|
Cécile Dolmetsch
Cécile Dolmetsch became Cécile Dolmetsch Ward (22 March 1904 – 9 August 1997) was a British pardessus de viole player. Biography Dolmetsch was born in Dorking, on 22 March 1904. She was the first child born to (Eugène) Arnold Dolmetsch and his third wife Mabel (born Johnston). Her family moved abroad shortly after her birth and her father had to make a special trip to collect her in June. They spent seven years in the United States and three years in France where her father worked as a musical instrument maker. She had three siblings and a half-sister but she and her father were estranged. The family would always speak French at home and the family's interest in early musical instruments resulted in a family concert every evening where they would all try different instruments and they would be joined by friends. This led to the formation of a family concert group. In 1917, the whole family moved to their new home at Hazlemore at a house called "Jesses". They were moved as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
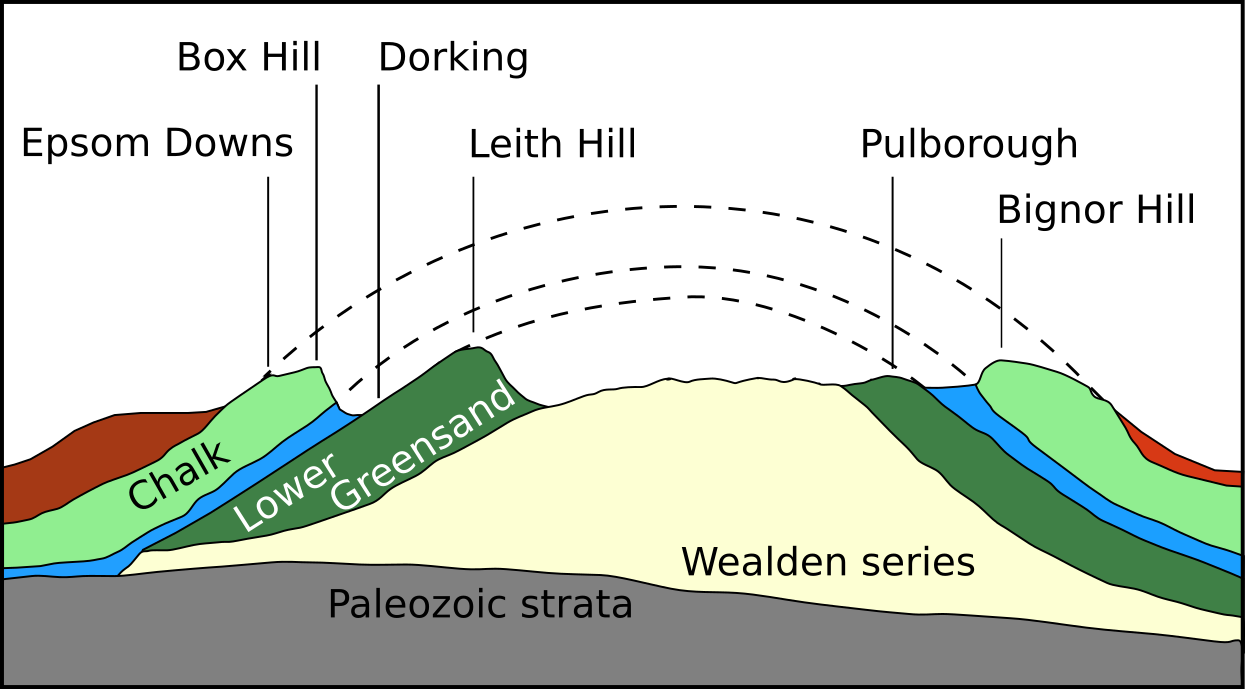
Dorking
Dorking () is a market town in Surrey in South East England about south-west of London. It is in Mole Valley, Mole Valley District and the non-metropolitan district, council headquarters are to the east of the centre. The High Street runs roughly east–west, parallel to the Pipp Brook and along the northern face of an outcrop of Lower Greensand Group, Lower Greensand. The town is surrounded on three sides by the Surrey Hills National Landscape and is close to Box Hill, Surrey, Box Hill and Leith Hill. The earliest archaeological evidence of human activity is from the Mesolithic and Neolithic periods, and there are several Bronze Age bowl barrows in the local area. The town may have been the site of a staging post on Stane Street (Chichester), Stane Street during Roman Britain, Roman times, however the name 'Dorking' suggests an History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon origin for the modern settlement. A marketplace, market is thought to have been held at least weekly sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guildford
Guildford () is a town in west Surrey, England, around south-west of central London. As of the 2011 census, the town has a population of about 77,000 and is the seat of the wider Borough of Guildford, which had around inhabitants in . The name "Guildford" is thought to derive from a ford (crossing), crossing of the River Wey, a tributary of the River Thames that flows through the town centre. The earliest evidence of human activity in the area is from the Mesolithic and Guildford is mentioned in the will and testament, will of Alfred the Great from . The exact location of the main Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon settlement is unclear and the current site of the modern town centre may not have been occupied until the early 11th century. Following the Norman Conquest, a motte-and-bailey castle was constructed; which was developed into a royal residence by Henry III of England, Henry III. During the England in the Middle Ages, late Middle Ages, Guildford prospered as a result of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pardessus De Viole
The pardessus de viole is the highest-pitched member of the viol family of instruments. It is a bowed string instrument, bowed string instrument with either five or six strings and a fretted neck. The pardessus first appeared in the early 18th century, and was commonly played by women, particularly in French-speaking countries. Description The pardessus de viole is the smallest of the viol family. Its size is similar to the violin's, and its range is correspondingly similar. The strings are made of catgut, gut (like on any bowed string instrument until the 1970s) and the top string was tuned to g'', a fourth higher than the top string of the treble viol. Like the treble viol, the pardessus de viole was almost never used to play accompaniment chords, but was always a melody instrument. When played, it is played upright on the lap with a bow. Unlike the treble viol and other viol instruments, the pardessus usually has only five strings. The five string pardessus is tuned in fifths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cécile Dolmetsch And Family 1919
Cécile or Cecile is a female given name or surname. People Given name * Ce'cile (Cecile Charlton, born 1976), Jamaican musician * Severin Cecile Abega (1955–2008), Cameroonian author * Cécile Aubry (1928–2010), retired French film actress and television screenwriter and director * Princess Cécile of Bourbon-Parma (1935–2021), French humanitarian and political activist * Cecile Bonnifait (born 1971), French architect based in New Zealand * Cécile Bozanga (born 1951), Central African politician and banker * Cécile Breccia, French actress * Cécile Brunschvicg (1877–1946), French feminist politician * Cécile Bruyère (1845–1909), Benedictine nun * Cécile Chaminade (1857–1944), French composer and pianist * Cecile de Brunhoff (1903–2003), French storyteller * Cécile de France (born 1975), Belgian actress * Cecile of France ( 1097–1145), French princess * Cécile Delpirou (born 1964), French politician * Cécile Fatiman ( 1791), voodoo priestess and a figure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Dolmetsch
Eugène Arnold Dolmetsch (24 February 185828 February 1940), was a French-born musician and instrument maker who spent much of his working life in England and established an instrument-making workshop in Haslemere, Surrey. He was a leading figure in the 20th-century revival of interest in early music. Early life The Dolmetsch family was originally of Bohemian origin, but Dolmetsch was born in Le Mans, on 24 February 1858, the son of Rudolph Arnold Dolmetsch and his wife Marie Zélie (née Guillouard), where the family had established a piano-making business. It was in the family's workshops that Dolmetsch acquired the skills of instrument-making that would later be put to use in his early music workshops. He studied music at the Brussels Conservatoire and learnt the violin with Henri Vieuxtemps. In 1883, he travelled to London to attend the Royal College of Music, where he studied under Henry Holmes and Frederick Bridge and was awarded a Bachelor of Music degree in 1889. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dowland
John Dowland ( – buried 20 February 1626) was an English Renaissance composer, lutenist, and singer. He is best known today for his melancholy songs such as "Come, heavy sleep", " Come again", " Flow my tears", " I saw my Lady weepe", " Now o now I needs must part", and " In darkness let me dwell". His instrumental music has undergone a major revival, and with the 20th century's early music revival, has been a continuing source of repertoire for lutenists and classical guitarists. Career and compositions Very little is known of Dowland's early life, but it is generally thought he was born in London; some sources even put his birth year as 1563. Irish historian W. H. Grattan Flood claimed that he was born in Dalkey, near Dublin, but no corroborating evidence has been found either for that or for Thomas Fuller's claim that he was born in Westminster. One piece of evidence points to Dublin as his place of origin: he dedicated the song "From Silent Night" to 'my loving cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percy Scholes
Percy Alfred Scholes (pronounced ''skolz''; 24 July 1877 – 31 July 1958) was an English musician, journalist, vegetarianism activist and prolific writer, whose best-known achievement was his compilation of the first edition of the '' Oxford Companion to Music''. His 1948 biography ''The Great Dr Burney'' was awarded the James Tait Black Memorial Prize. Career Scholes was born in Headingley, Leeds in 1877, the third of six children of Thomas Scholes, a commercial agent and Katharine Elizabeth Pugh. He was educated privately, owing to his poor health as a child. He became an organist, schoolteacher, music journalist, lecturer, an Inspector of Music in Schools to London University and the Organist and Music Master of Kent College, Canterbury (1900), All Saints, Vevey, Switzerland (1902) as well as Kingswood College, Grahamstown, South Africa (1904). He was Registrar at the City of Leeds (Municipal) School of Music (1908–1912).John Owen Ward. 'Scholes, Percy A(lfred)' in ''Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viola Da Gamba Society
The viola ( , () ) is a string instrument of the violin family, and is usually bowed when played. Violas are slightly larger than violins, and have a lower and deeper sound. Since the 18th century, it has been the middle or alto voice of the violin family, between the violin (which is tuned a perfect fifth higher) and the cello (which is tuned an octave lower). The strings from low to high are typically tuned to C3, G3, D4, and A4. In the past, the viola varied in size and style, as did its names. The word ''viola'' originates from the Italian language. The Italians often used the term ''viola da braccio'', meaning, literally, 'of the arm'. "Brazzo" was another Italian word for the viola, which the Germans adopted as ''Bratsche''. The French had their own names: ''cinquiesme'' was a small viola, ''haute contre'' was a large viola, and ''taile'' was a tenor. Today, the French use the term ''alto'', a reference to its range. The viola was popular in the heyday of five-part harm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viol
The viola da gamba (), or viol, or informally gamba, is a bowed and fretted string instrument that is played (i.e. "on the leg"). It is distinct from the later violin family, violin, or ; and it is any one of the earlier viol family of bow (music), bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments , stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and Tuning mechanisms for stringed instruments, pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitch of each of the strings. Although treble, tenor and bass were most commonly used, viols came in different sizes, including (high treble, developed in 18th century), treble, alto, small tenor, tenor, bass and contrabass (called ). These members of the viol family are distinguished from later bowed string instruments, such as the violin family, by both appearance and orientation when played—as typically the neck is oriented upwards and the rounded bottom downwards to settle on the lap or between the knees. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Barrière
Jean-Baptiste Barrière (2 May 1707 – 6 June 1747) was a French people, French cello, cellist and composer. He was born in Bordeaux and died in Paris, at 40 years of age. Musical career Barrière first studied the viol, and published a set of viol sonatas. In due course however he became a skilled cellist during a period when the cello was gaining popularity over the viol in France, and later came to completely replace it, as indeed had already happened in Italy some 40 years prior. He became one of the best known virtuoso cellists of his time. In 1731 he went to Paris, and entered the Académie Royale de Musique (also known as the Opera), with an annual salary of 445 livres. He was accorded special privileges by King Louis XV at Fontainebleau, on 22 October 1733 for six years, to compose and publish several sonatas and other instrumental works. One of his most famous pupils was the Count of Guergorlay, Seigneur of Trousily. After his first book ''Livre I - Sonates pour violoncel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1904 Births
Events January * January 7 – The distress signal ''CQD'' is established, only to be replaced 2 years later by ''SOS''. * January 8 – The Blackstone Library is dedicated, marking the beginning of the Chicago Public Library system. * January 12 – The Herero Wars in German South West Africa begin. * January 17 – Anton Chekhov's last play, ''The Cherry Orchard'' («Вишнëвый сад», ''Vishnevyi sad''), opens at the Moscow Art Theatre directed by Constantin Stanislavski, 6 month's before the author's death. * January 23 – The Ålesund fire destroys most buildings in the town of Ålesund, Norway, leaving about 10,000 people without shelter. * January 25 – Halford Mackinder presents a paper on "The Geographical Pivot of History" to the Royal Geographical Society of London in which he formulates the Heartland Theory, originating the study of geopolitics. February * February 7 – The Great Baltimore Fire in Baltimore, Maryland, destroys over 1,500 build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1997 Deaths
This is a list of lists of deaths of notable people, organized by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked below. 2025 2024 2023 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 1986 Earlier years ''Deaths in years earlier than this can usually be found in the main articles of the years.'' See also * Lists of deaths by day * Deaths by year (category) {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |