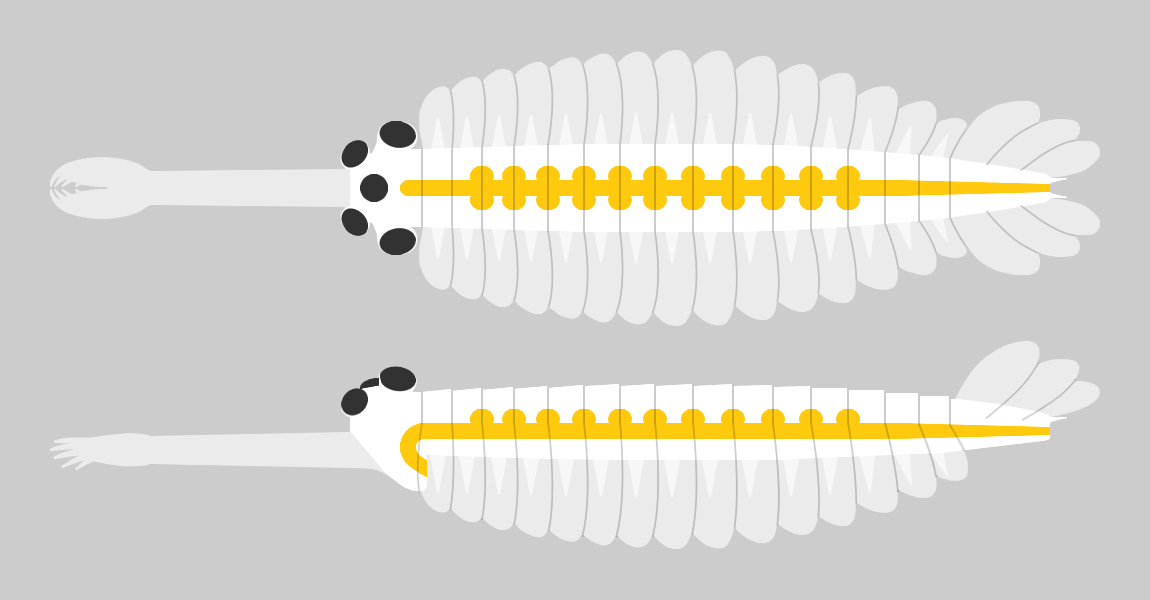
''Opabinia regalis'' is an extinct, stem group marine arthropod found in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale Lagerstätte (505 million years ago) of British Columbia. ''Opabinia'' was a soft-bodied animal, measuring up to 7 cm in body length, and had a segmented trunk with flaps along its sides and a fan-shaped tail. The head showed unusual features: five eyes, a mouth under the head and facing backwards, and a clawed proboscis that most likely passed food to its mouth. ''Opabinia'' lived on the seafloor, using the proboscis to seek out small, soft food. Free abstract at Fewer than twenty good specimens have been described; 3 specimens of ''Opabinia'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they constitute less than 0.1% of the community. When the first thorough examination of ''Opabinia'' in 1975 revealed its unusual features, it was thought to be unrelated to any known phylum, or perhaps a relative of arthropod and annelid ancestors. However, later studies since l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euarthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiodonta
Radiodonta is an extinct Order (biology), order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and were used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts were among the earliest large predators, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa ''Anomalocaris, Anomalocaris canadensis'', ''Hurdia, Hurdia victoria'', ''Peytoia nathorsti'', ''Titanokorys gainesii, Titanokorys gainesi, Cambroraster, Cambroraster falcatus'' and ''Amplectobelua, Amplectobelua symbrachiata''. The later surviving members include the subfamily Aegirocassisinae from the Early Ordovician of Morocco and the Early Devonian member ''Schinderhannes bartelsi'' from Germany. Etymology The name Radiodonta (Latin for ''radius'' "spoke of a wheel" and Greek for ''odoús'' "tooth") refers to the radial arrang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerygmachelidae
Kerygmachelidae is a family of gilled lobopodians (stem-arthropods with flapping trunk appendages and radial mouths) from the Cambrian period. Currently three genera are included in the family: ''Kerygmachela'' from the lower Cambrian of Greenland, '' Utahnax'' from the middle Cambrian of Utah, and '' Mobulavermis'' from the lower-middle Cambrian of Nevada. These animals are characterized by well developed frontal appendages similar to other dinocaridids like the radiodonts Radiodonta is an extinct order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and were used for a variety ..., except the ones present in these genera are horizontal to one another, and do not curve downward. These animals were most likely nektonic predators, using their large trunk flaps to swim in the water column, and using their frontal appendages to grab small-siz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Youti
''Youti'' (meaning "larva") is an extinct genus of dinocaridid arthropods from the Cambrian Maotianshan Shales of Yunnan Province, China. It was described after using computational approaches to visualize the internal details preserved inside the fossil. The genus contains a single species, ''Y. yuanshi'', known from a larval individual preserved in a carbonate nodule. The internal organs were well-preserved by the fossilization process and it was possible to study the structure using synchrotron scanning electron microscopy and X-ray computed tomography. The specimen shows lobopod legs, and a onychophora-like peripheral haemolymph system. Based on its anatomical characteristics, Smith et al. place the species in the arthropod clade containing ''Anomalocaris'', ''Opabinia'', ''Pambdelurion'' and ''Kerygmachela ''Kerygmachela kierkegaardi'' is a Kerygmachelidae, kerygmachelid Lobopodia#Gilled lobopodians, gilled lobopodian from the Cambrian Stage 3 aged Sirius Passet Lagerstä ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pambdelurion
''Pambdelurion'' is an extinct genus of Panarthropoda, panarthropod from the Cambrian aged Sirius Passet site in northern Greenland. Like the morphologically similar ''Kerygmachela'' from the same locality, ''Pambdelurion'' is thought to be closely related to arthropods, combining characteristics of "lobopodians" with those of primitive arthropods. Description ''Pambdelurion'' was large for a Cambrian animal, and is estimated to have reached a length of . ''Omnidens'', an organism from China that closely resembles ''Pambdelurion'' and may even be synonymous with it, reached even larger sizes, estimated to be based on the proportions of ''Pambdelurion''. The head of ''Pambdelurion'' bore a large pair of frontal appendages, homologous to the antennae of onychophorans and frontal appendages of Radiodonta, radiodonts. These frontal appendages were weakly muscled and relatively soft, suggesting they may have served primarily as sensory organs, rather than for grasping prey. Between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnidens
''Omnidens'', meaning "all-tooth", is an extinct genus of large Cambrian animal known only from a series of large mouth apparatus and sclerotized talon-like structures, originally mistaken as the mouthparts of anomalocaridids. When first named, it was interpreted as a giant priapulid, but is now considered a panarthropod. Its mouth apparatus closely resembles that of the smaller gilled lobopodian ''Pambdelurion'', indicating it is likely to have been a close relative of that species, potentially even synonymous. With a maximum estimated body length of , ''Omnidens'' is suggested to have been the largest known free-living Cambrian organism. ''Omnidens'' fossils are found in the Maotianshan Shales in the Yunnan Province of southern China, and are especially abundant from the slightly younger Xiaoshiba Lagerstätte locality. History The first-described specimen of ''Omnidens'' was first described in 1994. At the time, it was interpreted as the oral cone of an anomalocaridid, and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |