|
Curiosity (TV Series)
''Curiosity'' is an American documentary television series that premiered on August 7, 2011, on the Discovery Channel. Each episode focuses on one question in science, technology, and society (e.g., why the sank) and, for the first season, features a different celebrity host. Stephen Hawking hosted the premiere episode titled "Did God Create the Universe?", which aired simultaneously on seven Discovery Communications networks: Discovery Channel, TLC, Discovery Fit and Health, Animal Planet, Science, Investigation Discovery, and Destination America. Season one consists of 16 episodes. Curiosity: The Questions of Our Life The development of "Curiosity: The Questions of Our Life", was announced in September 2009. It was to answer questions and mysteries in fields like space, biology, geology, medicine, physics, technology, nature, archaeology, history, and the human mind. It was considered as a groundbreaking series for Discovery like the BBC's ''Planet Earth'' and ''Life''. Ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Documentary Television
Television documentaries are televised media productions that screen documentaries. Television documentaries exist either as a television documentary series or as a television documentary film. * Television documentary series, sometimes called docuseries, are television series screened within an ordered collection of two or more televised episodes. * Television documentary films exist as a singular documentary film to be broadcast via a documentary channel or a News broadcasting, news-related channel. Occasionally, documentary films that were initially intended for televised broadcasting may be screened in a Movie theater, cinema. Documentary television rose to prominence during the 1940s, spawning from earlier cinematic documentary filmmaking ventures. Early production techniques were highly inefficient compared to modern recording methods. Early television documentaries typically featured historical, wartime, investigative or event-related subject matter. Contemporary televisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curiosity (TV Series) Logo
Curiosity (from Latin , from "careful, diligent, curious", akin to "care") is a quality related to inquisitive thinking, such as exploration, investigation, and learning, evident in humans and other animals. Curiosity helps human development, from which derives the process of learning and desire to acquire knowledge and skill. The term ''curiosity'' can also denote the behavior, characteristic, or emotion of being curious, in regard to the desire to gain knowledge or information. Curiosity as a behavior and emotion is the driving force behind human development, such as progress in science, language, and industry. Curiosity can be considered to be an evolutionary adaptation based on an organism's ability to learn. Certain curious animals (namely, corvids, octopuses, dolphins, elephants, rats, ''etc.'') will pursue information in order to adapt to their surrounding and learn how things work. This behavior is termed neophilia, the love of new things. For animals, a fear of the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
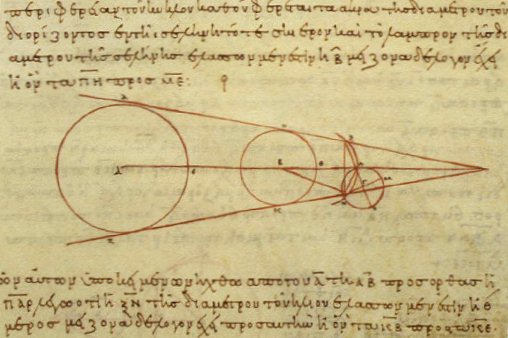
Aristarchus Of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos (; , ; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician who presented the first known heliocentric model that placed the Sun at the center of the universe, with the Earth revolving around the Sun once a year and rotating about its axis once a day. He also supported the theory of Anaxagoras according to which the Sun was just another star. He likely moved to Alexandria, and he was a student of Strato of Lampsacus, who later became the third head of the Peripatetic school in Greece. According to Ptolemy, he observed the summer solstice of 280 BC. Along with his contributions to the heliocentric model, as reported by Vitruvius, he created two separate sundials: one that is a flat disc; and one hemispherical. Aristarchus estimated the sizes of the Sun and Moon as compared to Earth's size. He also estimated the distances from the Earth to the Sun and Moon. His estimate that the Sun was 7 times larger than Earth (while inaccurate by an order of magnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season in its new moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to Ecliptic, the plane of Earth's orbit. In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In #Types, partial and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured. Unlike a lunar eclipse, which may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth, a solar eclipse can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world. As such, although total solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth every 18 months on average, they recur at any given place only once every 360 to 410 years. If the Moon were in a perfectly circular orbit and in the same orbital plane as Earth, there would be total solar eclipses once a month, at every new moon. Instead, because the Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sköll
In Norse mythology, Sköll (Old Norse: , "Treachery"Orchard (1997:150). or "Mockery"Simek (2007:292)) is a wolf that, according to Snorri Sturluson's ''Prose Edda'', chases the Sun (personified as a goddess, Sól) riding her chariot across the sky. Hati Hróðvitnisson chases the Moon (personified, as Máni) during the night. Skӧll and Hati are the sons of the wolf Fenrir, and an unnamed giantess. It is foretold the wolves will chase the Sun and Moon across the skies until Ragnarök In Norse mythology, (also Ragnarok; or ; ) is a foretold series of impending events, including a great battle in which numerous great Norse mythological figures will perish (including the Æsir, gods Odin, Thor, Týr, Freyr, Heimdall, a ..., at which point the wolves catch up and devour the celestial beings. In Snorri Sturluson's ''Prose Edda'', the mention of Sköll appears when describing the story of Sol, who drives the chariot of the Sun in Norse Mythology. The wolf is seen cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ægir
Ægir (anglicised as Aegir; Old Norse 'sea'), Hlér (Old Norse 'sea'), or Gymir (Old Norse less clearly 'sea, engulfer'), is a jötunn and a anthropomorphism, personification of the sea in Norse mythology. In the Old Norse record, Ægir hosts the gods in his halls and is associated with brewing ale. Ægir is attested as married to a goddess, Rán, who also personifies the sea, and together the two produced daughters who personify waves, the Nine Daughters of Ægir and Rán, and Ægir's son is Snær, personified snow. Ægir may also be the father of the beautiful jötunn Gerðr, wife of the god Freyr, or these may be two separate figures who share the same name (see below and Gymir (father of Gerðr)). One of Ægir's names, ''Hlér'', is the namesake of the island Læsø (Old Norse ''Hlésey'' 'Hlér's island') and perhaps also Lejre in Denmark. Scholars have long analyzed Ægir's role in the Old Norse corpus, and the concept of the figure has had some influence in modern popular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norse God
In Germanic paganism, the indigenous religion of the ancient Germanic peoples who inhabit Germanic Europe, there were a number of different gods and goddesses. Germanic deities are attested from numerous sources, including works of literature, various chronicles, runic inscriptions, personal names, place names, and other sources. This article contains a comprehensive list of Germanic deities outside the numerous Germanic Matres and Matronae inscriptions from the 1st to 5th century CE. Gods Goddesses Pseudo-deities and purported deities * Astrild, a synonym for the Roman deity Amor or Cupid invented and used by Nordic Baroque and Rococo authors * , a purported deity potentially stemming from a folk etymologyMeyers Großes Konversations-Lexikon, Band 2. Leipzig 1905, S. 832. * Ercol, a synonym for the Roman deity Hercules used in King Alfred's Anglo-Saxon version of Boethius de Consolatione Philosophiae * Frau Berchta, a purported deity and female equivalent of Berchtol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden), who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9–22. They also voyaged as far as the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, North Africa, the Middle East, Greenland, and Vinland (present-day Newfoundland in Canada, North America). In their countries of origin, and some of the countries they raided and settled in, this period is popularly known as the Viking Age, and the term "Viking" also commonly includes the inhabitants of the Scandinavian homelands as a whole. The Vikings had a profound impact on the Early Middle Ages, early medieval history of Northern Europe, northern and Eastern Europe, including the political and social development of England (and the English language) and parts of France, and established the embryo of Russia in Kievan Rus'. Expert sailors and navigators of their cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
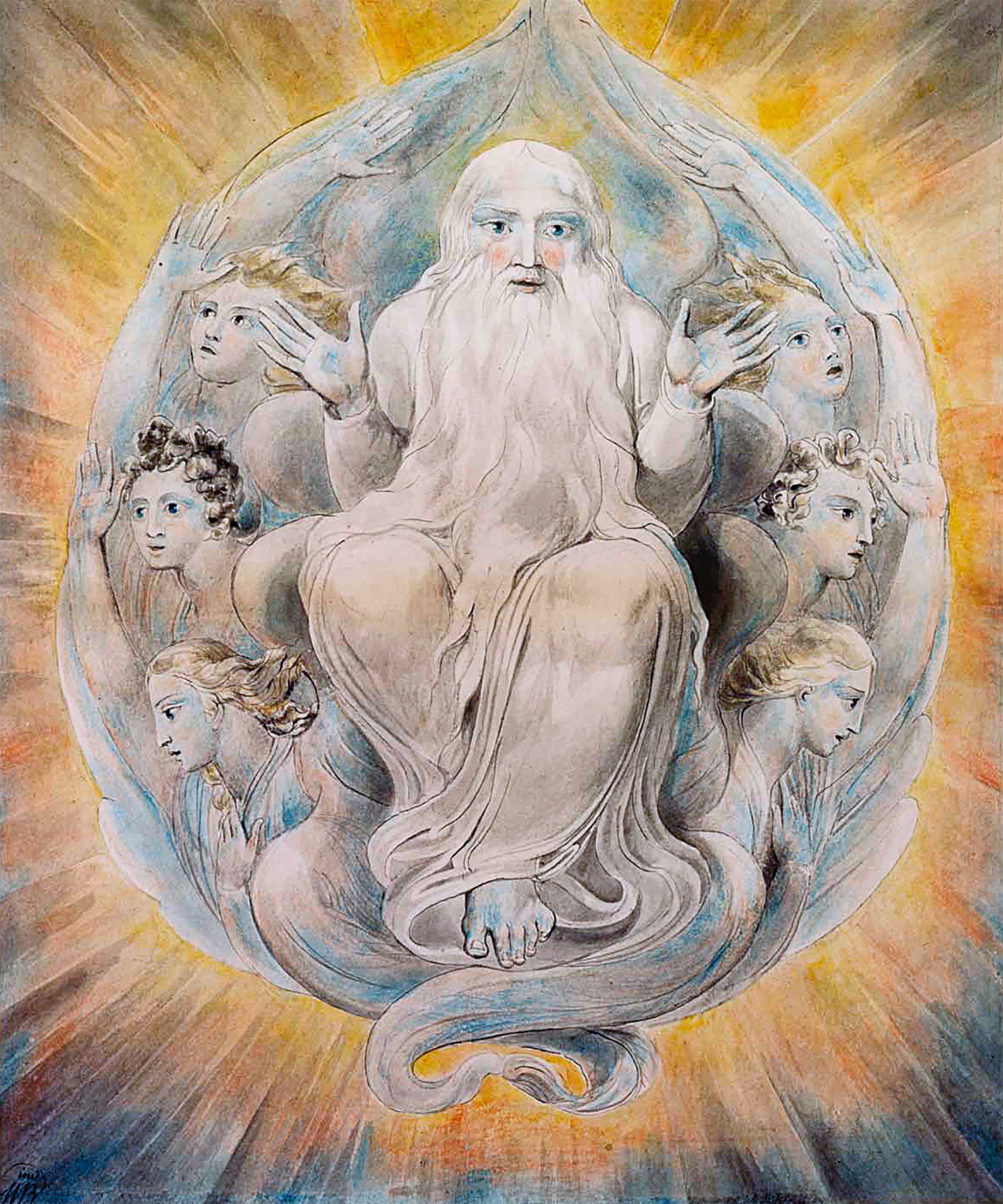
Creator Deity
A creator deity or creator god is a deity responsible for the creation of the Earth, world, and universe in human religion and mythology. In monotheism, the single God is often also the creator. A number of monolatristic traditions separate a secondary creator from a primary transcendent being, identified as a primary creator.(2004) Sacred Books of the Hindus Volume 22 Part 2: Pt. 2, p. 67, R.B. Vidyarnava, Rai Bahadur Srisa Chandra Vidyarnava Monotheism Atenism Initiated by Pharaoh Akhenaten and Queen Nefertiti around 1330 BCE, during the New Kingdom period in ancient Egyptian history. They built an entirely new capital city ( Akhetaten) for themselves and worshippers of their sole creator god in a wilderness. His father used to worship Aten alongside other gods of their polytheistic religion. Aten, for a long time before his father's time, was revered as a god among the many gods and goddesses in Egypt. Atenism was countermanded by later pharaoh Tutankhamun, as chro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that one God is the only, or at least the dominant deity.F. L. Cross, Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. A distinction may be made between exclusive monotheism, in which the one God is a singular existence, and both inclusive and pluriform monotheism, in which multiple gods or godly forms are recognized, but each are postulated as extensions of the same God. Monotheism is distinguished from henotheism, a religious system in which the believer worships one god without denying that others may worship different gods with equal validity, and monolatry, monolatrism, the recognition of the existence of many gods but with the consistent worship of only one deity. The term ''monolatry'' was perhaps first used by Julius Wellhausen. Monotheism characterizes the traditions of Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic religions such as Judaism, Samaritanism, Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Grand Design (book)
''The Grand Design'' is a popular-science book written by physicists Stephen Hawking and Leonard Mlodinow and published by Bantam Books in 2010. The book examines the history of scientific knowledge about the universe and explains eleven-dimensional M-theory. The authors of the book point out that a Unified Field Theory (a theory, based on an early model of the universe, proposed by Albert Einstein and other physicists) may not exist. It argues that invoking God is not necessary to explain the origins of the universe, and that the Big Bang is a consequence of the laws of physics alone. In response to criticism, Hawking said: "One can't prove that God doesn't exist, but science makes God unnecessary." When pressed on his own religious views by the 2010 Channel 4 documentary '' Genius of Britain'', he clarified that he did not believe in a personal God. Published in the United States on September 7, 2010, the book became the number one bestseller on Amazon.com just a few days aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedict Cumberbatch
Benedict Timothy Carlton Cumberbatch (born 19 July 1976) is an English actor. He has received List of awards and nominations received by Benedict Cumberbatch, various accolades, including a BAFTA TV Award, a Primetime Emmy Award and a Laurence Olivier Award, in addition to nominations for two Academy Awards and four Golden Globes. In 2014, ''Time (magazine), Time'' magazine named him one of the Time 100, 100 most influential people in the world, and in 2015, he was appointed Commander of the Order of the British Empire (CBE) for services to performing arts and charity. Cumberbatch studied drama at the Victoria University of Manchester and obtained a Master of Arts in classical acting at the London Academy of Music and Dramatic Art. He began acting in William Shakespeare, Shakespearean theatre productions before making his West End theatre, West End debut in Richard Eyre's revival of ''Hedda Gabler'' in 2005. Since then, he has starred in Royal National Theatre productions of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |