|
Cross Section (physics), Cross Section
Cross section may refer to: * Cross section (geometry) **Multiview orthographic projection#Section, Cross-sectional views in architecture and engineering 3D *Cross section (geology) * Cross section (electronics) * Radar cross section, measure of detectability * Cross section (physics) **Absorption cross section **Nuclear cross section **Neutron cross section **Photoionisation cross section **Gamma ray cross section * Cross Section (album), ''Cross Section'' (album), 1956 musical album by Billy Taylor See also *Cross section (fiber), microscopic view of textile fibers. *Section (fiber bundle), in differential and algebraic geometry and topology, a section of a fiber bundle or sheaf *Cross-sectional data, in statistics, econometrics, and medical research, a data set drawn from a single point in time **Cross-sectional study, a scientific investigation utilizing cross-sectional data ***Cross-sectional regression, a particular statistical technique for carrying out a cross-sectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Section (geometry)
In geometry and science, a cross section is the non-empty intersection (set theory), intersection of a solid body in three-dimensional space with a Plane (geometry), plane, or the analog in higher-dimensional spaces. Cutting an object into slices creates many parallel cross-sections. The boundary of a cross-section in three-dimensional space that is parallel to two of the Cartesian coordinate system, axes, that is, parallel to the plane determined by these axes, is sometimes referred to as a contour line; for example, if a plane cuts through mountains of a raised-relief map parallel to the ground, the result is a contour line in two-dimensional space showing points on the surface of the mountains of equal elevation. In technical drawing a cross-section, being a Planar projection, projection of an object onto a plane that intersects it, is a common tool used to depict the internal arrangement of a 3-dimensional object in two dimensions. It is traditionally crosshatched with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiview Orthographic Projection
In technical drawing and computer graphics, a multiview projection is a technique of illustration by which a standardized series of orthographic projection, orthographic two-dimensional pictures are constructed to represent the form of a three-dimensional object. Up to six pictures of an object are produced (called ''primary views''), with each projection plane parallel to one of the coordinate axes of the object. The views are positioned relative to each other according to either of two schemes: ''first-angle'' or ''third-angle'' projection. In each, the appearances of views may be thought of as being ''projected'' onto planes that form a six-sided box around the object. Although six different sides can be drawn, ''usually'' three views of a drawing give enough information to make a three-dimensional object. These three views are known as front view (also elevation view), top view or plan view and end view (also profile view or section view). When the plane or axis of the ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Section (geology)
In geology, a cross section or cross-section is a diagram representing the geologic features intersecting a vertical plane, and is used to illustrate an area's structure and stratigraphy that would otherwise be hidden underground. The features described in a cross section can include rock units, faults, topography, and more. They often accompany geological maps, complementing the overhead view with a side-on view, which can help to visualize the three-dimensional structure of the region and clarify the relationships between features. A cross section is drawn as a vertical map, as if the ground had been cut open and exposed along a given line. Various lines, colors, patterns, and symbols are used to represent different rock sections and features. Because the length of the studied area is often much greater than the depth, the diagram's scale can be vertically exaggerated to emphasize the depth or height of features and make them more visible. The plane a cross section illustrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Section (electronics)
In electronics, a cross section, cross-section, or microsection, is a prepared electronics sample that allows analysis at a plane that cuts through the sample. It is a destructive technique requiring that a portion of the sample be cut or ground away to expose the internal plane for analysis. They are commonly prepared for research, manufacturing quality assurance, supplier conformity, and failure analysis. Printed wiring boards (PWBs) and electronic components and their solder joints are common cross sectioned samples. The features of interest to be analyzed in cross section can be nanometer-scale metal and dielectric layers in semiconductors up to macroscopic features such as the amount of solder that has filled into a large, 0.125in (3.18mm) diameter plated-through hole. Preparation Cross sections can be prepared by several methods typically chosen based on the scale of the feature of interest because the technique affects the smoothness of the final polish. Smoother polishes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Cross Section
Radar cross-section (RCS), denoted σ, also called radar signature, is a measure of how detectable an object is by radar. A larger RCS indicates that an object is more easily detected. An object reflects a limited amount of radar energy back to the source. The factors that influence this include: *the material with which the target is made; *the size of the target relative to the wavelength of the illuminating radar signal; *the absolute size of the target; *the incident angle (angle at which the radar beam hits a particular portion of the target, which depends upon the shape of the target and its orientation to the radar source); *the reflected angle (angle at which the reflected beam leaves the part of the target hit; it depends upon incident angle); *the polarization of the radiation transmitted and received with respect to the orientation of the target. While important in detecting targets, strength of emitter and distance are not factors that affect the calculation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Section (physics)
In physics, the cross section is a measure of the probability that a specific process will take place in a collision of two particles. For example, the Rutherford cross-section is a measure of probability that an alpha particle will be deflected by a given angle during an interaction with an atomic nucleus. Cross section is typically denoted (sigma) and is expressed in units of area, more specifically in barns. In a way, it can be thought of as the size of the object that the excitation must hit in order for the process to occur, but more exactly, it is a parameter of a stochastic process. When two discrete particles interact in classical physics, their mutual cross section is the area transverse to their relative motion within which they must meet in order to scatter from each other. If the particles are hard inelastic sphere A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Cross Section
In physics Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ..., absorption cross-section is a measure of the probability of an absorption process. More generally, the term cross section (physics), cross-section is used in physics to quantify the probability of a certain particle-particle interaction, e.g., scattering, absorption (electromagnetic radiation), electromagnetic absorption, etc. (Note that light in this context is described as consisting of elementary particle, particles, i.e., photons.) A typical absorption cross-section has units of cm2⋅molecule−1. In honor of the fundamental contribution of Maria Goeppert Mayer to this area, the unit for the two-photon absorption cross section is named the "GM". One GM is 10−50 cm4⋅s⋅photon−1. In the context of ozone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Cross Section
The nuclear cross section of a nucleus is used to describe the probability that a nuclear reaction will occur. The concept of a nuclear cross section can be quantified physically in terms of "characteristic area" where a larger area means a larger probability of interaction. The standard unit for measuring a nuclear cross section (denoted as σ) is the barn, which is equal to , or . Cross sections can be measured for all possible interaction processes together, in which case they are called total cross sections, or for specific processes, distinguishing elastic scattering and inelastic scattering; of the latter, amongst neutron cross sections the absorption cross sections are of particular interest. In nuclear physics it is conventional to consider the impinging particles as point particles having negligible diameter. Cross sections can be computed for any nuclear process, such as capture scattering, production of neutrons, or nuclear fusion. In many cases, the number of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
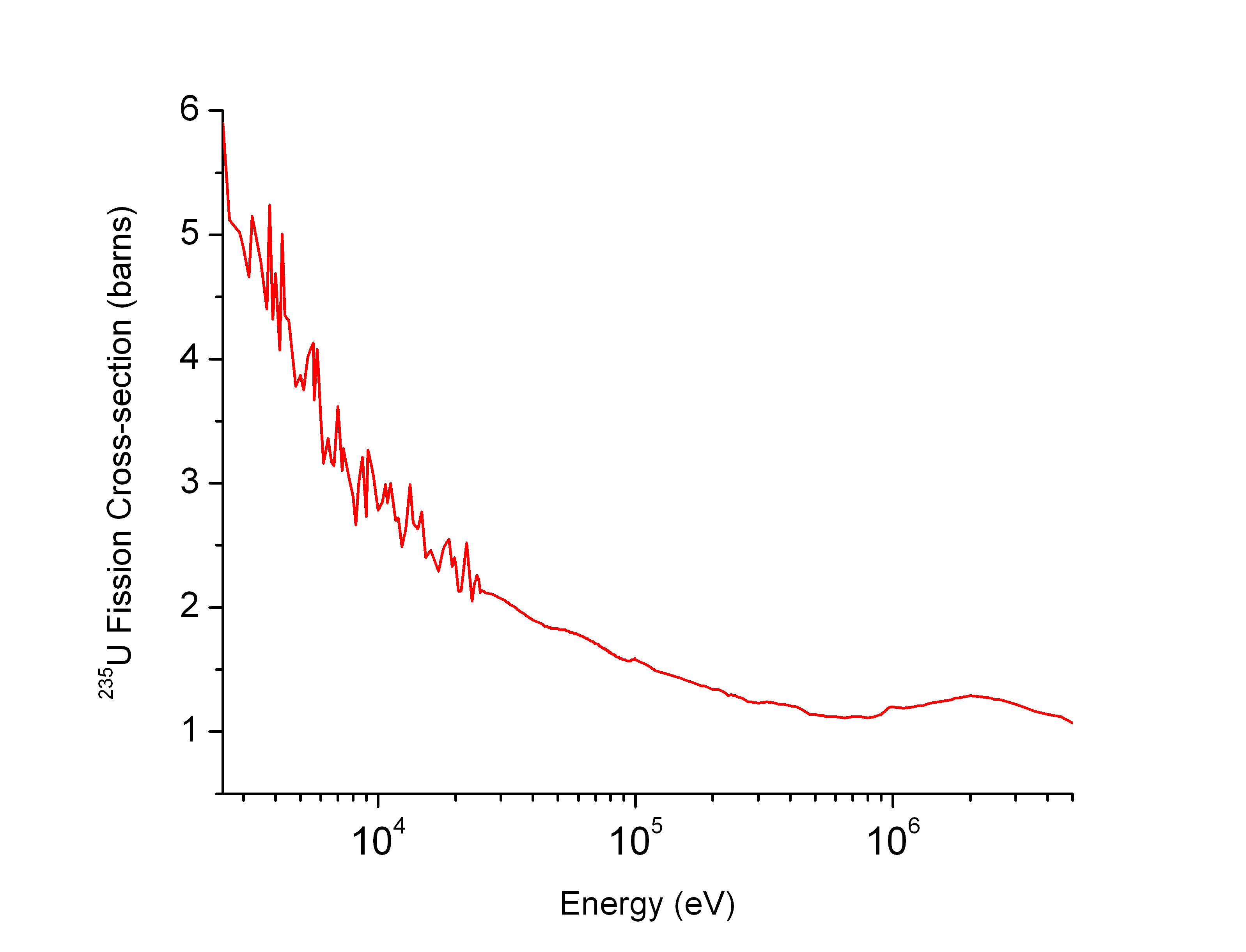
Neutron Cross Section
In nuclear physics, the concept of a neutron cross section is used to express the likelihood of interaction between an incident neutron and a target nucleus. The neutron cross section σ can be defined as the area in cm2 for which the number of neutron-nuclei reactions taking place is equal to the product of the number of incident neutrons that would pass through the area and the number of target nuclei. In conjunction with the neutron flux, it enables the calculation of the reaction rate, for example to derive the thermal power of a nuclear power plant. The standard unit for measuring the cross section is the barn, which is equal to 10−28 m2 or 10−24 cm2. The larger the neutron cross section, the more likely a neutron will react with the nucleus. An isotope (or nuclide) can be classified according to its neutron cross section and how it reacts to an incident neutron. Nuclides that tend to absorb a neutron and either decay or keep the neutron in its nucleus are neutron a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoionisation Cross Section
Photoionisation cross section in the context of condensed matter physics refers to the probability of a particle (usually an electron) being emitted from its electronic state. Cross section in photoemission The photoemission is a useful experimental method for the determination and the study of the electronic states. Sometimes the small amount of deposited material over a surface has a weak contribution to the photoemission spectra, which makes its identification very difficult. The knowledge of the cross section of a material can help to detect thin layers or 1D nanowires over a substrate. A right choice of the photon energy can enhance a small amount of material deposited over a surface, otherwise the display of the different spectra won't be possible. See also * Gamma ray cross section * ARPES * Synchrotron radiation *Cross section (physics) *Absorption cross section *Nuclear cross section The nuclear cross section of a nucleus is used to describe the probability tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Ray Cross Section
A gamma ray cross section is a measure of the probability that a gamma ray interacts with matter. The total cross section of gamma ray interactions is composed of several independent processes: photoelectric effect, Compton (incoherent) scattering, electron–positron pair production in the nucleus field and electron–positron pair production in the electron field (triplet production). The cross section for single process listed above is a part of the total gamma ray cross section. Other effects, like the photonuclear absorption, Thomson or Rayleigh (coherent) scattering can be omitted because of their nonsignificant contribution in the gamma ray range of energies. The detailed equations for cross sections (barn/atom) of all mentioned effects connected with gamma ray interaction with matter are listed below. Photoelectric effect cross section The photoelectric effect phenomenon describes the interaction of a gamma photon with an electron located in the atomic structure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Section (album)
''Cross Section'' is an album by American jazz pianist Billy Taylor featuring tracks recorded in 1953 and 1954 for the Prestige label. The album rereleased eight tracks from 1954 which had originally been issued on the 10-inch LP ''Billy Taylor Plays for DJs'' along with four Mambo sides from 1953. accessed August 21, 2012 Reception The review by stated: "the four originals (which alternate with standards) were all dedicated to disc jockeys of the time. The trio was pretty tight with Taylor in the lead and, although boppish, it also looked ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |