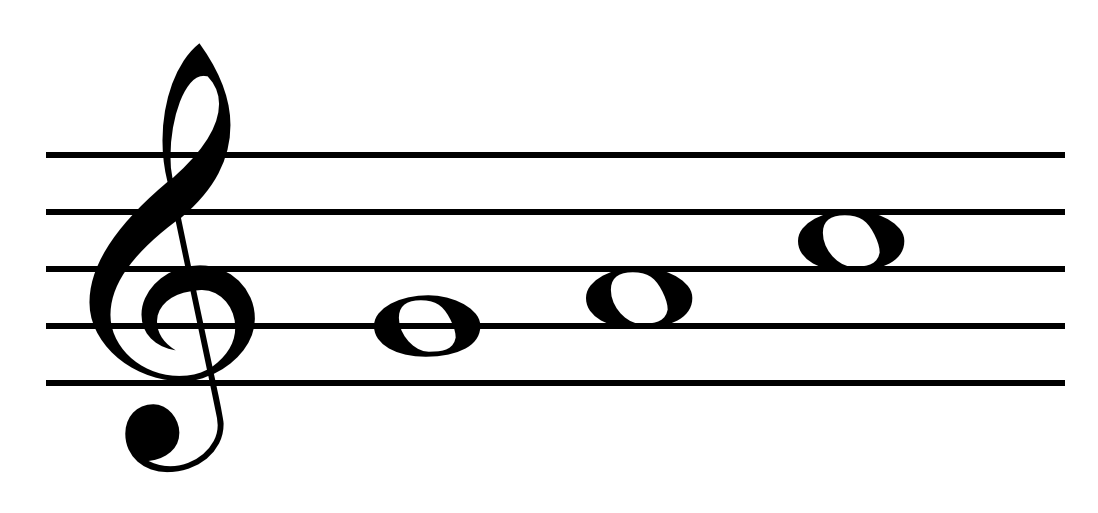|
Cruciform Churches In Norway
A cruciform is a physical manifestation resembling a common cross or Christian cross. These include architectural shapes, biology, art, and design. Cruciform architectural plan Christian churches are commonly described as having a cruciform architecture. In Early Christian, Byzantine and other Eastern Orthodox forms of church architecture this is likely to mean a tetraconch plan, a Greek cross, with arms of equal length or, later, a cross-in-square plan. In the Western churches, a cruciform architecture usually, though not exclusively, means a church built with the layout developed in Gothic architecture. This layout comprises: *An east end, containing an altar and often with an elaborate, decorated window, through which light will shine in the early part of the day. *A west end, which sometimes contains a baptismal font, being a large decorated bowl, in which water can be firstly, blessed (dedicated to the use and purposes of God) and then used for baptism. *North and south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross
A cross is a religious symbol consisting of two Intersection (set theory), intersecting Line (geometry), lines, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a saltire in heraldic terminology. The cross shape has been widely officially recognized as an absolute and exclusive religious symbol of Christianity from an early period in that religion's history.''Christianity: an introduction'' by Alister E. McGrath 2006 pages 321-323 Before then, it was used as a religious or cultural symbol throughout Europe, in West Asia, west and south Asia (the latter, in the form of the original Swastika); and in Ancient Egypt, where the Ankh was a hieroglyph that represented "life" and was used in the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapels
A chapel (from , a diminutive of ''cappa'', meaning "little cape") is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. First, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common type of these. Second, a chapel is a place of worship, sometimes interfaith, that is part of a building, complex, or vessel with some other main purpose, such as a school, college, hospital, palace or large aristocratic house, castle, barracks, prison, funeral home, hotel, airport, or military or commercial ship. Third, chapels are small places of worship, built as satellite sites by a church or monastery, for example in remote areas; these are often called a chapel of ease. A feature of all these types is that often no clergy are permanently resident or specifically attached to the chapel. For historical reasons, ''chapel'' is also often the term used by independent or nonconformist den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melody
A melody (), also tune, voice, or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of Pitch (music), pitch and rhythm, while more figuratively, the term can include other musical elements such as Timbre, tonal color. It is the foreground to the background accompaniment. A line or Part (music), part need not be a foreground melody. Melodies often consist of one or more musical Phrase (music), phrases or Motif (music), motifs, and are usually repeated throughout a Musical composition, composition in various forms. Melodies may also be described by their melodic motion or the pitches or the interval (music), intervals between pitches (predominantly steps and skips, conjunct or disjunct or with further restrictions), pitch range, tension (music), tension and release, continuity and coherence, cadence (music), cadence, and shape. Function and elements Johann Philipp Kirnberger arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Cryptogram
A musical cryptogram is a cryptogrammatic sequence of musical symbols which can be taken to refer to an extra-musical text by some 'logical' relationship, usually between note names and letters. The most common and best known examples result from composers using musically translated versions of their own or their friends' names (or initials) as themes or motifs in their compositions. These are not really rigorous cipher algorithms in the formal sense, but more like musical monograms. The methods used historically by composers were either too incomplete (i.e., did not include all of the letters of the alphabet) or too simplistic to meaningfully encrypt long text messages. There is a separate history of music ciphers utilizing music notation to encode messages for reasons of espionage or personal security that involved encryption and/or steganography. Because of the multitudinous ways in which notes and letters can be related, detecting hidden ciphers in music and proving acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Motif
In music, the cross motif is a motif. A motif (''Crux fidelis'') was used by Franz Liszt to represent the Christian cross ('tonisches Symbol des Kreuzes' or tonic symbol of the cross) and taken from Gregorian melodies.Merrick, Paul (2008). ''Revolution and Religion in the Music of Liszt'', p.284. . See also *Bach motif In music, the BACH motif is the motif (music), motif, a succession of note (music), notes important or characteristic to a musical composition, piece, ''B flat, A, C, B natural''. In Letter notation, German musical nomenclature, in whi ... * Cruciform#Cruciform melody Sources Motifs (music) Franz Liszt {{Classical-music-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BACH Motif
In music, the BACH motif is the motif (music), motif, a succession of note (music), notes important or characteristic to a musical composition, piece, ''B flat, A, C, B natural''. In Letter notation, German musical nomenclature, in which the note ''B natural'' is named ''H'' and the ''B flat'' named ''B'', it forms Johann Sebastian Bach's family name. One of the most frequently occurring examples of a musical cryptogram, the motif has been used by countless composers, especially after the Bach Revival in the first half of the 19th century. Origin Johann Gottfried Walther's ''Musicalisches Lexikon'' (1732) contains the only biographical sketch of Johann Sebastian Bach published during the composer's lifetime. There the motif is mentioned thus:This reference work thus indicates Bach as the inventor of the motif. Usage in compositions In a comprehensive study published in the catalogue for the 1985 exhibition "300 Jahre Johann Sebastian Bach" ("300 years of Johann Sebasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular Art
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon art, was produced in the sub-Roman Britain, post-Roman era of Great Britain and Ireland. The term derives from ''insula'', the Latin language, Latin term for "island"; in this period Britain and Ireland shared a largely common style different from that of the rest of Europe. Art historians usually group Insular art as part of the Migration Period art movement as well as Early Medieval Western art, and it is the combination of these two traditions that gives the style its special character. Most Insular art originates from the Hiberno-Scottish mission, Irish monastic movement of Celtic Christianity, or metalwork for the secular elite, and the period begins around 600 with the combining of Celtic art, Celtic and Anglo-Saxon art, Anglo-Saxon styles. One major distinctive feature is interlace (art), interlace decoration, in particular the interlace (visual arts), interlace decoration as found at Sutton Hoo, in East Anglia. This is now appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to Germanic peoples, Germanic settlers who became one of the most important cultural groups in Britain by the 5th century. The Anglo-Saxon period in Britain is considered to have started by about 450 and ended in 1066, with the Norman conquest of England, Norman Conquest. Although the details of Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, their early settlement and History of Anglo-Saxon England, political development are not clear, by the 8th century an Anglo-Saxon cultural identity which was generally called had developed out of the interaction of these settlers with the existing Romano-British culture. By 1066, most of the people of what is now England spoke Old English, and were considered English. Viking and Norman invasions chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holliday Junction
A Holliday junction is a branched nucleic acid structure that contains four double-stranded arms joined. These arms may adopt one of several conformations depending on buffer salt concentrations and the sequence of nucleobases closest to the junction. The structure is named after Robin Holliday, the molecular biologist who proposed its existence in 1964. In biology, Holliday junctions are a key intermediate in many types of genetic recombination, as well as in double-strand break repair. These junctions usually have a symmetrical sequence and are thus mobile, meaning that the four individual arms may slide through the junction in a specific pattern that largely preserves base pairing. Additionally, four-arm junctions similar to Holliday junctions appear in some functional RNA molecules. Immobile Holliday junctions, with asymmetrical sequences that lock the strands in a specific position, were artificially created by scientists to study their structure as a model for natura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lectionary 150
Lectionary 150, designated by siglum ℓ ''150'' (in the Gregory-Aland numbering), is also known as Codex Harleianus. It is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on vellum leaves and one of four extant Greek lectionaries with explicit dates from before 1000. Description The manuscript is written in compressed Greek Uncial letters, on 374 parchment leaves (35.2 cm by 26.7 cm), in 2 columns per page, 21 lines per page, with ornaments. The capital letters and nomina sacra are in red ink. The codex includes ten leaves of paper containing a series of Lessons from the Gospels, John, Matthew and the Luke lectionary (''Evangelistarium''). The image shows the text of John 1:18. It is one of the most beautiful lectionary codices, with a scribal date of 27 May 995 A.D. 'It is a most splendid specimen of the uncial class of Evangelistaria, and its text presents many instructive variations.' It also contains musical notation. History According to the colophon it was wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humfrey Wanley
Humfrey Wanley (21 March 1672 – 6 July 1726) was an English librarian, palaeographer and scholar of Old English, employed by manuscript collectors such as Robert Harley, 1st Earl of Oxford and Earl Mortimer, Robert and Edward Harley, 2nd Earl of Oxford and Earl Mortimer, Edward Harley. He was the first keeper of the Harleian Library, now the Harleian Collection. Early life and education Wanley was born at Coventry on 21 March 1671/2 and baptised on 10 April, the son of Nathaniel Wanley. Around 1687, he was apprenticed to a draper called Wright at Coventry, and remained with him until 1694, but he spent every vacant hour in studying old books and documents and copying the various styles of handwriting. His studies are said to have begun with a transcript of the Old English, Anglo-Saxon dictionary of William Somner. His skill in unravelling ancient writing became known to William Lloyd (Bishop of Worcester), William Lloyd, the bishop of Lichfield, who at a visitation sent for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruciform Joint
In metalworking, a welding joint is a point or edge where two or more pieces of metal or plastic are joined together. They are formed by welding two or more workpieces according to a particular geometry. There are five types of joints referred to by the American Welding Society: butt, corner, edge, lap, and tee. These types may have various configurations at the joint where actual welding can occur. Butt welds Butt welds are welds where two pieces of metal to be joined are in the same plane. These welds require only some preparation and are used with thin sheet metals that can be welded with a single pass. Common issues that can weaken a butt weld are the entrapment of slag, excessive porosity, or cracking. For strong welds, the goal is to use the least amount of welding material possible. Butt welds are prevalent in automated welding processes, such as submerged-arc welding, due to their relative ease of preparation. When metals are welded without human guidance, there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |