|
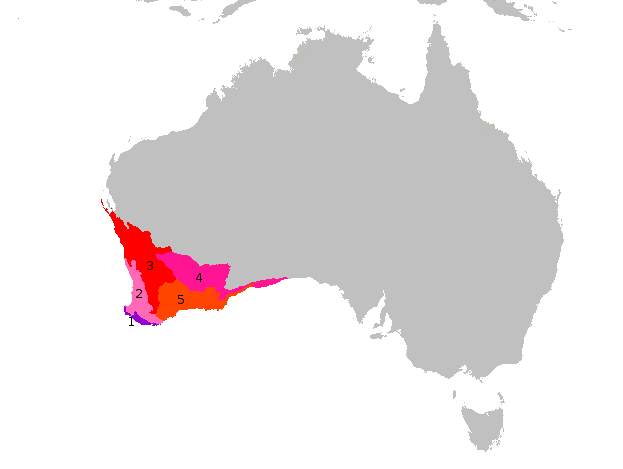
Cyrtostylis Robusta
''Cyrtostylis robusta'', commonly known as large gnat-orchid or mosquito orchid, is a species of orchid Endemism, endemic to southern Australia. It usually has a single more or less round leaf and a flowering spike with up to seven reddish flowers with a shelf-like Labellum (botany), labellum. Description ''Cyrtostylis robusta'' is a terrestrial, Perennial plant, perennial, deciduous, Herbaceous plant, herb with a single heart-shaped, kidney-shaped or almost round leaf long and wide. The leaf is light to medium green on the upper surface and silvery on the lower side. Between two and seven pinkish red flowers long and about wide are borne on a flowering stem high. The Pedicel (botany), pedicel is long with a bract at its base. The wikt:dorsal, dorsal sepal is erect and curved forward, linear but tapered, long and about wide. The wikt:lateral, lateral sepals are linear, long, wide and curve forwards or downwards. The petals are similar in size and shape to the lateral se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serendip Sanctuary
Serendip Sanctuary is a 250 ha protected area in Victoria, Australia, near the You Yangs and the town of Lara, some 22 km north of Geelong and 60 km south-west of Melbourne. Originally used for farming and other purposes, it was purchased in 1959 by the State Government of Victoria for wildlife research and the captive management and breeding of species threatened in Victoria, such as the brolga, magpie goose, Australian bustard, and bush stone-curlew. The sanctuary contains many different types of wetland and is home to many plant species as well, such as river red gums, tall spikerush, and tussock grass. Serendip now focuses more on environmental education about the flora and fauna of the wetlands and open grassy woodlands of the Volcanic Western Plains of Victoria. It was opened to the public in 1991 and is now managed by Parks Victoria. Background & Origins Serendip Sanctuary is located in the traditional Country of the Wadawurrung People. Wadawurrung Country co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrtostylis Reniformis
''Cyrtostylis reniformis'', commonly known as common gnat-orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to eastern Australia. It usually has a single kidney-shaped leaf and a flowering spike with up to eight reddish flowers with a shelf-like labellum. Description ''Cyrtostylis reniformis'' is a terrestrial, perennial, deciduous, herb with a single kidney-shaped, heart-shaped or almost round leaf long and wide. Up to eight dark reddish brown, or rarely yellowish flowers long are borne on a flowering stem high. The dorsal sepal is erect and curved forward, linear to lance-shaped, long and about wide. The lateral sepals are linear, long, about wide and curve forwards or downwards. The petals are similar in size and shape to the lateral sepals and curve downwards. The labellum is oblong, long and about wide and shelf-like with a few serrations near its pointed tip. Flowering occurs from May to October. Taxonomy and naming ''Cyrtostylis reniformis'' was first formally desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrtostylis
''Cyrtostylis'', commonly known as gnat orchids, is a genus of five or six species of flowering plants in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is native to Australia and New Zealand. Cyrtostylis orchids often form dense colonies of genetically identical plants. They have a single heart-shaped leaf and a thin flowering stem with pale coloured insect-like flowers. The lateral sepals and petals are similar in size and colour but the labellum is shelf-like and conspicuous with two prominent glands at its base. Description Orchids in the genus ''Cyrtostylis'' are terrestrial, perennial, deciduous, sympodial herbs, usually with a few inconspicuous, fine roots and one or two tubers. They often form dense colonies of cloned plants. There is a single green, heart-shaped, ground-hugging leaf at the base of the flowering stem. The thin flowering stem bears one to a few flowers with the column at the top. The flowers are usually pale coloured with an erect dorsal sepal and spreading la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threatened Species Protection Act 1995
The ''Threatened Species Protection Act 1995'' (TSP Act), is an act of the Parliament of Tasmania that provides the statute relating to conservation of flora and fauna. Its long title is An Act to provide for the protection and management of threatened native flora and fauna and to enable and promote the conservation of native flora and fauna. It received the royal assent on 14 November 1995. As of 25 November 2020, the TSP Act is administered by the Department of Primary Industries, Parks, Water and Environment (Tasmania) and is the primary legislation for the listing, protection and conservation of threatened native flora and fauna in Tasmania. Threatened species in Tasmania can also be listed on the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999, which is the primary national legislation for the protection of threatened species in Australia. The objectives of the TSP Act are to ensure the survival of native flora and fauna as well to encourage, educate and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israelite Bay, Western Australia
Israelite Bay is a bay and locality on the south coast of Western Australia. Situated in the Shire of Esperance local government area, it lies east of Esperance and the Cape Arid National Park, within the Nuytsland Nature Reserve and the Great Australian Bight. Point Malcolm is about west of Israelite Bay, and there is a long sandy beach there. Climate data was recorded at Israelite Bay from 1885 to 1927, and it is frequently mentioned in Bureau of Meteorology weather reports as a geographical marker. It was the site of a significant telegraph station in the early 1900s. It was also a location serviced by the W.A. Government State Steamship Service, the South Coast Service, in the early 1900s. The Eastern Group, the eastern-most islands of the Recherche Archipelago, identified by Matthew Flinders Captain (Royal Navy), Captain Matthew Flinders (16 March 1774 – 19 July 1814) was a British navigator and cartographer who led the first littoral zone, inshore circumn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perth
Perth is the list of Australian capital cities, capital and largest city of the Australian states and territories of Australia, state of Western Australia. It is the list of cities in Australia by population, fourth most populous city in Australia and Oceania, with a population of 2.1 million (80% of the state) living in Greater Perth in 2020. Perth is part of the South West Land Division of Western Australia, with most of the metropolitan area on the Swan Coastal Plain between the Indian Ocean and the Darling Scarp. The city has expanded outward from the original British settlements on the Swan River (Western Australia), Swan River, upon which the city's #Central business district, central business district and port of Fremantle are situated. Perth is located on the traditional lands of the Whadjuk Noongar people, where Aboriginal Australians have lived for at least 45,000 years. James Stirling (Royal Navy officer), Captain James Stirling founded Perth in 1829 as the administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Australia
Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna. The region is also known as the Southwest Australia Global Diversity Hotspot, as well as Kwongan. Geography The region includes the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregions of Western Australia. The region covers 356,717 km2, consisting of a broad coastal plain 20-120 kilometres wide, transitioning to gently undulating uplands made up of weathered granite, gneiss and laterite. Bluff Knoll in the Stirling Range is the highest peak in the region, at 1,099 metres (3,606 ft) elevation. Desert and xeric shrublands lie to the north and east across the centre of Australia, separating Southwest Australia from the other Mediterranean and humid-climate regions of the continent. Climate The region has a wet-winter, dry-summer Mediterranean climate, one of five such region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
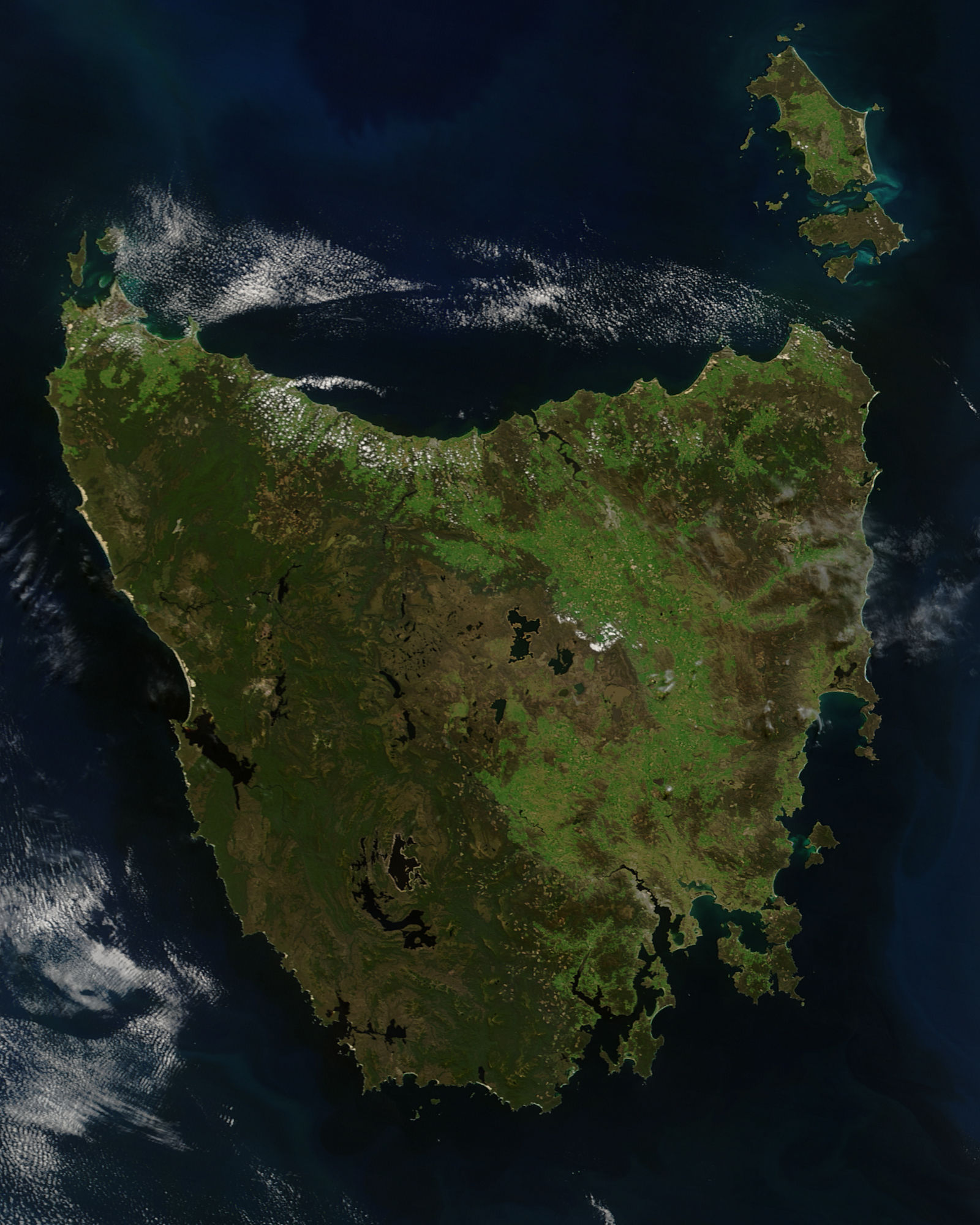
Tasmania
) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Tasmania , established_title2 = Federation , established_date2 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Abel Tasman , demonym = , capital = Hobart , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 29 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangaroo Island
Kangaroo Island, also known as Karta Pintingga (literally 'Island of the Dead' in the language of the Kaurna people), is Australia's third-largest island, after Tasmania and Melville Island. It lies in the state of South Australia, southwest of Adelaide. Its closest point to the mainland is Snapper Point in Backstairs Passage, which is from the Fleurieu Peninsula. The native population of Aboriginal Australians that once occupied the island (sometimes referred to as the Kartan people) disappeared from the archaeological record sometime after the land became an island following the rising sea levels associated with the Last Glacial Period around 10,000 years ago. It was subsequently settled intermittently by sealers and whalers in the early 19th century, and from 1836 on a permanent basis during the British colonisation of South Australia. Since then the island's economy has been principally agricultural, with a southern rock lobster fishery and with tourism growing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is a state in southeastern Australia. It is the second-smallest state with a land area of , the second most populated state (after New South Wales) with a population of over 6.5 million, and the most densely populated state in Australia (28 per km2). Victoria is bordered by New South Wales to the north and South Australia to the west, and is bounded by the Bass Strait to the south (with the exception of a small land border with Tasmania located along Boundary Islet), the Great Australian Bight portion of the Southern Ocean to the southwest, and the Tasman Sea (a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean) to the southeast. The state encompasses a range of climates and geographical features from its temperate coastal and central regions to the Victorian Alps in the northeast and the semi-arid north-west. The majority of the Victorian population is concentrated in the central-south area surrounding Port Phillip Bay, and in particular within the metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Nomenclature
Botanical nomenclature is the formal, scientific naming of plants. It is related to, but distinct from taxonomy. Plant taxonomy is concerned with grouping and classifying plants; botanical nomenclature then provides names for the results of this process. The starting point for modern botanical nomenclature is Linnaeus' ''Species Plantarum'' of 1753. Botanical nomenclature is governed by the ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (''ICN''), which replaces the ''International Code of Botanical Nomenclature'' (''ICBN''). Fossil plants are also covered by the code of nomenclature. Within the limits set by that code there is another set of rules, the '' International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (ICNCP)'' which applies to plant cultivars that have been deliberately altered or selected by humans (see cultigen). History and scope Botanical nomenclature has a long history, going back beyond the period when Latin was the scientific language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |