|
Cysts Of The Jaws
Cysts of the jaws are cysts—pathological epithelium, epithelial-lined cavities filled with fluid or soft material—occurring on the bones of the jaws, the human mandible, mandible and maxilla. Those are the bones with the highest prevalence of cysts in the human body, due to the abundant amount of epithelial remnants that can be left in the bones of the jaws. The Tooth enamel, enamel of teeth is formed from ectoderm (the precursor germ layer to skin and mucosa), and so remnants of epithelium can be left in the bone during Human tooth development, odontogenesis (tooth development). The bones of the jaws develop from embryology, embryologic processes which fuse, and ectodermal tissue may be trapped along the lines of this fusion. This "resting" epithelium (also termed cell rests) is usually dormant or undergoes atrophy, but, when stimulated, may form a cyst. The reasons why resting epithelium may proliferate and undergo cystic transformation are generally unknown, but inflammatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral And Maxillofacial Surgery
Oral and maxillofacial surgery (OMFS) is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the Human mouth, mouth, Human head, head and neck, and jaws, as well as facial plastic surgery including cleft lip and cleft palate surgery. Specialty An oral and maxillofacial surgeon is a specialist surgery, surgeon who treats the entire Craniofacial, craniomaxillofacial complex: Anatomy, anatomical area of the Human mouth, mouth, jaws, face, and Human skull, skull, head and neck as well as associated structures. Depending upon the national jurisdiction, oral and maxillofacial surgery may require a degree in medicine, dentistry or both. United States In the U.S., oral and maxillofacial surgeons, whether possessing a single or dual degree, may further specialise after residency, undergoing additional one or two year sub-specialty oral and maxillofacial surgery fellowship training in the following areas: *Cosmetic surgery#Cosmetic surgery, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
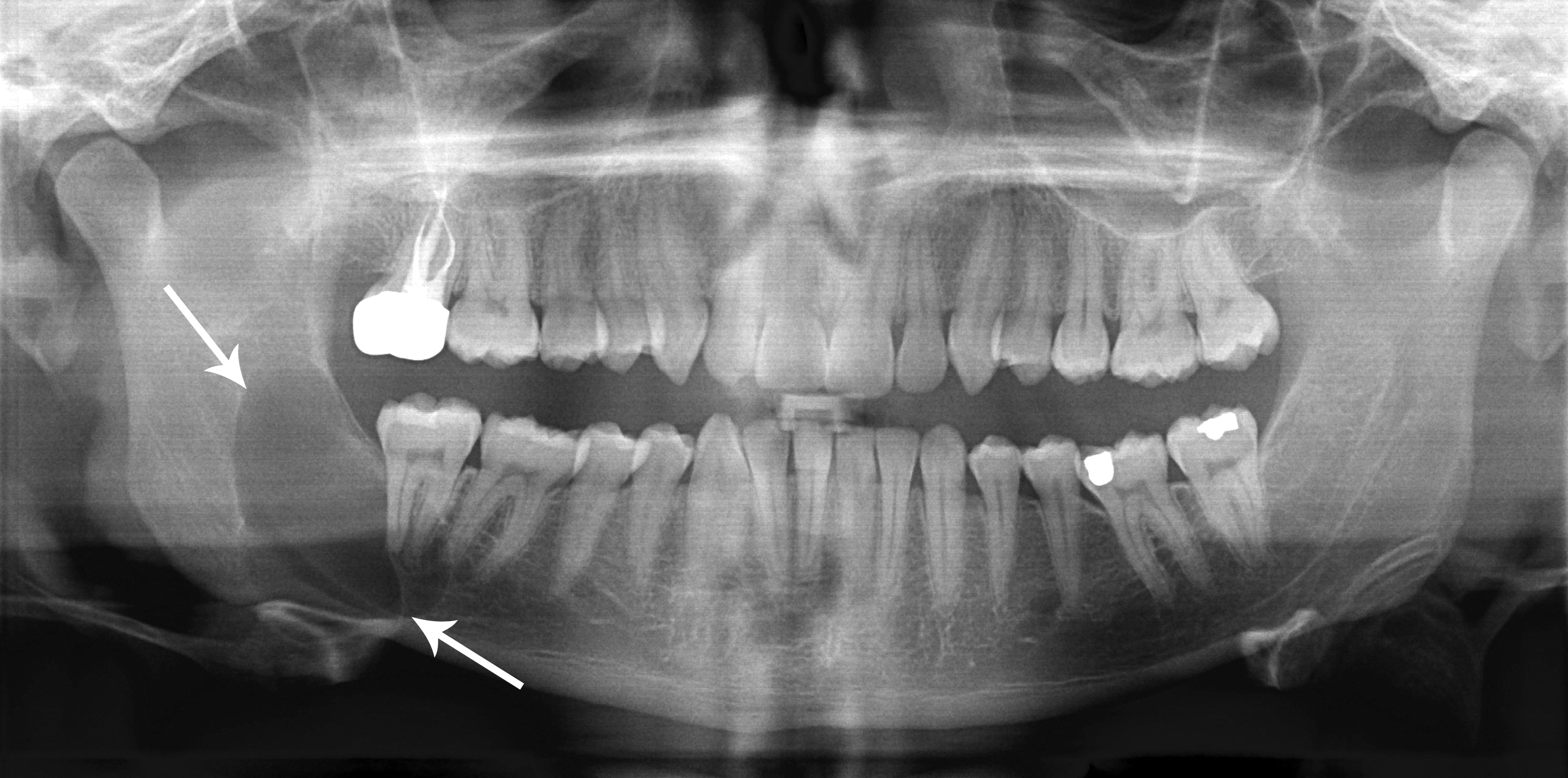
Odontogenic Cyst
Odontogenic cysts are a group of cysts of the jaws, jaw cysts that are formed from tissues involved in Human tooth development, odontogenesis (tooth development). Odontogenic cysts are closed sacs, and have a distinct biological membrane, membrane derived from the rest of odontogenic epithelium. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. Intra-bony cysts are most common in the jaws, because the human mandible, mandible and maxilla are the only bones with epithelial components. That odontogenic epithelium is critical in normal tooth development. However, epithelial rests may be the origin for the cyst lining later. Not all oral cysts are odontogenic cysts. For example, mucous cyst of the oral mucosa and nasolabial duct cyst are not of odontogenic origin. In addition, there are several conditions with so-called (x-ray, radiographic) 'pseudocystic appearance' in jaws; ranging from anatomic variants such as Stafne static bone cyst, to the aggressive aneurysmal bone cyst. Cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheek
The cheeks () constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. ''Buccal'' means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside of the cheek and the teeth and gums is called the vestibule or ''buccal'' pouch or ''buccal'' cavity and forms part of the mouth. In other animals, the cheeks may also be referred to as " jowls". Structure Cheeks are fleshy in humans, the skin being suspended by the chin and the jaws, and forming the lateral wall of the human mouth, visibly touching the cheekbone below the eye. The inside of the cheek is lined with a mucous membrane (''buccal'' mucosa, part of the oral mucosa). During mastication (chewing), the cheeks and tongue between them serve to keep the food between the teeth. Clinical significance The cheek is the most common location from which a DNA sample can be taken. (Some saliva is collected from inside the mouth, e.g. using a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccal Bifurcation Cyst
Buccal bifurcation cyst is an inflammatory odontogenic cyst, of the paradental cysts family, that typically appears in the buccal bifurcation region of the mandibular first molars in the second half of the first decade of life. Infected cysts may be associated with pain. Around 5% of all odontogenic cysts are mandibular buccal bifurcation cysts (MBBC), an unusual inflammatory odontogenic cyst. Stoneman and Worth initially characterised MBBC, and named MBBC as mandibular infected buccal cyst. On occasion, MBBC has been referred to as a paradental cyst (PC). However, according to the World Health Organization, MBBC should be used for cysts related to mandibular first or second molars, while PC should be saved for cysts related to mandibular third molars. The phrase "inflammatory collateral cysts" encompasses both PC and MBBC. Buccal Bifurcation Cyst (BBC) affects the vestibular aspect of roots of the mandibular first molar. The causes of BBC remains unsure and various explanatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
Nevoid basal-cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS) is a rare inherited medical condition involving defects within multiple body systems such as the skin, nervous system, eyes, endocrine system, and bones. People with NBCCS are prone to developing various cancers, including a common and usually non-life-threatening form of non-melanoma skin cancer called basal-cell carcinomas (BCCs). Only about 10% of people with the condition do not develop BCCs; the vast majority of patients develop numerous BCCs. The name ''Gorlin syndrome'' refers to the American oral pathologist and human geneticist Robert J. Gorlin (1923–2006). The American dermatologist Robert W. Goltz (1923–2014) was his co-author, which is the basis for the term 'Gorlin-Goltz syndrome'. First described in 1960 by Gorlin and Goltz, NBCCS is an autosomal dominant condition that can cause unusual facial appearances and a predisposition for basal-cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer which rarely spreads to other parts of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals. Types There is no designated classification or naming convention for lesions. Because lesions can occur anywhere in the body and their definition is so broad, the varieties of lesions are virtually endless. Generally, lesions may be classified by their patterns, sizes, locations, or causes. They can also be named after the person who discovered them. For example, Ghon lesions, which are found in the lungs of those with tuberculosis, are named after the lesion's discoverer, Anton Ghon. The characteristic skin lesions of a varicella zoster virus infection are called '' chickenpox''. Lesions of the teeth are usually called dental caries, or "cavities". Location Lesions are often classified by their tissue types or locations. For example, "skin lesions" or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odontogenic Keratocyst
An odontogenic keratocyst is a rare and benign but locally aggressive developmental cyst. It most often affects the posterior human mandible, mandible and most commonly presents in the third decade of life. Odontogenic keratocysts make up around 19% of jaw cysts. Despite its more common appearance in the bone region, it can affect soft tissue. In the World Health Organization, WHO/International Agency for Research on Cancer, IARC classification of head and neck pathology, this clinical entity had been known for years as the odontogenic keratocyst; it was reclassified as keratocystic odontogenic tumour (KCOT) from 2005 to 2017. In 2017 it reverted to the earlier name, as the new WHO/IARC classification reclassified OKC back into the cystic category. Under The WHO/IARC classification, Odontogenic Keratocyst underwent the reclassification as it is no longer considered a neoplasm due to a lack of quality evidence regarding this hypothesis, especially with respect to clonality. Within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentigerous Cyst
A dentigerous cyst, also known as a follicular cyst, is an epithelial-lined developmental cyst formed by accumulation of fluid between the reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth. It is formed when there is an alteration in the reduced enamel epithelium and encloses the crown of an unerupted tooth at the cemento-enamel junction. Fluid is accumulated between reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth. Dentigerous cysts are the second most prevalent type of odontogenic cysts after radicular cyst. Seventy percent of the cases occur in the mandible. Dentigerous cysts are usually painless. The patient usually comes with a concern of delayed tooth eruption or facial swelling. A dentigerous cyst can go unnoticed and may be discovered coincidentally on a regular radiographic examination. Pathogenesis Odontogenesis happens by means of a complex interaction between oral epithelium and surrounding mesenchymal tissue. Abnormal tissue interaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotic Pulp
Pulp necrosis is a clinical diagnostic category indicating the death of cells and tissues in the pulp chamber of a tooth with or without bacterial invasion. It is often the result of many cases of dental trauma, caries and irreversible pulpitis. In the initial stage of the infection, the pulp chamber is partially necrosed for a period of time and if left untreated, the area of cell death expands until the entire pulp necroses. The most common clinical signs present in a tooth with a necrosed pulp would be a grey discoloration of the crown and/or periapical radiolucency. This altered translucency in the tooth is due to disruption and cutting off of the apical neurovascular blood supply. Sequelae of a necrotic pulp include acute apical periodontitis, dental abscess or radicular cyst and discolouration of the tooth. Tests for a necrotic pulp include: vitality testing using a thermal test or an electric pulp tester. Discolouration may be visually obvious, or more subtle. Treatmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore is considered a mechanism of innate immunity, whereas adaptive immunity is specific to each pathogen. Inflammation is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out damaged cells and tissues, and initiate tissue repair. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. However inflammation can also have negative effects. Too much inflammation, in the form of chronic inflammation, is associated with variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radicular Cyst
Commonly known as a dental cyst, the periapical cyst is the most common odontogenic cyst. It may develop rapidly from a periapical granuloma, as a consequence of untreated chronic periapical periodontitis. Periapical is defined as "the tissues surrounding the Dental anatomy#Surfaces, apex of the root of a tooth" and a cyst is "a pathological cavity lined by epithelium, having fluid or gaseous content that is not created by the accumulation of pus." Most frequently located in the maxillary anterior region, the cyst is caused by Pulp (tooth), pulpal necrosis secondary to dental caries or dental trauma, trauma. Its lining is derived from the epithelial cell rests of Malassez which proliferate to form the cyst. Such cysts are very common. Although initially asymptomatic, they are clinically significant because secondary infection can cause toothache, pain and damage. In radiographs, the cyst appears as a radiolucency (dark area) around the apex of a tooth's root. Signs and symptoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Incidence Of Odontogenic Cysts
Relative may refer to: General use *Kinship and family, the principle binding the most basic social units of society. If two people are connected by circumstances of birth, they are said to be ''relatives''. Philosophy *Relativism, the concept that points of view have no absolute truth or validity, having only relative, subjective value according to differences in perception and consideration, or relatively, as in the relative value of an object to a person *Relative value (philosophy) Economics *Relative value (economics) Popular culture Film and television * ''Relatively Speaking'' (1965 play), 1965 British play * ''Relatively Speaking'' (game show), late 1980s television game show * ''Everything's Relative'' (episode)#Yu-Gi-Oh! (Yu-Gi-Oh! Duel Monsters), 2000 Japanese anime ''Yu-Gi-Oh! Duel Monsters'' episode *'' Relative Values'', 2000 film based on the play of the same name. *''It's All Relative'', 2003-4 comedy television series *''Intelligence is Relative'', tag line f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |