|
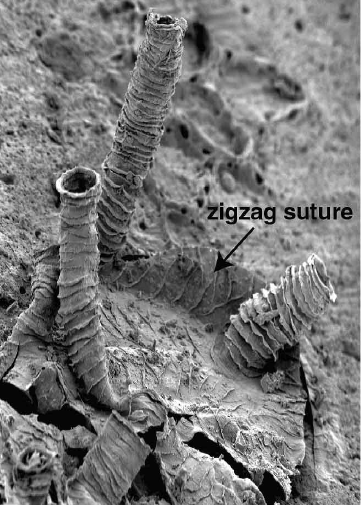
Dendroidea
Graptolites are a group of colonial animals, members of the subclass Graptolithina within the class Pterobranchia. These filter-feeding organisms are known chiefly from fossils found from the Middle Cambrian (Miaolingian, Wuliuan) through the Lower Carboniferous ( Mississippian). A possible early graptolite, ''Chaunograptus'', is known from the Middle Cambrian. Recent analyses have favored the idea that the living pterobranch '' Rhabdopleura'' represents an extant graptolite which diverged from the rest of the group in the Cambrian. Fossil graptolites and ''Rhabdopleura'' share a colony structure of interconnected zooids housed in organic tubes (theca) which have a basic structure of stacked half-rings (fuselli). Most extinct graptolites belong to two major orders: the bush-like sessile Dendroidea and the planktonic, free-floating Graptoloidea. These orders most likely evolved from encrusting pterobranchs similar to ''Rhabdopleura''. Due to their widespread abundance, pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterobranchia
Pterobranchia, members of which are often called pterobranchs, is a class of small worm-shaped animals. They belong to the Hemichordata, and live in secreted tubes on the ocean floor. Pterobranchia feed by filtering plankton out of the water with the help of cilia attached to tentacles. There are about 25 known living pterobranch species in three genera, which are '' Rhabdopleura'', '' Cephalodiscus'', and '' Atubaria''. On the other hand, there are several hundred extinct genera, some of which date from the Cambrian Period. The class Pterobranchia was established by Ray Lankester in 1877. It contained, at that time, the single genus '' Rhabdopleura''. ''Rhabdopleura'' was at first regarded as an aberrant polyzoon, but when the ''Challenger'' report on '' Cephalodiscus'' was published in 1887, it became clear that ''Cephalodiscus'', the second genus now included in the order, had affinities with the Enteropneusta. Electron microscope studies have suggested that pterobranch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sessility (motility)
Sessility is the biological property of an animal describing its lack of a means of self-locomotion. Sessile animals for which natural ''motility'' is absent are normally immobile. This is distinct from the botanical concept of sessility, which refers to an organism or biological structure attached directly by its base without a stalk. Sessile animals can move via external forces (such as water currents), but are usually permanently attached to something. Organisms such as corals lay down their own substrate from which they grow. Other organisms grow from a solid object, such as a rock, a dead tree trunk, or a human-made object such as a buoy or ship's hull. Mobility Sessile animals typically have a motile phase in their development. Sponges have a motile larval stage and become sessile at maturity. Conversely, many jellyfish develop as sessile polyps early in their life cycle. In the case of the cochineal, it is in the nymph stage (also called the crawler stage) that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Carboniferous
Lower may refer to: * ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker *Lower (surname) *Lower Township, New Jersey *Lower Receiver (firearms) *Lower Wick Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is situated about five miles south west of Dursley, eighteen miles southwest of Gloucester and fifteen miles northeast of Bristol. Lower Wick is within the civil ... Gloucestershire, England See also * Nizhny {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian (geology)
The Mississippian ( ), also known as Lower Carboniferous or Early Carboniferous, is a subperiod in the geologic timescale or a subsystem of the geologic record. It is the earlier of two subperiods of the Carboniferous period lasting from roughly 358.9 to 323.2 million years ago. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Mississippian are well identified, but the exact start and end dates are uncertain by a few million years. The Mississippian is so named because rocks with this age are exposed in the Mississippi Valley. The Mississippian was a period of marine transgression in the Northern Hemisphere: the sea level was so high that only the Fennoscandian Shield and the Laurentian Shield were dry land. The cratons were surrounded by extensive delta systems and lagoons, and carbonate sedimentation on the surrounding continental platforms, covered by shallow seas. In North America, where the interval consists primarily of marine limestones, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaunograptus
''Chaunograptus'' is a genus of putative graptolite known from the Middle Cambrian The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ... Burgess Shale. 11 specimens of ''Chaunograptus'' are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.02% of the community. Species * ''Chaunograptus contortus'' * ''Chaunograptus gemmatus'' * ''Chaunograptus scandens'' References External links * Burgess Shale fossils Graptolite genera Cambrian genus extinctions {{cambrian-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish, and baleen whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa, microscopic fungi, and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. fresh water, Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in lakes and rivers. Mostly, plankton just drift where currents take them, though some, like jellyfish, swim slowly but not fast enough to generally overcome the influence of currents. Although plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, there are also airborne versions that live part of their lives drifting in the at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miaolingian
The Miaolingian is the third Series of the Cambrian Period, and was formally named in 2018. It lasted from about to million years ago and is divided in ascending order into 3 stages: the Wuliuan, Drumian, and Guzhangian. The Miaolingian is preceded by the unnamed Cambrian Series 2 and succeeded by the Furongian series. It is named after the Miaoling Mountains in southeastern Guizhou Province, China. Definition A number of proposals for fossils and type sections were made before it was formally ratified in 2018. The most promising fossil markers were seen to be the respective first appearances of either trilobite species ''Ovatoryctocara granulata'' or ''Oryctocephalus indicus'', which both have an age close to million years ago. After some deliberation, the FAD of ''Oryctocephalus indicus'' was chosen to be the lower boundary marker, and the GSSP was placed in the Kaili Formation, Wuliu-Zengjiayan, Guizhou, China. The Miaolingian-Furongian boundary has the same definition a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Fossils
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. "Biostratigraphy." ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Biology'', 8th ed., Oxford University Press, 2019. The primary objective of biostratigraphy is ''correlation'', demonstrating that a particular horizon in one geological section represents the same period of time as another horizon at a different section. Fossils within these strata are useful because sediments of the same age can look completely different, due to local variations in the sedimentary environment. For example, one section might have been made up of clays and marls, while another has more chalky limestones. However, if the fossil species recorded are similar, the two sediments are likely to have been laid down around the same time. Ideally these fossils are used to help identify biozones, as they make up the basic biostratigraphy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period Megaannum, Ma (million years ago) to the start of the Silurian Period Ma. The Ordovician, named after the Celtic Britons, Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same Rock (geology), rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed Stratum, strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |